JSON数据构造及解析详解
JSON数据构造及解析详解
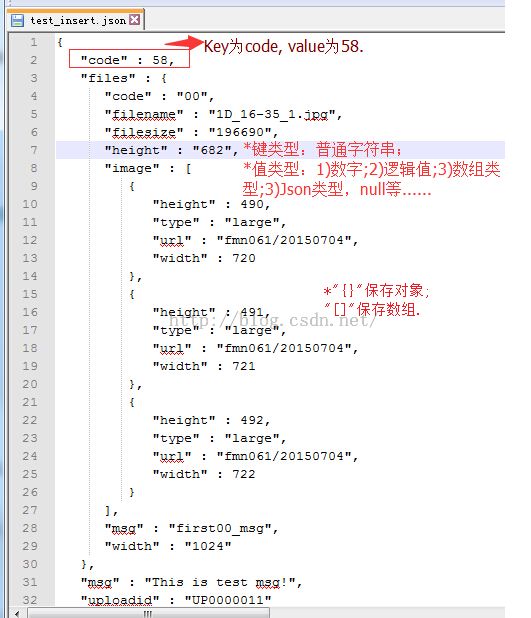
1、JSON格式数据长啥样?
2、JSON简介
JSON(Javascript Object Notation)
是一种轻量级的数据交换格式,易于阅读和编写,也易于机器解析和生成。
1)可读性:Json和XML相比可谓不相上下,一边是简单的语法,一边是规范的标签形式,很难分出胜负。
2)可扩展性:XML天生有很好的可扩展性,Json也有。
3)编码难度:XML有丰富的编码工具,Json也有提供,但是XML要输入很多结构字符。
4)解码难度:凡是可扩展的数据结构,解析起来都很困难。
5)数据量: Json具有轻小的特点,降低了数据传输量。
3、JSON适用场景
JSON始于JS,本身就是一种轻量级数据交互类型http://json.org/,所以JSON自然适用于进行数据交互的场景。典型的是Ajax中实现异步加载,因为前段页面已经加载,剩下需要的是真实的数据。
同样的,为了支持跨平台、数据安全等的web service也是一种数据传输,自然也可以使用。
同样的,为了支持跨平台、数据安全等的web service也是一种数据传输,自然也可以使用。
4、常用开源的CPPJson注意事项?
1)下载地址:https://github.com/open-source-parsers/jsoncpp
2) 编译对应下载路径的jsoncpp-src-0.5.0\makefiles\vs71中的工程jsoncpp.sln,在jsoncpp-src-0.5.0\build\vs71\debug路径三个文件下生成对应的jsontest.exe、json_vc71_libmtd.lib、test_lib_json.exe文件。
3)
json_vc71_libmtd.lib即为我们第三方的库,可供开发使用。
注意:编译的时候需要修改以下两个地方:
(1)lib_json工程属性-->配置属性-->C/C++-->代码生成 运行库改为“多线程调试DLL(/MDd)";
(2)lib_json工程属性-->配置属性-->库管理器-->常规 忽略特定库中改为“msvcprtd.lib;%(IgnoreSpecificDefaultLibraries)”。
以避免编译错误。
4)自己开发时候,只需要包含:include\json下的头文件,和3)生成的json_vc71_libmtd.lib库即可。
5、构造Json格式数据
//1. json格式化数据,输出到控制台和文件
void JsonInsert()
{
//根节点
Json::Value root;
Json::FastWriter fastWriter; //可以把Json::Value对象写入到字符串流或者文件中。
Json::StyledWriter styleWriter;
//根节点属性
root["uploadid"] = Json::Value("UP0000011");
root["code"] = Json::Value(58);
root["msg"] = Json::Value("This is test msg!");
Json::Value files;
files["code"] = "00";
files["msg"] = "first00_msg";
files["filename"] = "1D_16-35_1.jpg";
files["filesize"] = "196690";
files["width"] = "1024";
files["height"] = "682";
Json::Value images;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
{
images[i]["url"] = "fmn061/20150704";
images[i]["type"] = "large";
images[i]["width"] = 720 + i;
images[i]["height"] = 490 + i;
files["image"].append(images[i]); //插入数组
}
//子节点挂载到根节点上
root["files"] = Json::Value(files);
//**直接输出
cout << "FastWriter:" << endl;
std::string json_file = fastWriter.write(root);
cout << json_file << endl << endl;
//**缩进输出
cout << "StyledWriter:" << endl;
std::string style_json_file = styleWriter.write(root);
cout << style_json_file << endl << endl;
//输出到文件
ofstream ofs(INSERT_FILE_NAME);
if (ofs.is_open())
{
ofs << style_json_file; //将缩进格式输出到文件.
