C# XML文件操作总结 SAX DOM 解析
去年写过一篇关于C# XML文件操作的两种方式,但是没有给出样例代码,这里再次给出两种操作XML文件的方式,并且包含部分样例代码。
以下两种XML操作方式,不仅只是适合C# 语言进行开发,其实语言也都适用。
原文链接: 点击打开链接 http://blog.csdn.net/weixingstudio/article/details/7026712
1. 解析类型介绍
XML的解析器主要有DOM和SAX两种。
先简要介绍SAX解析器(Simple API for XML),其实解析器就是对XML进行处理的一套API,相当于一个模块。
SAX解析器是基于事件处理的,需要从头到尾把XML文档扫描一遍,在扫描的过程中,每次遇到一个语法结构时,就会调用这个特定语法结构的事件处理程序,向应用程序发送一个事件。
XmlReader的类提供了一种非常迅速、只向前的只读光标来处理XML数据,因为它是一个流模型,所以内存要求不是很高。但是,没有提供DOM模型的导航功能和读写功能。
DOM是文档对象模型解析,构建文档的分层语法结构,在内存中建立DOM树,DOM树的节点以对象的形式来标识,文档解析文成以后,文档的整个DOM树都会放在内存中。
DOM的优点:
1. 当文档的某一部分被多次的访问时,非常方便。
2. 需要对文档进行调整或者一次性的访问整个文档。
3. DOM可以随时的访问文档中的某个部分。
4. 可以避免一些无效的操作。
DOM结构是完全的存储在内存中的,所以如果文档较大的话,会占用大量的内存。
因为XML文档没有大小限制,所以一些文档可能就不能以DOM方式读取,SAX解析则不存在这样的问题,并且SAX解析的速度要比DOM快一些。
2. SAX解析方式
在C#中,使用SAX进行解析的类为XmlReader, XmlWriter,这两个类都是抽象类,由具体的子类来实现相关的功能。
具体的子类: XmlTextReader, XmlTextWriter
接下来简单看看XmlReader的成员:
| Name | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Close | When overridden in a derived class, changes the ReadState to Closed. | |
| Create(Stream) | Creates a new XmlReader instance using the specified stream. | |
| Create(String) | Creates a new XmlReader instance with specified URI. | |
| Create(TextReader) | Creates a new XmlReader instance with the specified TextReader. | |
| Create(Stream, XmlReaderSettings) | Creates a new XmlReader instance with the specified stream and XmlReaderSettings object. | |
| Create(String, XmlReaderSettings) | Creates a new instance with the specified URI and XmlReaderSettings. | |
| Create(TextReader, XmlReaderSettings) | Creates a new XmlReader instance using the specified TextReader and XmlReaderSettings objects. | |
| Create(XmlReader, XmlReaderSettings) | Creates a new XmlReader instance with the specified XmlReader and XmlReaderSettings objects. | |
| Create(Stream, XmlReaderSettings, String) | Creates a new XmlReader instance using the specified stream, base URI, and XmlReaderSettings object. | |
| Create(Stream, XmlReaderSettings, XmlParserContext) | Creates a new XmlReader instance using the specified stream, XmlReaderSettings, and XmlParserContext objects. | |
| Create(String, XmlReaderSettings, XmlParserContext) | Creates a new XmlReader instance using the specified URI, XmlReaderSettings, and XmlParserContext objects. | |
| Create(TextReader, XmlReaderSettings, String) | Creates a new XmlReader instance using the specified TextReader, XmlReaderSettings, and base URI. | |
| Create(TextReader, XmlReaderSettings, XmlParserContext) | Creates a new XmlReader instance using the specified TextReader, XmlReaderSettings, and XmlParserContext objects. | |
| Dispose | Releases the unmanaged resources used by the XmlReader and optionally releases the managed resources. | |
| Equals(Object) | Determines whether the specified Object is equal to the current Object. (Inherited from Object.) | |
| Finalize | Allows an Object to attempt to free resources and perform other cleanup operations before theObject is reclaimed by garbage collection. (Inherited from Object.) | |
| GetAttribute(Int32) | When overridden in a derived class, gets the value of the attribute with the specified index. | |
| GetAttribute(String) | When overridden in a derived class, gets the value of the attribute with the specifiedName. | |
| GetAttribute(String, String) | When overridden in a derived class, gets the value of the attribute with the specifiedLocalName and NamespaceURI. | |
| GetHashCode | Serves as a hash function for a particular type. (Inherited from Object.) | |
| GetType | Gets the Type of the current instance. (Inherited from Object.) | |
| IsName | Gets a value indicating whether the string argument is a valid XML name. | |
| IsNameToken | Gets a value indicating whether or not the string argument is a valid XML name token. | |
| IsStartElement() | Calls MoveToContent and tests if the current content node is a start tag or empty element tag. | |
