SpringMVC传值
SpringMVC传值
1 地址栏传值
URI Template Patterns使用@PathVariable
将需要传递的数据写在URI 中。
在Spring MVC中
首先,通过@RequestMapping表明变量所在URI 的位置和变量名称,像这样
@RequestMapping(path="/owners/{ownerId}", method=RequestMethod.GET)表明/owners/后面的路径将会别当作变量获取到,变量名称为ownerId
其次,需要使用@PathVariable注解来从uri中的获取变量。像这样
@PathVariable String ownerId
代码如下
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/mvctest")
public class MVCController {
@RequestMapping(path="/owners/{ownerId}", method=RequestMethod.GET)
public @ResponseBody String findOwner(@PathVariable String ownerId) {
return ownerId;
}
}还有一种写法就是指明变量名称
@PathVariable("ownerId") String ownerId
上面之所以没有指明是因为 Spring MVC 是按照名字匹配的,只要名称一致就可以匹配到。
将数据获取到并直接输出
@PathVariable续
A method can have any number of @PathVariable annotations:
- 在方法上可以有很多@PathVariable注解
@RequestMapping(path="/owners/{ownerId}/pets/{petId}", method=RequestMethod.GET)
public String findPet(@PathVariable String ownerId, @PathVariable String petId, Model model) {
Owner owner = ownerService.findOwner(ownerId);
Pet pet = owner.getPet(petId);
model.addAttribute("pet", pet);
return "displayPet";
}还可以获取类上声明的变量
路径:/owners/42/pets/21
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/owners/{ownerId}")
public class RelativePathUriTemplateController {
@RequestMapping("/pets/{petId}")
public void findPet(@PathVariable String ownerId, @PathVariable String petId, Model model) {
// implementation omitted
}
}还可以使用正则表达式
语法:{varName:regex}
路径:/spring-web/spring-web-3.0.5.jar
@RequestMapping("/spring-web/{symbolicName:[a-z-]+}-{version:\\d\\.\\d\\.\\d}{extension:\\.[a-z]+}")
public void handle(@PathVariable String version, @PathVariable String extension) {
// ...
}
}通配符也可以
/owners/*/pets/{petId}
Matrix Variables 使用@MatrixVariable
In the MVC namespace, the element has an enable-matrix-variables attribute that should be set to true. By default it is set to false.
要使用@MatrixVariable首先需要将配置文件中的
<mvc:annotation-driven />
改为
<mvc:annotation-driven enable-matrix-variables="true" />
@MatrixVariable可以获取到路径中
/cars;color=red;year=2012
color和year的值
其中color和year也可以是数组
color=red,green,blue
示例:
@RequestMapping(path = "/pets/{petId}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public @ResponseBody String findPet(@PathVariable String petId, @MatrixVariable String q) {
return "petId="+petId+";"+"q="+q;
}路径:
http://localhost:8080/testwechat/mvctest/pets/42;q=1;q=2
结果:
因为所有路径中都可以携带matrix 变量,所有需要明确指出matrix 变量所在的位置
// GET /owners/42;q=11/pets/21;q=22
@RequestMapping(path = "/owners/{ownerId}/pets/{petId}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public void findPet(
@MatrixVariable(name="q", pathVar="ownerId") int q1,
@MatrixVariable(name="q", pathVar="petId") int q2) {
// q1 == 11
// q2 == 22
}matrix 变量是可选的,也可以是指默认值
/ GET /pets/42
@RequestMapping(path = "/pets/{petId}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public void findPet(@MatrixVariable(required=false, defaultValue="1") int q) {
// q == 1
}所有的matrix 变量都可以通过map获取
// GET /owners/42;q=11;r=12/pets/21;q=22;s=23
@RequestMapping(path = "/owners/{ownerId}/pets/{petId}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public void findPet(
@MatrixVariable Map<String, String> matrixVars,
@MatrixVariable(pathVar="petId"") Map<String, String> petMatrixVars) { // matrixVars: ["q" : [11,22], "r" : 12, "s" : 23] // petMatrixVars: ["q" : 11, "s" : 23] }Request parameters 使用@RequestParam
最常见的请求参数的一般在?后面携带,参数与参数之间用&连接格式如下
https://www.baidu.com/s?ie=UTF-8&wd=springmvc
这种参数的获取可以采用@RequestParam
//需要一个petId的参数
@RequestMapping(path="useRequestParam",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public @ResponseBody String requestParam(@RequestParam("petId") int petId) {
return "petId:"+petId;
}如果传递的参数是可选的需要将@RequestParam的required设为false
@RequestMapping(path="useRequestParam",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public @ResponseBody String requestParam(@RequestParam(value="petId",required=false) int petId) {