}
ofs.close();
cout << "insert " << INSERT_FILE_NAME << " successful!" << endl;
}
6、解析Json格式数据
1)解析Json串
//0.解析串
int ParseJsonFromString()
{
const char* str = "{\"uploadid\": \"UP000000\",\"code\": 100,\"msg\": \"\",\"files\": \"\"}";
Json::Reader reader;
Json::Value root;
if (reader.parse(str, root)) // reader将Json字符串解析到root,root将包含Json里所有子元素
{
std::string upload_id = root["uploadid"].asString(); // 访问节点,upload_id = "UP000000"
int code = root["code"].asInt(); // 访问节点,code = 100
cout << "upload_id = " << upload_id << "\t code =" << code << endl;
}
return 0;
}
2)解析Json文件
//2.解析1插入的文件
int ParseJsonFromFile(const char* pszFileName)
{
// 解析json用Json::Reader
Json::Reader reader;
// Json::Value是一种很重要的类型,可以代表任意类型。如int, string, object, array...
Json::Value root;
std::ifstream is;
is.open (pszFileName, std::ios::binary );
if (reader.parse(is, root)) // reader将Json字符串解析到root,root将包含Json里所有子元素
{
std::string strUpload_id = root["uploadid"].asString(); // 访问节点,upload_id = "UP000000"
int iCode = root["code"].asInt(); // 访问节点,code = 100
std::string strMsg = root["msg"].asString();
cout << "-upload_id = " << strUpload_id << "\t iCode = " << iCode << "\tmsg = " << strMsg << endl;
std::string code;
if (!root["files"].isNull()) // 访问节点,Access an object value by name, create a null member if it does not exist.
{
// 得到"files"的数组个数
int file_size = root["files"].size();
cout << "-file_size = " << file_size << endl;
// 遍历数组
std::string val_code = root["files"]["code"].asString();
std::string val_msg = root["files"]["msg"].asString();
std::string val_filename = root["files"]["filename"].asString();
std::string val_filesize = root["files"]["filesize"].asString();
std::string val_width = root["files"]["width"].asString();
std::string val_height = root["files"]["height"].asString();
cout << "--code =" << val_code << "\t msg=" << val_msg << "\t filename=" << val_filename \
<< "\t filesize=" << val_filesize << "\t width" << val_width << "\t height =" << val_height << endl << endl;
Json::Value val_image = root["files"]["image"];
int image_size = val_image.size();
cout << "image_size =" << image_size << endl;
for(int j = 0; j < image_size; ++j)
{
std::string url = val_image[j]["url"].asString();
std::string type = val_image[j]["type"].asString();
int width = val_image[j]["width"].asInt();
int height = val_image[j]["height"].asInt();
cout << "--url =" << url << "\t type =" << type \
<< "\t width =" << width << "\t height =" << height << endl;
}
}
}
is.close();
return 0;
}
6、Json解析源码
下载地址: http://download.csdn.net/detail/wojiushiwo987/8870855
7、运行结果示意:
后记:
1、有人可能会说,Json解析包括cppJson的使用方法,一搜一大把,为什么还要重复?
答:
1)别人的终究是别人的,别人的都是之前整理的。自己着实在前人的基础上,去下载、新建工程、单步调试代码、按照自己的想法构造Json,这是我想要的。
1)别人的终究是别人的,别人的都是之前整理的。自己着实在前人的基础上,去下载、新建工程、单步调试代码、按照自己的想法构造Json,这是我想要的。
2)有一个通盘的认识,不至于项目使用时候“临阵报佛脚”。
2、可能还不够深入,后续根据项目开发会继续总结和更新博文。
2014-7-4 pm21:29 思于家中床前
作者:铭毅天下
转载请标明出处,原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/laoyang360/article/details/46757751
如果感觉本文对您有帮助,请点击‘顶’支持一下,您的支持是我坚持写作最大的动力,谢谢!