Redis源码学习-Master&Slave的命令交互
0. 写在前面
Version Redis2.2.2
Redis中可以支持主从结构,本文主要从master和slave的心跳机制出发(PING),分析redis的命令行交互。
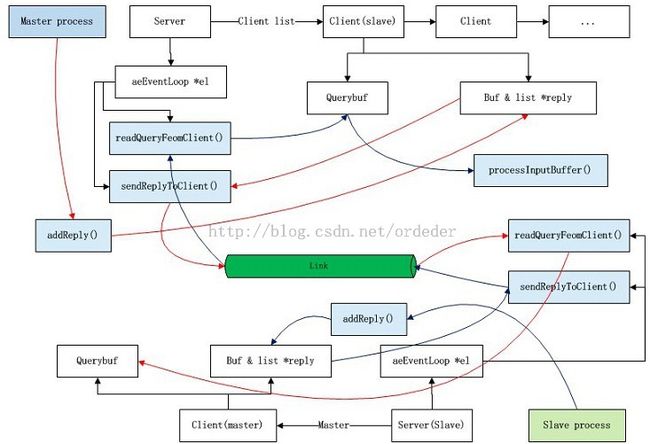
在Redis中,server为每个连接建立一个redisClient数据对象,来描述对应的连接。其中,redisClient为命令交互设置了缓冲区。querybuf用于存储客户端送过来的命令,buf和reply是用于应答的缓冲。querybuf是在文件事件readQueryFromClient中被填充,每次填充的最大字节数默认为1024B。而应答缓冲区是由addReply()函数填充,并由文件事件sendReplyToClient中发送给客户端。具体数据流如图1所示。MasterPorcess与SlaveProcess进行命令交互。其中,蓝色矩形框代表函数,白色矩形框代表数据,曲线描述数据流,折线描述数据间的从属关系。
图1. Master&Slave交互的数据流(蓝色矩形框代表函数,白色矩形框代表数据,曲线描述数据流,折线描述数据间的从属关系)
1、相关数据结构
typedef struct redisClient {
int fd; //connect fd
...
sds querybuf; //命令缓冲区,由readQueryFromClient()事件进行填充(sds equals to char*)
int argc; //for command;记录参数个数
robj **argv; //for command;记录命令行参数
int reqtype; //命令解析协议:INLINE or MULTIBULK
...
time_t lastinteraction; /* 最近交互时间 */
...
list *reply; //Replay object list
/* Response buffer */
char buf[REDIS_REPLY_CHUNK_BYTES]; //Reply buffer,由addReply()函数进行填充
int bufpos; //记录buf已填充的长度
int sentlen; //Replay阶段,记录当前buf已发送了多少字节
} redisClient;
struct redisServer {
...
list *clients;
dict *commands; /* Command table hahs table */
...
list *slaves, *monitors; //Master : slave链表
char neterr[ANET_ERR_LEN];
aeEventLoop *el; //Event list
int cronloops; //ServerCorn 执行次数
...
redisClient *master; //Slave :记录 master 的连接信息的client
int replstate; //Slave :当前的状态
...
};
struct redisCommand readonlyCommandTable[] = {
...
{"sync",syncCommand,1,0,NULL,0,0,0},
...
{"ping",pingCommand,1,0,NULL,0,0,0},
...
}
2、query的读取和命令的解析
从图1可以看出,命令交互数据query的读取是在文件事件readQueryFromClient中填充到c->querybuf中。
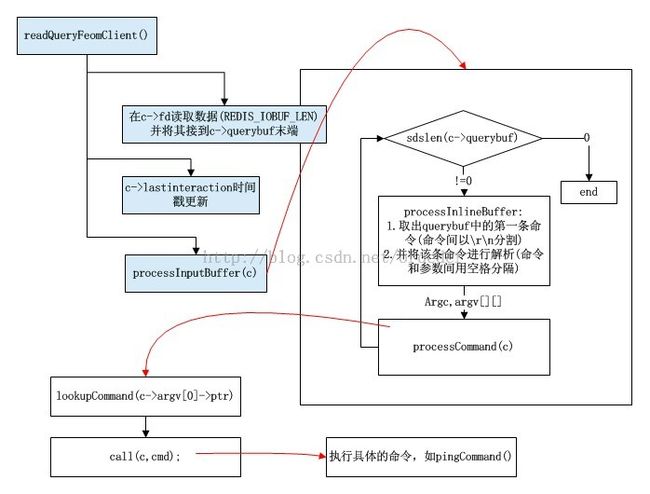
之后,querybuf由函数processInputBuffer进行命令的解析。命令的解析过程如图2所示。在函数processInputBuffer中,将缓存与querybuf中的所有命令(命令间按\n\r分隔)进行解析。
之后,查询命令hashtabe查找相关命令函数。最后调用相应命令hander执行命令。
图2.querybuf的解析
具体代码分析如下:
void readQueryFromClient(aeEventLoop *el, int fd, void *privdata, int mask) {
redisClient *c = (redisClient*) privdata;
char buf[REDIS_IOBUF_LEN];
int nread;
REDIS_NOTUSED(el);
REDIS_NOTUSED(mask);
nread = read(fd, buf, REDIS_IOBUF_LEN);
...check...