return "petId:"+petId;
}多个参数
@RequestMapping(path="useRequestParam1",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public @ResponseBody String requestParam1(@RequestParam("petId") int petId,@RequestParam(value="petName",required=false) String petName) {
return "petId:"+petId+"+petName:"+petName;
}多个参数还可以用map来接收
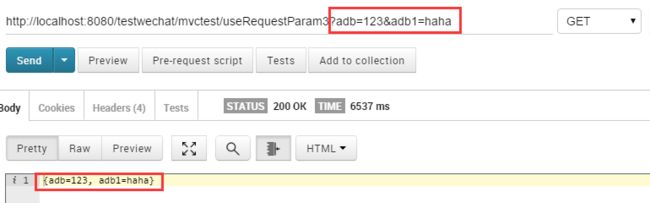
@RequestMapping(path="useRequestParam3",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public @ResponseBody String requestParam3(@RequestParam Map<String,String> map) {
return map.toString();
}2 表单传值
表单传值分可为带文件上传的(需要将enctype设为multipart/form-data)和不带文件上传的(默认enctype为application/x-www-form-urlencoded)
不带文件的表单
不带文件的表单和上面介绍的uri传值中的Request parameters用法一样,
使用@RequestParam接收参数
@RequestMapping(path="postForm",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public @ResponseBody String postForm(@RequestParam("username") String username,@RequestParam("password") String password) {
return "username:"+username+"+password:"+password;
}enctype为application/x-www-form-urlencoded
enctype为multipart/form-data
带文件上传的表单
springmvc对文件上传的支持是通过multipartResolver来实现的,multipartResolver需要依赖commons-fileupload-x.x.jar和commons-io-x.x.jar
处理上传文件需要在springmvc的配置文件中加入如下bean
<!-- 文件上传的bean 10*1024*1024 10M -->
<bean id="multipartResolver" class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver">
<property name="maxUploadSize" value="10485760"></property>
<property name="defaultEncoding" value="UTF-8"></property>
<property name="resolveLazily" value="true"></property>
</bean>Controller
springmvc会将参数中的变量自动绑定到对象中,如果对象的属性和参数的名称一致就可以绑定,在这个示例中,将参数绑定到一个User对象上,User对象如下
package com.wechat.controller.entiry;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement;
@XmlRootElement(name = "user")
public class User {
private String username;
private String password;
private int age;
@XmlElement
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
@XmlElement
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@XmlElement
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [username=" + username + ", password=" + password + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
}
对象上的注解可以先不管,它是用来输出xml用的
Controller如下:
// 带文件的表单提交
@RequestMapping(value = "postFile", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public String postFile(User user, @RequestParam MultipartFile[] myfiles, HttpServletRequest request)
throws IOException {
System.out.println(user.toString());
for (MultipartFile myfile : myfiles) {
if (myfile.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("文件未上传");
} else {
System.out.println("文件长度: " + myfile.getSize());
System.out.println("文件类型: " + myfile.getContentType());
System.out.println("表单名称: " + myfile.getName());
System.out.println("文件原名: " + myfile.getOriginalFilename());
System.out.println("========================================");
// 如果用的是Tomcat服务器,则文件会上传到\\%TOMCAT_HOME%\\webapps\\YourWebProject\\WEB-INF\\upload\\文件夹中
String realPath = request.getSession().getServletContext().getRealPath("/WEB-INF/upload");
// 这里不必处理IO流关闭的问题,因为FileUtils.copyInputStreamToFile()方法内部会自动把用到的IO流关掉
FileUtils.copyInputStreamToFile(myfile.getInputStream(),
new File(realPath, myfile.getOriginalFilename()));
}
}
return "ok";
}可以同时上传多个文件
3 提交数据json或xml等
通常在开发中会将数据以json或xml的形式提交到服务器端,这个时候需要采用@RequestBody来接收
可以提交任意字符串
@RequestMapping(value = "postJson", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public String postJson(@RequestBody String body) {
System.out.println(body);
return body;
}需要提交json,只需要将提交的字符串按照json的格式提交即可,如果服务器的pojo能与之对应,则会自动绑定
json需要classpath中有json相应的jar包,我的classpath中采用的是gson-2.4.jar
springmvc可以根据视图协商,为客户端提供不同的视图,可以通过后缀来告诉springmvc需要输出的数据格式为json还是xml
By default Spring MVC performs “.” suffix pattern matching so that a controller mapped to /person is also implicitly mapped to /person.. This makes it easy to request different representations of a resource through the URL path (e.g. /person.pdf, /person.xml).
