GetLogicalDrives()函数
原型:DWORD GetLogicalDrivers (void);
说明:函数返回值是一个long型,将其用二进制显示时,其中第0位表示A盘,第1位表示B盘,当某位为1时说明存在这个盘,即00000011表示有A盘和B盘。
看这个例子:
#include <windows.h>
int main()
{
DWORD dw;
TCHAR TC1[50],TC2[50];
dw = GetLogicalDrives();
wsprintf(TC1,"%ld",dw);
MessageBox(NULL,TC1,"十进制",MB_OK);
_itoa(dw,TC2,2);
MessageBox(NULL,TC2,"十进制",MB_OK);
return 0;
}

 一目了然哈
一目了然哈
改下:
#include <windows.h>
int main()
{
DWORD dw;
TCHAR TC[50];
int count = 0;
dw = GetLogicalDrives();
while(dw != 0)
{
if( (dw&1) != 0)
{
count++;
}
dw >>= 1;
}
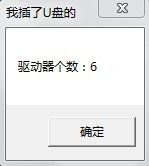
wsprintf(TC,"驱动器个数:%d",count);
MessageBox(NULL,TC,"我插了U盘的",MB_OK);
return 0;
}
判断某个盘符是否存在:
#include <windows.h>
int main()
{
DWORD dw;
TCHAR TC[50];
dw = GetLogicalDrives();
char ch;
ch = 'Q';
int n = ch - 'A';
if( (dw != 0) && (dw >>= n) != 0 )
{
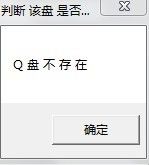
wsprintf(TC,"%c 盘 存 在",ch);
}
else
{
wsprintf(TC,"%c 盘 不 存 在",ch);
}
MessageBox(NULL,TC,"判断 该盘 是否存在",MB_OK);
return 0;
}
MSDN:
GetLogicalDrives
The GetLogicalDrives function retrieves a bitmask representing the currently available disk drives.
DWORD GetLogicalDrives(VOID);
Parameters
This function has no parameters.
Return Values
If the function succeeds, the return value is a bitmask representing the currently available disk drives. Bit position 0 (the least-significant bit) is drive A, bit position 1 is drive B, bit position 2 is drive C, and so on.
If the function fails, the return value is zero. To get extended error information, call GetLastError.
Remarks
Windows XP: This function returns a concatenation of the logical disks in the Global and Local MS-DOS Device namespaces. If a logical disk exists in both namespaces, this function will return the entry in the Local MS-DOS Devices namespace.
For more information on the Global and Local MS-DOS Device namespaces and changes to the accessibility of MS-DOS device names in Windows XP, refer to MS-DOS Device Names.
Requirements
Windows NT/2000/XP: Included in Windows NT 3.1 and later.
Windows 95/98/Me: Included in Windows 95 and later.
Header: Declared in Winbase.h; include Windows.h.
Library: Use Kernel32.lib.