poj 1324
| Time Limit: 5000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 8690 | Accepted: 2075 |
Description
Holedox is a special snake, but its body is not very long. Its lair is like a maze and can be imagined as a rectangle with n*m squares. Each square is either a stone or a vacant place, and only vacant places allow Holedox to move in. Using ordered pair of row and column number of the lair, the square of exit located at (1,1).
Holedox's body, whose length is L, can be represented block by block. And let B1(r1,c1) B2(r2,c2) .. BL(rL,cL) denote its L length body, where Bi is adjacent to Bi+1 in the lair for 1 <= i <=L-1, and B1 is its head, BL is its tail.
To move in the lair, Holedox chooses an adjacent vacant square of its head, which is neither a stone nor occupied by its body. Then it moves the head into the vacant square, and at the same time, each other block of its body is moved into the square occupied by the corresponding previous block.
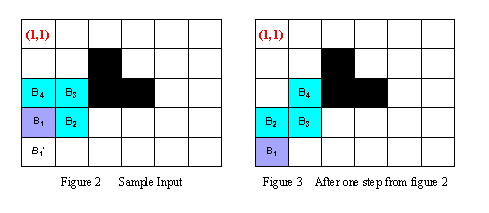
For example, in the Figure 2, at the beginning the body of Holedox can be represented as B1(4,1) B2(4,2) B3(3,2)B4(3,1). During the next step, observing that B1'(5,1) is the only square that the head can be moved into, Holedox moves its head into B1'(5,1), then moves B2 into B1, B3 into B2, and B4 into B3. Thus after one step, the body of Holedox locates in B1(5,1)B2(4,1)B3(4,2) B4(3,2) (see the Figure 3).
Given the map of the lair and the original location of each block of Holedox's body, your task is to write a program to tell the minimal number of steps that Holedox has to take to move its head to reach the square of exit (1,1).
Input
The input is terminated by a line with three zeros.
Note: Bi is always adjacent to Bi+1 (1<=i<=L-1) and exit square (1,1) will never be a stone.
Output
Sample Input
5 6 4 4 1 4 2 3 2 3 1 3 2 3 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 2 3 1 3 1 4 2 4 4 2 1 2 2 3 4 4 2 0 0 0
Sample Output
Case 1: 9 Case 2: -1
Hint
Source
/* 没了位运算,这个宽搜纯悲剧。。。。。 首先就是蛇的移动,避免重新搜索,那么就对整个地图每个点记录蛇的状态,开了一个g[20][20][1<<14]的数组 接着用14位保存蛇的状态,用位运算判断蛇是否与蛇身相冲突 时间是1450ms,太慢,继续更新 */ #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> int n,m,l; struct Snack { int x,y; int step; int state; }; Snack queue[20*20*(1<<14)]; bool map[20][20]; bool g[20][20][1<<14]; int mask; int front,rear; void inputSnack() { int x,y,x1,y1; Snack s; scanf("%d%d",&x,&y); x--,y--; s.x=x; s.y=y; s.step=0; s.state=0; for(int i=0;i<l-1;++i) { scanf("%d%d",&x1,&y1); x1--,y1--; if(x==x1)//就是这一点与上一点在同一个横坐标上 { if(y1>y)//这点在上一点上面,上一点要向上走 { s.state=s.state | (3<<(i<<1)); } else { s.state=s.state | (2<<(i<<1)); } } else { if(x1>x)//这点在上一点右边 { s.state=s.state | (1<<(i<<1)); } else { s.state=s.state | (0<<(i<<1));//左 } } x=x1; y=y1; } g[s.x][s.y][s.state]=true; queue[0]=s; int m; scanf("%d",&m); for(int i=0;i<m;++i) { scanf("%d%d",&x,&y); x--; y--; map[x][y]=1; } } void move(Snack now,int flag) { int x=now.x; int y=now.y; switch(flag) { case 0: now.x--; flag=1; break; case 1: now.x++; flag=0; break; case 2: now.y--; flag=3; break; case 3: now.y++; flag=2; } if(now.x<0||now.x>=n||now.y<0||now.y>=m||map[now.x][now.y]==1) return;//越界或是走到石头上 for(int i=0;i<l-1;++i)//判断与蛇身是否相撞 { int flag1=( now.state>>(i<<1) )&3; switch (flag1) { case 0: x--; break; case 1: x++; break; case 2: y--; break; case 3: y++; break; } if(x==now.x&&y==now.y) return; } now.state=(now.state << 2) & mask; now.state=now.state | flag; now.step++; if(g[now.x][now.y][now.state]==0) { g[now.x][now.y][now.state]=1; queue[rear++]=now; } } int bfs() { front=0,rear=1; Snack now; while(front<rear) { now=queue[front++]; if(now.x==0&&now.y==0) return now.step; move(now,0); move(now,1); move(now,2); move(now,3); } return -1; } int main() { int cas=0; while(scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&l)!=EOF) { if(n==0&&m==0&&l==0) break; memset(map,false,sizeof(map)); memset(g,false,sizeof(g)); mask = (1<<((l - 1) <<1)) - 1; inputSnack(); int steps=bfs(); printf("Case %d: %d/n",++cas,steps); } return 0; }
/* 用了启发函数,我去,141MS!!!,看来要大改特改了 启发函数是,首先BFS找到所有点到0,0的距离,接着的话就是用距离+搜索的层次进行启发式搜索 我要进100MS!!!! */ #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<queue> using namespace std; int n,m,l; //Snack queue[20*20*(1<<14)]; bool map[20][20]; bool g[20][20][1<<14]; int mat[20][20]; int dx[4]= {0,1,0,-1}; int dy[4]= {1,0,-1,0}; struct Snack { short x,y; short step; short state; bool operator < (const Snack& a) const { return mat[x][y]+step > mat[a.x][a.y]+a.step; } }; priority_queue < Snack > q;//, vector< Snack > ,greater< Snack > int mask; int front,rear; Snack inputSnack() { int x,y,x1,y1; Snack s; scanf("%d%d",&x,&y); x--,y--; s.x=x; s.y=y; s.step=0; s.state=0; for(int i=0; i<l-1; ++i) { scanf("%d%d",&x1,&y1); x1--,y1--; if(x==x1)//就是这一点与上一点在同一个横坐标上 { if(y1>y)//这点在上一点上面,上一点要向上走 { s.state=s.state | (3<<(i<<1)); } else { s.state=s.state | (2<<(i<<1)); } } else { if(x1>x)//这点在上一点右边 { s.state=s.state | (1<<(i<<1)); } else { s.state=s.state | (0<<(i<<1));//左 } } x=x1; y=y1; } g[s.x][s.y][s.state]=true; int m; scanf("%d",&m); for(int i=0; i<m; ++i) { scanf("%d%d",&x,&y); x--; y--; map[x][y]=1; } return s; } void move(Snack now,int flag) { int x=now.x; int y=now.y; switch(flag) { case 0: now.x--; flag=1; break; case 1: now.x++; flag=0; break; case 2: now.y--; flag=3; break; case 3: now.y++; flag=2; } if(now.x<0||now.x>=n||now.y<0||now.y>=m||map[now.x][now.y]==1) return;//越界或是走到石头上 for(int i=0; i<l-1; ++i) //判断与蛇身是否相撞 { int flag1=( now.state>>(i<<1) )&3; switch (flag1) { case 0: x--; break; case 1: x++; break; case 2: y--; break; case 3: y++; break; } if(x==now.x&&y==now.y) return; } now.state=(now.state << 2) & mask; now.state=now.state | flag; now.step++; if(g[now.x][now.y][now.state]==0) { g[now.x][now.y][now.state]=1; //queue[rear++]=now; q.push(now); } } int bfs(Snack s) { //front=0,rear=1; Snack now; q.push(s); while(!q.empty()) { now=q.top(); q.pop(); if(now.x==0&&now.y==0) return now.step; move(now,0); move(now,1); move(now,2); move(now,3); } return -1; } void search(int s) { for(int i=0; i<n; ++i) for(int j=0; j<m; ++j) { mat[i][j]=1<<25; } int q[410]; int front=0,rear=1; int x,y,step,r,c;//全部压缩到一个整数里 x=(s&31); y=((s>>5)&31); mat[x][y]=0; q[front]=s; while(front<rear) { s=q[front++]; x=(s&31); y=((s>>5)&31); step=(s>>10); for(int i=0; i<4; i++) { r=x+dx[i]; c=y+dy[i]; if(r>=0&&r<n&&c>=0&&c<m&&map[r][c]==0&&mat[r][c]>mat[x][y]+1) { mat[r][c]=mat[x][y]+1; q[rear++]=(r|(c<<5)|((step+1)<<10)); } } } } int main() { int cas=0; while(scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&l)!=EOF) { if(n==0&&m==0&&l==0) break; while(!q.empty()) q.pop(); memset(map,false,sizeof(map)); memset(g,false,sizeof(g)); mask = (1<<((l - 1) <<1)) - 1; Snack s=inputSnack(); search(0); if(mat[s.x][s.y]==1<<25) { printf("Case %d: -1/n",++cas); continue; } int steps=bfs(s); printf("Case %d: %d/n",++cas,steps); } return 0; }