| IsStartElement(String) | Calls MoveToContent and tests if the current content node is a start tag or empty element tag and if theName property of the element found matches the given argument. | |
| IsStartElement(String, String) | Calls MoveToContent and tests if the current content node is a start tag or empty element tag and if theLocalName and NamespaceURI properties of the element found match the given strings. | |
| LookupNamespace | When overridden in a derived class, resolves a namespace prefix in the current element's scope. | |
| MemberwiseClone | Creates a shallow copy of the current Object. (Inherited from Object.) | |
| MoveToAttribute(Int32) | When overridden in a derived class, moves to the attribute with the specified index. | |
| MoveToAttribute(String) | When overridden in a derived class, moves to the attribute with the specifiedName. | |
| MoveToAttribute(String, String) | When overridden in a derived class, moves to the attribute with the specifiedLocalName and NamespaceURI. | |
| MoveToContent | Checks whether the current node is a content (non-white space text, CDATA, Element, EndElement,EntityReference, orEndEntity) node. If the node is not a content node, the reader skips ahead to the next content node or end of file. It skips over nodes of the following type:ProcessingInstruction,DocumentType,Comment, Whitespace, or SignificantWhitespace. | |
| MoveToElement | When overridden in a derived class, moves to the element that contains the current attribute node. | |
| MoveToFirstAttribute | When overridden in a derived class, moves to the first attribute. | |
| MoveToNextAttribute | When overridden in a derived class, moves to the next attribute. | |
| Read | When overridden in a derived class, reads the next node from the stream. | |
| ReadAttributeValue | When overridden in a derived class, parses the attribute value into one or moreText,EntityReference, or EndEntity nodes. | |
| ReadContentAs | Reads the content as an object of the type specified. | |
| ReadContentAsBase64 | Reads the content and returns the Base64 decoded binary bytes. | |
| ReadContentAsBinHex | Reads the content and returns the BinHex decoded binary bytes. | |
| ReadContentAsBoolean | Reads the text content at the current position as a Boolean. | |
| ReadContentAsDateTime | Reads the text content at the current position as a DateTime object. | |
| ReadContentAsDecimal | Reads the text content at the current position as a Decimal object. | |
| ReadContentAsDouble | Reads the text content at the current position as a double-precision floating-point number. | |
| ReadContentAsFloat | Reads the text content at the current position as a single-precision floating point number. | |
| ReadContentAsInt | Reads the text content at the current position as a 32-bit signed integer. | |
| ReadContentAsLong | Reads the text content at the current position as a 64-bit signed integer. | |
| ReadContentAsObject | Reads the text content at the current position as an Object. | |
| ReadContentAsString | Reads the text content at the current position as a String object. | |
| ReadElementContentAs(Type, IXmlNamespaceResolver) | Reads the element content as the requested type. | |
| ReadElementContentAs(Type, IXmlNamespaceResolver, String, String) | Checks that the specified local name and namespace URI matches that of the current element, then reads the element content as the requested type. | |
| ReadElementContentAsBase64 | Reads the element and decodes the Base64 content. | |
| ReadElementContentAsBinHex | Reads the element and decodes the BinHex content. | |
| ReadElementContentAsBoolean() | Reads the current element and returns the contents as a Boolean object. | |
| ReadElementContentAsBoolean(String, String) | Checks that the specified local name and namespace URI matches that of the current element, then reads the current element and returns the contents as aBoolean object. | |
