1566: The Maze Makers
Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 128 MB
Submit: 90 Solved: 33
[Submit][Status][Web Board]
Description
The Maze Makers is a publisher of puzzle books. One of their most popular series is maze books. They have a program that generates rectangular two-dimensional mazes like the one shown in Figure 1. The rules for these mazes are: (1) A maze has exactly two exterior cell walls missing, opening to two distinct terminal cells, (2) starting from any one cell, all other cells are reachable, (3) between any two cells in the maze there is exactly one simple path. Formally, a path is a sequence of cells where each cell and its successor on the path share an edge without a wall. A simple path is a path that never repeats a cell.
The Maze Maker program uses hexadecimal digits to encode the walls and passages of a maze. For each cell in the maze there is a corresponding hex digit. As shown in Figure 2, the 1's and 0's in the 4 digit binary representation of a hex digit correspond to the walls (1's) and passages (0's) for each cell in the maze. For example, the binary encoding for the hex digit B is 1011. Starting at the top of the cell and moving clockwise around it, this digit represents a cell with a wall at the top, a passage to the right and walls at the bottom and to the left. A path between two maze cells successively moves one cell up, down, left or right, going through passages only.
Figure 1: Sample Maze
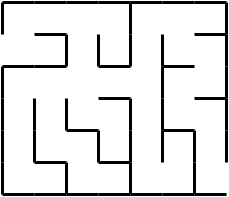
Figure 2: Hex Code for Walls and Passageways
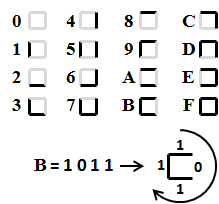
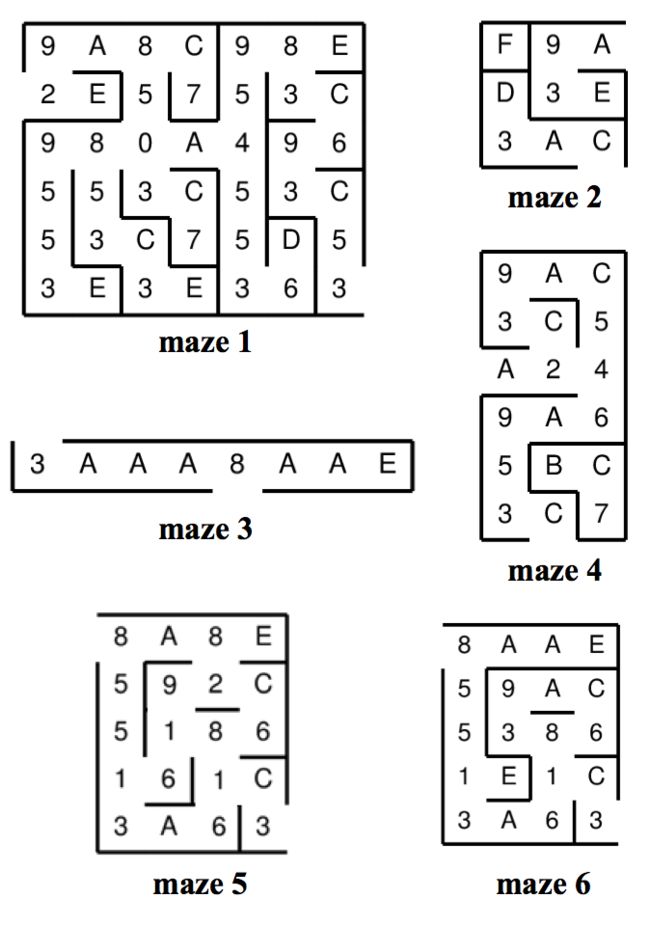
Figure 3: Maze with Cell Labels
Figure 3 shows the sample maze with the hexadecimal labels in each cell. For example, the hexadecimal digit E in the top-right cell indicates that it has a wall above it, to its right, below it, yet a passageway to its left. The hexadecimal digit 8 to its left indicates that its cell has only a wall above it. The inputs will always be self-consistent, in that the hexadecimal digits in neighboring cells will agree on whether they share a wall or passageway, and each input will always have precisely two terminal cells, each with one missing exterior wall.
Our sample maze is a legitimate maze in that all cells are reachable and there is a unique simple path between any pairs of cells in the maze. Your goal is to write a program that reads the hexadecimal descriptions of a potential maze and tests to determine if it is legitimate. If there is a problem, your program must report only the first problem, as detailed below in the section titled "Output".
Input
The input consists of the descriptions of one or more candidate mazes. Each maze description will start with two integers, H and W, indicating the height and width of the maze, respectively, such that 1 ≤ H ≤ 50 and 2 ≤ W ≤ 50. Following this first line will be H rows of hexadecimal digits, with each row consisting of W digits. The input is terminated with a line displaying a pair of zeros.
Output
For each candidate maze, the program should output the first one of the following statements that applies:
NO SOLUTION
UNREACHABLE CELL
MULTIPLE PATHS
MAZE OK
The classification statements are defined formally as follows:
NO SOLUTION - There is no path through the interior of the maze between the two exterior openings.
UNREACHABLE CELL - There is at least one cell in the maze that is not reachable by following passageways from either of the openings in the exterior walls of the maze.