示例:
输出用户对象,根据客户端需求进行格式化,json需要引入的jar包采用gson就可以了,xml需要两个jar包,
分别是xmlpull-1.1.3.1.jar和xstream-1.4.8.jar,同时需要在user对象上添加注解,注解已经添加在上面的程序中。
Controller
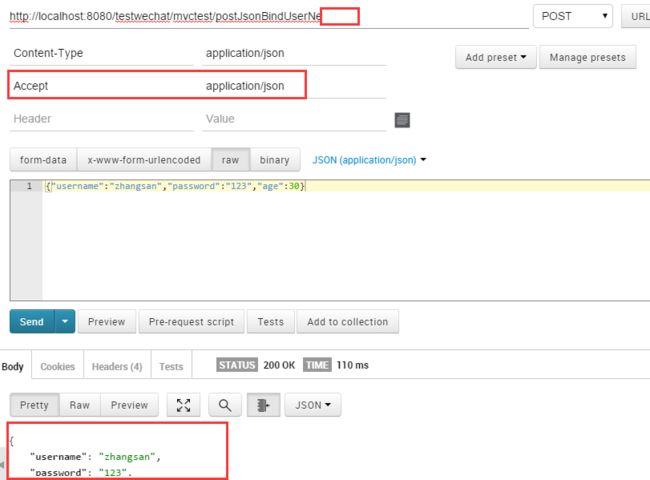
@RequestMapping(value = "postJsonBindUserNe", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public User postJsonBindUserNe(@RequestBody User user,@RequestHeader("Accept") String accept,@RequestHeader("Content-Type") String contentType) {
System.out.println("Accept:"+accept);
System.out.println("Content-Type:"+contentType);
return user;
}返回json
返回xml
4 读取http头中的数据
通常用户发往服务器的请求信息中除了数据本身,协议中也会携带非常有价值的内容,springmvc提供了强大的注解可以读取http头中的信息,使用的注解为@RequestHeader
示例仍然采用上面的请求用户示例,这次不用后缀名,将需要接收的类型包含在http头中
接受参数为json
提交的报文和返回的数据
xml如下
报文和数据
中文乱码
上面的所有示例中均没有处理中文乱码,下面说一下乱码的处理方式
首先需要判断乱码出现的位置,以第一个示例为例
/owners/张学友
断点,发现提交到Controller时并没有乱码,而是Controller输出的时候出现的乱码
原来
一切出自StringHttpMessageConverter
By default, this converter supports all media types (*/*), and writes with a Content-
Type of text/plain. This can be overridden by setting the supportedMediaTypes property.
而它的编码方式为“ISO-8859-1”
解决方法
<mvc:annotation-driven enable-matrix-variables="true"/>
改为如下
<mvc:annotation-driven enable-matrix-variables="true">
<!-- 消息转换器 -->
<mvc:message-converters register-defaults="true">
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter">
<property name="supportedMediaTypes" value="text/html;charset=UTF-8" />
</bean>
</mvc:message-converters>
</mvc:annotation-driven>或者在路径上添加如下参数
@RequestMapping(path="/owners/{ownerId}", method=RequestMethod.GET,produces = "text/html;charset=UTF-8")
public @ResponseBody String findOwner(@PathVariable String ownerId) {
return ownerId;
}参考
http://my.oschina.net/u/140421/blog/176625
http://www.360doc.com/content/14/1024/23/18637323_419613562.shtml
springMVC传值就写到这里
参考文献
http://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/htmlsingle/
Spring官方文档