| ReadElementContentAsDateTime() | Reads the current element and returns the contents as a DateTime object. | |
| ReadElementContentAsDateTime(String, String) | Checks that the specified local name and namespace URI matches that of the current element, then reads the current element and returns the contents as aDateTime object. | |
| ReadElementContentAsDecimal() | Reads the current element and returns the contents as a Decimal object. | |
| ReadElementContentAsDecimal(String, String) | Checks that the specified local name and namespace URI matches that of the current element, then reads the current element and returns the contents as aDecimal object. | |
| ReadElementContentAsDouble() | Reads the current element and returns the contents as a double-precision floating-point number. | |
| ReadElementContentAsDouble(String, String) | Checks that the specified local name and namespace URI matches that of the current element, then reads the current element and returns the contents as a double-precision floating-point number. | |
| ReadElementContentAsFloat() | Reads the current element and returns the contents as single-precision floating-point number. | |
| ReadElementContentAsFloat(String, String) | Checks that the specified local name and namespace URI matches that of the current element, then reads the current element and returns the contents as a single-precision floating-point number. | |
| ReadElementContentAsInt() | Reads the current element and returns the contents as a 32-bit signed integer. | |
| ReadElementContentAsInt(String, String) | Checks that the specified local name and namespace URI matches that of the current element, then reads the current element and returns the contents as a 32-bit signed integer. | |
| ReadElementContentAsLong() | Reads the current element and returns the contents as a 64-bit signed integer. | |
| ReadElementContentAsLong(String, String) | Checks that the specified local name and namespace URI matches that of the current element, then reads the current element and returns the contents as a 64-bit signed integer. | |
| ReadElementContentAsObject() | Reads the current element and returns the contents as an Object. | |
| ReadElementContentAsObject(String, String) | Checks that the specified local name and namespace URI matches that of the current element, then reads the current element and returns the contents as anObject. | |
| ReadElementContentAsString() | Reads the current element and returns the contents as a String object. | |
| ReadElementContentAsString(String, String) | Checks that the specified local name and namespace URI matches that of the current element, then reads the current element and returns the contents as aString object. | |
| ReadElementString() | Reads a text-only element. | |
| ReadElementString(String) | Checks that the Name property of the element found matches the given string before reading a text-only element. | |
| ReadElementString(String, String) | Checks that the LocalName and NamespaceURI properties of the element found matches the given strings before reading a text-only element. | |
| ReadEndElement | Checks that the current content node is an end tag and advances the reader to the next node. | |
| ReadInnerXml | When overridden in a derived class, reads all the content, including markup, as a string. | |
| ReadOuterXml | When overridden in a derived class, reads the content, including markup, representing this node and all its children. | |
| ReadStartElement() | Checks that the current node is an element and advances the reader to the next node. | |
| ReadStartElement(String) | Checks that the current content node is an element with the given Name and advances the reader to the next node. | |
| ReadStartElement(String, String) | Checks that the current content node is an element with the given LocalName and NamespaceURI and advances the reader to the next node. | |