if (nread) {
c->querybuf = sdscatlen(c->querybuf,buf,nread);
c->lastinteraction = time(NULL);//更新时间戳
} else {
return;
}
processInputBuffer(c);//处理client传输过来的数据
}
void processInputBuffer(redisClient *c) {
/* 执行querybub中的所有命令*/
while(sdslen(c->querybuf)) {
...check...
/*判定命令的解析协议 */
if (!c->reqtype) {
if (c->querybuf[0] == '*') {
c->reqtype = REDIS_REQ_MULTIBULK;
} else {
c->reqtype = REDIS_REQ_INLINE;//按行解析
}
}
if (c->reqtype == REDIS_REQ_INLINE) {
/*processInlineBuffer:
1. 取出c->querybuf起始端到\r\n位置的字符串,更新c->querybuf
2. 将取出的字符串按照“ ”空格进行分段解析,得到命令及其参数
格式为: argc,*argv[],其中argv[0]为命令,argv[1~argc-1]为参数*/
if (processInlineBuffer(c) != REDIS_OK) break;
} else if (c->reqtype == REDIS_REQ_MULTIBULK) {
...
}
/* Multibulk processing could see a <= 0 length. */
if (c->argc == 0) {
resetClient(c);
} else {
/* Only reset the client when the command was executed. */
if (processCommand(c) == REDIS_OK) //执行命令
resetClient(c);
}
}
}
/* If this function gets called we already read a whole
* command, argments are in the client argv/argc fields.
* processCommand() execute the command or prepare the
* server for a bulk read from the client.
*/
int processCommand(redisClient *c) {
struct redisCommand *cmd;
...
/* Now lookup the command and check ASAP about trivial error conditions
* such wrong arity, bad command name and so forth. */
cmd = lookupCommand(c->argv[0]->ptr);
...check...
/* Exec the command */
if (c->flags & REDIS_MULTI &&
cmd->proc != execCommand && cmd->proc != discardCommand &&
cmd->proc != multiCommand && cmd->proc != watchCommand)
{
queueMultiCommand(c,cmd);
addReply(c,shared.queued);
} else {
if (server.vm_enabled && server.vm_max_threads > 0 &&
blockClientOnSwappedKeys(c,cmd))
return REDIS_ERR;
call(c,cmd); //执行命令
}
return REDIS_OK;
}
/* Call() is the core of Redis execution of a command */
void call(redisClient *c, struct redisCommand *cmd) {
long long dirty;
dirty = server.dirty;
cmd->proc(c); //执行命令
dirty = server.dirty-dirty;
if (server.appendonly && dirty)
feedAppendOnlyFile(cmd,c->db->id,c->argv,c->argc);
if ((dirty || cmd->flags & REDIS_CMD_FORCE_REPLICATION) &&
listLength(server.slaves))
replicationFeedSlaves(server.slaves,c->db->id,c->argv,c->argc);
if (listLength(server.monitors))
replicationFeedMonitors(server.monitors,c->db->id,c->argv,c->argc);
server.stat_numcommands++;
}
3、具体命令的执行(ping命令)
addReply将相关命令执行结果放入client的reply缓冲区中。reply缓冲区的发送时机是在事件sendReplyToClient中进行。
#define REDIS_STRING 0
shared.pong = createObject(REDIS_STRING,sdsnew("+PONG\r\n"));
//{"ping",pingCommand,1,0,NULL,0,0,0}
void pingCommand(redisClient *c) {
addReply(c,shared.pong); //ping的回复是pong,打乒乓,呵呵
}
//将命令执行的返回结构写入c->buf 或者 c->reply
void addReply(redisClient *c, robj *obj) {
if (_installWriteEvent(c) != REDIS_OK) return;//创建event sendReplyToClient
redisAssert(!server.vm_enabled || obj->storage == REDIS_VM_MEMORY);
/* This is an important place where we can avoid copy-on-write
* when there is a saving child running, avoiding touching the
* refcount field of the object if it's not needed.