/* 用C++提交, 368K 188MS 犀利啊 */ #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<queue> #include<map> using namespace std; int n,m,l,len; bool gap[21][21]; int mat[21][21]; int dx[4]= {0,1,0,-1}; int dy[4]= {1,0,-1,0}; int x[10],y[10]; struct Snack { int state; int step; Snack() {} Snack(int sta,int ste) { state=sta; step=ste; } bool operator < (const Snack& a) const { return mat[(state>>len)&31][((state>>5)>>len)&31]+step > mat[(a.state>>len)&31][((a.state>>5)>>len)&31]+a.step; } }; int front,rear; int inputSnack() { int state=0,ll=0; scanf("%d%d",&x[0],&y[0]); x[0]--,y[0]--; for(int i=1; i<l; ++i) { scanf("%d%d",&x[i],&y[i]); x[i]--,y[i]--;//[i-1]----->[i] if(x[i-1]==x[i])//就是这一点与上一点在同一个横坐标上 { if(y[i]>y[i-1]) state=state | (0<<ll);//UP else state=state | (2<<ll);//DOWN } else { if(x[i]>x[i-1]) state=state | (1<<ll);//RIGHT else state=state | (3<<ll);//LEFT } ll+=2; } state |=(x[0]<<len); state |=((y[0]<<5)<<len); int m;//读入图中 scanf("%d",&m); int x,y; for(int i=0; i<m; ++i) { scanf("%d%d",&x,&y); x--; y--; gap[x][y]=1; } return state; } int bfs(int s) { priority_queue < Snack > q ; int i , state , step ,rr , cc , k ; map < int , bool > hash ; q.push ( Snack ( s , 0 ) ) ; hash[s] = true ; while ( !q.empty () ) { s = q.top().state , step = q.top().step , q.pop() ; x[0] = ((s>>(len))&31) ; y[0] = (((s>>5)>>((len)))&31) ; if ( (s>>(len)) == 0 ) { return step ; } for ( i = 1 ; i < l ; i++ ) { k = ((s>>((i-1)<<1))&3) ; x[i] = dx[k] + x[i - 1] ; y[i] = dy[k] + y[i - 1] ; } for ( i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++ ) { rr = x[0] - dx[i] ; cc = y[0] - dy[i] ; if ( rr < 0 || rr >= n || cc < 0 || cc >= m || gap[rr][cc] == 1 ) { continue ; } for ( k = 0 ; k < l ; k++ ) { if ( rr == x[k] && cc == y[k] ) { break ; } } if ( k < l ) { continue ; } if ( rr == 0 && cc == 0 ) { return step + 1 ; } state = ((((s&((1<<((l-2)<<1))-1))<<2)|i)|(rr<<(len))|(((cc<<5)<<(len)))) ; if ( hash.find ( state ) == hash.end () ) { hash[state] = true ; q.push ( Snack ( state , step + 1 ) ) ; } } } return -1 ; } void search(int s) { for(int i=0; i<n; ++i) for(int j=0; j<m; ++j) { mat[i][j]=1<<25; } int q[410]; int front=0,rear=1; int x,y,step,r,c;//全部压缩到一个整数里 mat[0][0]=0; q[front]=s; while(front<rear) { s=q[front++]; x=(s&31); y=((s>>5)&31); step=(s>>10); for(int i=0; i<4; i++) { r=x+dx[i]; c=y+dy[i]; if(r>=0&&r<n&&c>=0&&c<m&&gap[r][c]==0&&mat[r][c]>mat[x][y]+1) { mat[r][c]=mat[x][y]+1; q[rear++]=(r|(c<<5)|((step+1)<<10)); } } } } int main() { int cas=0; while(scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&l)!=EOF) { if(n==0&&m==0&&l==0) break; memset(gap,false,sizeof(gap)); len=(l-1)<<1; int s=inputSnack(); search(0); if(mat[x[0]][y[0]]==1<<25) { printf("Case %d: -1/n",++cas); continue; } int steps=bfs(s);//s储存着蛇头的信息 printf("Case %d: %d/n",++cas,steps); } return 0; }