| ReadString | When overridden in a derived class, reads the contents of an element or text node as a string. | |
| ReadSubtree | Returns a new XmlReader instance that can be used to read the current node, and all its descendants. | |
| ReadToDescendant(String) | Advances the XmlReader to the next descendant element with the specified qualified name. | |
| ReadToDescendant(String, String) | Advances the XmlReader to the next descendant element with the specified local name and namespace URI. | |
| ReadToFollowing(String) | Reads until an element with the specified qualified name is found. | |
| ReadToFollowing(String, String) | Reads until an element with the specified local name and namespace URI is found. | |
| ReadToNextSibling(String) | Advances the XmlReader to the next sibling element with the specified qualified name. | |
| ReadToNextSibling(String, String) | Advances the XmlReader to the next sibling element with the specified local name and namespace URI. | |
| ReadValueChunk | Reads large streams of text embedded in an XML document. | |
| ResolveEntity | When overridden in a derived class, resolves the entity reference for EntityReference nodes. | |
| Skip | Skips the children of the current node. | |
| ToString | Returns a String that represents the current Object. (Inherited from Object.) |
| Name | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| AttributeCount | When overridden in a derived class, gets the number of attributes on the current node. | |
| BaseURI | When overridden in a derived class, gets the base URI of the current node. | |
| CanReadBinaryContent | Gets a value indicating whether the XmlReader implements the binary content read methods. | |
| CanReadValueChunk | Gets a value indicating whether the XmlReader implements the ReadValueChunk method. | |
| CanResolveEntity | Gets a value indicating whether this reader can parse and resolve entities. | |
| Depth | When overridden in a derived class, gets the depth of the current node in the XML document. | |
| EOF | When overridden in a derived class, gets a value indicating whether the reader is positioned at the end of the stream. | |
| HasAttributes | Gets a value indicating whether the current node has any attributes. | |
| HasValue | When overridden in a derived class, gets a value indicating whether the current node can have aValue. | |
| IsDefault | When overridden in a derived class, gets a value indicating whether the current node is an attribute that was generated from the default value defined in the DTD or schema. | |
| IsEmptyElement | When overridden in a derived class, gets a value indicating whether the current node is an empty element (for example,<MyElement/>). | |
| Item[Int32] | When overridden in a derived class, gets the value of the attribute with the specified index. | |
| Item[String] | When overridden in a derived class, gets the value of the attribute with the specifiedName. | |
| Item[String, String] | When overridden in a derived class, gets the value of the attribute with the specifiedLocalName and NamespaceURI. | |
| LocalName | When overridden in a derived class, gets the local name of the current node. | |
| Name | When overridden in a derived class, gets the qualified name of the current node. | |
| NamespaceURI | When overridden in a derived class, gets the namespace URI (as defined in the W3C Namespace specification) of the node on which the reader is positioned. | |
| NameTable | When overridden in a derived class, gets the XmlNameTable associated with this implementation. | |
| Prefix | When overridden in a derived class, gets the namespace prefix associated with the current node. | |
| QuoteChar | When overridden in a derived class, gets the quotation mark character used to enclose the value of an attribute node. | |
