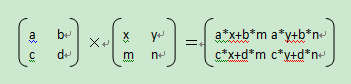Android画图之Matrix
Matrix ,中文里叫矩阵,高等数学里有介绍,在图像处理方面,主要是用于平面的缩放、平移、旋转等操作。
首先介绍一下矩阵运算。加法和减法就不用说了,太简单了,对应位相加就好。图像处理,主要用到的是乘法 。下面是一个乘法的公式:
在 Android 里面,二维图形的 Matrix 由 9 个 float 值构成,是一个 3*3 的矩阵。如下图。
解释一下,上面的 sinX 和 cosX ,表示旋转角度的 cos 值和 sin 值,注意,旋转角度是按顺时针方向计算的。 translateX 和 translateY 表示 x 和 y 的平移量。 scale 是缩放的比例, 1 是不变, 2 是表示缩放 1/2,这样子。
import scl.view.R;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Matrix;
import android.graphics.drawable.BitmapDrawable;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
public class MatrixView extends View {
private Bitmap mBitmap;
private Matrix mMatrix = new Matrix();
public MatrixView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
initialize();
}
public MatrixView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
initialize();
}
public MatrixView(Context context) {
super(context);
initialize();
}
private void initialize(){
//从资源文件中获取bitmap
BitmapDrawable bitmapDrawable = (BitmapDrawable) getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.matrix);
mBitmap = bitmapDrawable.getBitmap();
float cosValue = (float) Math.cos(-Math.PI/6);
float sinValue = (float) Math.sin(-Math.PI/6);
mMatrix.setValues(new float[]{
cosValue, -sinValue, 100,
sinValue, cosValue, 100,
0 , 0 , 2
});
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
//super.onDraw(canvas);
//画bitmap
canvas.drawBitmap(mBitmap, mMatrix, null);
}
}效果如下图:
以左上角为顶点,缩放一半,逆时针旋转30度,然后沿x轴和y轴分别平移50个像素,代码 里面写的是100,为什么是平移50呢,因为缩放了一半。
大家可以自己设置一下Matrix的值,或者尝试一下两个Matrix相乘,得到的值设置进去,这样才能对Matrix更加熟练。
这里讲的直接赋值的方式也许有点不好理解,不过还好, andrid 提供了对矩阵的更方便的方法
转载,并修改了一些代码:
原网址:http://chroya.iteye.com/blog/712078
上面讲了一下Matrix的原理和运算方法,涉及到高等数学,有点难以理解。还好Android里面提供了对Matrix操作的一系
列方便的接口。
Matrix的操作,总共分为translate(平移),rotate(旋转),scale(缩放)和skew(倾斜)四种,每一种变换在
Android的API里都提供了set, post和pre三种操作方式,除了translate,其他三种操作都可以指定中心点。
set是直接设置Matrix的值,每次set一次,整个Matrix的数组都会变掉,前面的变换都无效,只留最后一次的变换。
post是后乘,当前的矩阵乘以参数给出的矩阵。可以连续多次使用post,来完成所需的整个变换。例如,要将一个图片旋
转30度,然后平移到(100,100)的地方,那么可以这样做:
Matrix m = new Matrix(); m.postRotate(30 ); m.postTranslate(100 , 100 );
这样就达到了想要的效果。
pre是前乘,参数给出的矩阵乘以当前的矩阵。所以操作是在当前矩阵的最前面发生的。例如上面的例子,如果用pre的话,就要这样:
Matrix m = new Matrix(); m.setTranslate(100, 100); m.preRotate(30);
旋转、缩放和倾斜都可以围绕一个中心点来进行,如果不指定,默认情况下,是围绕(0,0)点来进行。
public class MatrixView2 extends View {
private Bitmap mBitmap;
private Matrix mMatrix = new Matrix();
public MatrixView2(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
initialize();
}
public MatrixView2(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
initialize();
}
public MatrixView2(Context context) {
super(context);
initialize();
}
private void initialize(){
//从资源文件中获取bitmap
BitmapDrawable bitmapDrawable = (BitmapDrawable) getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.matrix);
mBitmap = bitmapDrawable.getBitmap();
//设置缩放 x轴方向缩放2被, y轴方向不缩放。默认情况下以使用此Matrix的左上角(0,0)为缩放中心。
mMatrix.setScale(1.5f, 1);
//平移到(100,100),x轴方向向右平移100,y轴方向向下平移80
mMatrix.postTranslate(100, 80);
//设置倾斜度,
mMatrix.postSkew(0.2f, 0.2f);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
//super.onDraw(canvas);
//画bitmap
canvas.drawBitmap(mBitmap, mMatrix, null);
}
}