*
* If the encoding is RAW and there is room in the static buffer
* we'll be able to send the object to the client without
* messing with its page. */
if (obj->encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_RAW) {
if (_addReplyToBuffer(c,obj->ptr,sdslen(obj->ptr)) != REDIS_OK)
_addReplyObjectToList(c,obj);
} else {
/* FIXME: convert the long into string and use _addReplyToBuffer()
* instead of calling getDecodedObject. As this place in the
* code is too performance critical. */
obj = getDecodedObject(obj);
if (_addReplyToBuffer(c,obj->ptr,sdslen(obj->ptr)) != REDIS_OK)
_addReplyObjectToList(c,obj);
decrRefCount(obj);
}
}
4、 reply缓冲区数据的发送
将c->buf 和 c->reply中的数据发送到客户端(slave or master)。在每次文件事件中发送所有的reply缓冲区中的数据。
void sendReplyToClient(aeEventLoop *el, int fd, void *privdata, int mask) {
redisClient *c = privdata;
int nwritten = 0, totwritten = 0, objlen;
robj *o;
REDIS_NOTUSED(el);
REDIS_NOTUSED(mask);
while(c->bufpos > 0 || listLength(c->reply)) {
if (c->bufpos > 0) {
//发送c->buf中的数据
if (c->flags & REDIS_MASTER) {
/* Don't reply to a master */
nwritten = c->bufpos - c->sentlen;
} else {
nwritten = write(fd,c->buf+c->sentlen,c->bufpos-c->sentlen);
if (nwritten <= 0) break;
}
c->sentlen += nwritten;
totwritten += nwritten;
/* If the buffer was sent, set bufpos to zero to continue with
* the remainder of the reply. */
if (c->sentlen == c->bufpos) {
c->bufpos = 0;
c->sentlen = 0;
}
} else {
//发送c->reply中的数据
o = listNodeValue(listFirst(c->reply));
objlen = sdslen(o->ptr);
if (objlen == 0) {
listDelNode(c->reply,listFirst(c->reply));
continue;
}
if (c->flags & REDIS_MASTER) {
/* Don't reply to a master */
nwritten = objlen - c->sentlen;
} else {
nwritten = write(fd, ((char*)o->ptr)+c->sentlen,objlen-c->sentlen);
if (nwritten <= 0) break;
}
c->sentlen += nwritten;
totwritten += nwritten;
/* If we fully sent the object on head go to the next one */
if (c->sentlen == objlen) {
listDelNode(c->reply,listFirst(c->reply));
c->sentlen = 0;
}
}
/* Note that we avoid to send more thank REDIS_MAX_WRITE_PER_EVENT
* bytes, in a single threaded server it's a good idea to serve
* other clients as well, even if a very large request comes from
* super fast link that is always able to accept data (in real world
* scenario think about 'KEYS *' against the loopback interfae) */
if (totwritten > REDIS_MAX_WRITE_PER_EVENT) break;
}
...check...
if (totwritten > 0) c->lastinteraction = time(NULL);
/*reply数据全部发送完毕后,要关闭该文件的写事件。
该事件重新开启的时机为addReply()>>_installWriteEvent(c)(见3小节)*/
if (listLength(c->reply) == 0) {
c->sentlen = 0;
aeDeleteFileEvent(server.el,c->fd,AE_WRITABLE);
/* Close connection after entire reply has been sent. */
if (c->flags & REDIS_CLOSE_AFTER_REPLY) freeClient(c);
}
}
5、总结
命令行交互过程中:
1)为每个连接有相应的数据进行描述(redisClient),这样便于连接的管理。
2)命令行交互中,引入命令缓冲区querybuf,这样可以延时处理命令,这在事件轮询机制中,是至关重要的。