| ReadState | When overridden in a derived class, gets the state of the reader. | |
| SchemaInfo | Gets the schema information that has been assigned to the current node as a result of schema validation. | |
| Settings | Gets the XmlReaderSettings object used to create this XmlReader instance. | |
| Value | When overridden in a derived class, gets the text value of the current node. | |
| ValueType | Gets The Common Language Runtime (CLR) type for the current node. | |
| XmlLang | When overridden in a derived class, gets the current xml:lang scope. | |
| XmlSpace | When overridden in a derived class, gets the current xml:space scope. |
整体来说,XmlReader包含了非常多的属性以及函数,足够够我们使用。
我们先给出一个测试用的xml文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<!--comment: this file is the book store inventory database, for xml test-->
<bookstroe>
<book genre="autobiography" publicationdate="1991" ISBN="1-838938-22-0">
<title>The C# Programming Language</title>
<author>
<first-name>Song</first-name>
<last-name>Wei</last-name>
</author>
<price>13.56</price>
</book>
<book genre="data structure" publicationdate="2006" ISBN="0-2384823-2-78">
<title>how to construct your data?</title>
<author>
<first-name>Zhang</first-name>
<last-name>Hua</last-name>
</author>
<price>78.03</price>
</book>
<book genre="coding" publicationdate="2012" ISBN="1-388928-3-282">
<title>c++ primer</title>
<author>
<first-name>watkins</first-name>
<last-name>song</last-name>
</author>
<price>963.23</price>
</book>
</bookstroe>
接下来的所有操作都使用这个测试文件进行。
XmlReader的类提供了一种非常迅速、只向前的只读光标来处理XML数据,因为它是一个流模型,所以内存要求不是很高。但是,没有提供DOM模型的导航功能和读写功能。
标准的SAX解析方式是一种推模型,将数据推送的内存,但是C#的SAX解析是一种拉模型,主动的去内存中提取下一个结点数据。
最常用的操作就是XmlReader.Read()函数,这里必须注意,Read()函数会读取所有的Xml文件数据,包括元素的开始,元素的结束,换行符,内容(Text),这些所有的,包括注释,都会读取,所以在使用Read()函数的时候一定要自己判断读取进来的是什么样的结点,通过XmlNodeType进行识别。当读入一个结点之后,还可以判断当前结点是否有属性,也可以使用MoveToContent()函数跳过当前结点的结束,以及空白的Text,自动跳到内容结点,例如开始结点,内容啊神马的。
下面给出通过流模型(SAX)进行读取,查找,写数据等操作。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Xml;
namespace XmlTest
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
XmlReader reader = XmlReader.Create("book.xml");
richTextBox1.Clear();
while (reader.Read())
{
this.richTextBox1.Text += reader.Name +" "+ reader.AttributeCount+Environment.NewLine;
}
reader.Close();
}
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
XmlReader xr = XmlReader.Create("book.xml");
richTextBox2.Clear();
while (!xr.EOF)
{
if (xr.MoveToContent() == XmlNodeType.Element && xr.Name == "title")
{
this.richTextBox2.Text += xr.ReadElementString() + Environment.NewLine;
}
else
{
xr.Read();
}
}
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// 针对指定的属性查找相关结点以及结点信息
XmlReader reader = XmlReader.Create("book.xml");
while (reader.Read())
{
if (reader.NodeType==XmlNodeType.Element)
{
if (reader.HasAttributes)
{
if (reader.GetAttribute("publicationdate")==textBox1.Text.ToString())
{
MessageBox.Show(reader.GetAttribute("ISBN"));
}
}
}
}
}
private void button3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
XmlWriterSettings xws = new XmlWriterSettings();
xws.Indent = true;
xws.NewLineOnAttributes = true;
XmlWriter xw = XmlWriter.Create("newbook.xml", xws);
xw.WriteStartDocument();
xw.WriteStartElement("book");
xw.WriteAttributeString("genre", "人类探索");
xw.WriteAttributeString("publicationdate", "2015");
xw.WriteAttributeString("ISBN", "10-256456-0-45");
xw.WriteElementString("title", "人类发展史");
xw.WriteStartElement("author");
xw.WriteElementString("first-name","aaa");
xw.WriteElementString("last-name", "bbb");
xw.WriteEndElement();
xw.WriteElementString("price", "89");
xw.WriteEndElement();
xw.WriteEndDocument();
xw.Flush();
xw.Close();
}
}
}
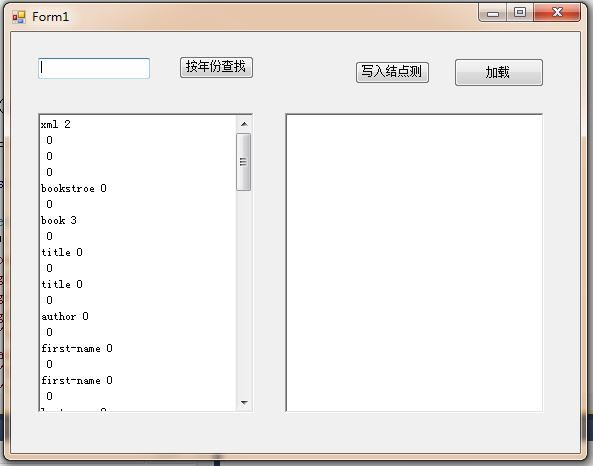
看看程序运行结果:
可以看到在构造函数中的Read()函数,在左侧的列表中,首先读取<?xml>这个开始元素,然后获得了当前结点两个属性,接下来读入第一行的回车,判断回车的属性个数为0个,接下来是注释,属性0个,然后是注释的换行符,属性0个,接下来的就比较理解了。
上面的程序中还给出了通过XmlWriter写入Xml数据的方式,XmlWriter提供了只向前的、未缓存的方式进行写入。一定要注意写入的要相匹配,写入一个开始元素,一定要在适当的位置写入结束元素。