MULTIPLE PATHS - There exists a pair of cells in the maze that have more than one simple path between them. Two simple paths are considered to be distinct if any part of the paths differ.
MAZE OK - None of the above problems exist.
Note well that for the second case given in the following examples, there is no path between the start and finish and there is an unreachable cell; the correct output should simply be NO SOLUTION, because that error message is listed first in the above list. Similarly, in the fourth example given, UNREACHABLE CELL is reported because that error has priority over the multiple paths.
Sample Input
6 7
9A8C98E
2E5753C
980A496
553C53C
53C75D5
3E3E363
3 3
F9A
D3E
3AC
1 8
3AAA8AAE
6 3
9AC
3C5
A24
9A6
5BC
3C7
5 4
8A8E
592C
5186
161C
3A63
5 4
8AAE
59AC
5386
1E1C
3A63
0 0
Sample Output
MAZE OK
NO SOLUTION
MAZE OK
UNREACHABLE CELL
MULTIPLE PATHS
MULTIPLE PATHS
HINT
Source
通过构图(用1表示墙,0表示通路),再转成dfs();
用一个father[]表示他的直接父结点,如果现在的点的直接父节点不是上一个父节点,那么vist[][]++;
如果,dfs()返回的值是false,表示没有路NO SOLUTION
如果,vist[][]>1表示有多路,MULTIPLE PATHS
如果最后有vist[][]==0,则说明有不能到达的点,则 UNREACHABLE CELL
都没有,则说明是:MAZE OK
转载请注明出处: 寻找&星空の孩子
寻找&星空の孩子
题目链接:http://acm.csu.edu.cn/OnlineJudge/problem.php?id=1566
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int N =105;
struct node
{
int x,y;
};
int mmap[N][N],vist[N][N],father[N*N];
int mi,mj,x,y,l[8];
void init(int num)
{
if(num>=0&&num<=7) l[1]=0;
else l[1]=1;
if(num&1) l[3]=1;
else l[3]=0;
if(num<4||num>7&&num<12) l[4]=0;
else l[4]=1;
if(num==0||num==1||num==4||num==5||num==8||num==9||num==12||num==13) l[6]=0;
else l[6]=1;
}
void build()
{
if(mj>2*y) mi+=2,mj=1;
mmap[mi][mj]=0;
mmap[mi-1][mj-1]=mmap[mi-1][mj+1]=1;
mmap[mi+1][mj-1]=mmap[mi+1][mj+1]=1;
mmap[mi-1][mj]|=l[1];
mmap[mi][mj-1]|=l[3];
mmap[mi][mj+1]|=l[4];
mmap[mi+1][mj]|=l[6];
mj+=2;
}
bool bfs()
{
node pre,now;
queue<node>q;
bool flag=false;
int dir[4][2]= {0,1,0,-1,1,0,-1,0};
memset(vist,0,sizeof(vist));
for(int i=0; i<x&&!flag; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<y&&!flag; j++)
{
if(i==0||j==0||i==x-1||j==y-1)
{
if(mmap[i][j]==0)
{
memset(father,-1,sizeof(father));//¸¸½áµã
now.x=i;
now.y=j;
q.push(now);
vist[i][j]=1;
while(!q.empty())
{
pre=q.front();
q.pop();
for(int e=0; e<4; e++)
{
now.x=pre.x+dir[e][0];
now.y=pre.y+dir[e][1];
if(now.x>=0&&now.x<x&&now.y>=0&&now.y<y&&mmap[now.x][now.y]==0)
{
if(vist[now.x][now.y]==0)
{
vist[now.x][now.y]=1;
father[now.x*y+now.y]=pre.x*y+pre.y;
if(now.x==0||now.y==0||now.x==x-1||now.y==y-1)
flag=1;
q.push(now);
}
else if(father[pre.x*y+pre.y]!=now.x*y+now.y)
vist[now.x][now.y]++;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
return flag;
}
void print()
{
for(int i=0; i<=x*2; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<=y*2; j++)
printf("%d ",mmap[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
}
int main()
{
char ch[105];
while(scanf("%d%d",&x,&y),x+y)
{
mi=1;
mj=1;
memset(mmap,0,sizeof(mmap));
for(int i=0; i<x; i++)
{
scanf("%s",ch);
int tp;
for(int j=0; j<strlen(ch); j++)
{
if(ch[j]>='0'&&ch[j]<='9')
tp=ch[j]-'0';
else
tp=ch[j]-'A'+10;
init(tp);
build();
}
}
//print();
x=x*2+1;
y=y*2+1;
if(bfs())
{
int f[2]= {0};
for(int i=1; i<x; i+=2)
{
for(int j=1; j<y; j+=2)
{
if(vist[i][j]==0)
f[0]=1;
else if(vist[i][j]>=2)
f[1]=1;
}
}
if(f[0])
{
printf("UNREACHABLE CELL\n");
continue;
}
if(f[1])
{
printf("MULTIPLE PATHS\n");
continue;
}
printf("MAZE OK\n");
}
else printf("NO SOLUTION\n");
}
return 0;
}
/**************************************************************
Problem: 1566
User: aking2015
Language: C++
Result: Accepted
Time:44 ms
Memory:1200 kb
****************************************************************/