private void button3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
XmlWriterSettings xws = new XmlWriterSettings();
xws.Indent = true;
xws.NewLineOnAttributes = true;
XmlWriter xw = XmlWriter.Create("newbook.xml", xws);
xw.WriteStartDocument();
xw.WriteStartElement("book");
xw.WriteAttributeString("genre", "人类探索");
xw.WriteAttributeString("publicationdate", "2015");
xw.WriteAttributeString("ISBN", "10-256456-0-45");
xw.WriteElementString("title", "人类发展史");
xw.WriteStartElement("author");
xw.WriteElementString("first-name","aaa");
xw.WriteElementString("last-name", "bbb");
xw.WriteEndElement();
xw.WriteElementString("price", "89");
xw.WriteEndElement();
xw.WriteEndDocument();
xw.Flush();
xw.Close();
}
3. DOM解析
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Xml;
namespace XmlTest
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
XmlReader reader = XmlReader.Create("book.xml");
richTextBox1.Clear();
while (reader.Read())
{
this.richTextBox1.Text += reader.Name +" "+ reader.AttributeCount+Environment.NewLine;
}
reader.Close();
}
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
XmlReader xr = XmlReader.Create("book.xml");
richTextBox2.Clear();
while (!xr.EOF)
{
if (xr.MoveToContent() == XmlNodeType.Element && xr.Name == "title")
{
this.richTextBox2.Text += xr.ReadElementString() + Environment.NewLine;
}
else
{
xr.Read();
}
}
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// 针对指定的属性查找相关结点以及结点信息
XmlReader reader = XmlReader.Create("book.xml");
while (reader.Read())
{
if (reader.NodeType==XmlNodeType.Element)
{
if (reader.HasAttributes)
{
if (reader.GetAttribute("publicationdate")==textBox1.Text.ToString())
{
MessageBox.Show(reader.GetAttribute("ISBN"));
}
}
}
}
}
private void button3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
XmlWriterSettings xws = new XmlWriterSettings();
xws.Indent = true;
xws.NewLineOnAttributes = true;
XmlWriter xw = XmlWriter.Create("newbook.xml", xws);
xw.WriteStartDocument();
xw.WriteStartElement("book");
xw.WriteAttributeString("genre", "人类探索");
xw.WriteAttributeString("publicationdate", "2015");
xw.WriteAttributeString("ISBN", "10-256456-0-45");
xw.WriteElementString("title", "人类发展史");
xw.WriteStartElement("author");
xw.WriteElementString("first-name","aaa");
xw.WriteElementString("last-name", "bbb");
xw.WriteEndElement();
xw.WriteElementString("price", "89");
xw.WriteEndElement();
xw.WriteEndDocument();
xw.Flush();
xw.Close();
}
private void button4_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
XmlDocument doc = new XmlDocument();
// 去掉注释
XmlReaderSettings settings = new XmlReaderSettings();
settings.IgnoreComments = true;
XmlReader reader = XmlReader.Create("book.xml");
doc.Load(reader);
// 获取根节点
XmlNode root = doc.DocumentElement;
// 遍历所有的直接子节点
XmlNodeList books = root.ChildNodes;
foreach (XmlNode node in books)
{
// 判断当前结点的属性是否和输入的年一直
string publicationdate = node.Attributes.GetNamedItem("publicationdate").Value.ToString();
if (publicationdate==textBox1.Text.Trim())
{
// 当前结点符合搜索的内容
// 获取当前结点的子节点信息
XmlNode title = node.ChildNodes[0];
XmlNode name = node.ChildNodes[1];
XmlNode price = node.ChildNodes[2];
XmlNode first_name = name.ChildNodes[0];
XmlNode last_name = name.ChildNodes[1];
string msg = title.InnerText + " " + first_name.InnerText + " " + last_name.InnerText + " " + price.InnerText;
MessageBox.Show(msg);
}
}
}
}
}
同时,C#在查找结点的时候还支持XPath,这个是在查找结点内容或者属性的时候用的非常普遍的查找方式,XPath查找的样例代码,如果想深入了解XPath的相关内容,还请在查找其他相关资料。
private void button5_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
XmlDocument doc = new XmlDocument();
// 去掉注释
XmlReaderSettings settings = new XmlReaderSettings();
settings.IgnoreComments = true;
XmlReader reader = XmlReader.Create("book.xml");
doc.Load(reader);
// 获取根节点
XmlNode root = doc.DocumentElement;
XmlNode tofind = root.SelectSingleNode("//book[@publicationdate='" + textBox1.Text.Trim() + "']");
MessageBox.Show(tofind.Name);
}