简介
按照在哪里跌倒就在哪里爬起来的精神,本章继续做车牌号的检测识别。所有步骤分为3步完成:车牌号定位,车牌号字符分割、字符识别。
本章为第一部分:车牌号定位。
效果演示
正式开始讲解之前,先看下车牌号定位出来的效果演示。注:本文所有图片均来源于网络。


如图所示,定位到车牌号之后,将车牌号用黄色框选起来,同时将该车牌复制为新图片显示出来。
代码及实现原理讲解
图像灰阶/二值化
首先也是常用的操作,将图像灰阶化,然后从像素值为255一侧开始,以累积像素占总像素5%的的地方作为二值化的阀值,进而获得对应的二值化图像。
对应代码如下:
void pic_gray(Mat& mat1, Mat& mat2){
IplImage pI = mat1;
uchar* ptr;
CvScalar s;
int width = mat1.rows;
int height = mat1.cols;
mat2 = cv::Mat(width, height, CV_8UC1, 1);
ptr = mat2.ptr(0);
for(int i = 0; i < width; i++){
for(int j=0; j<height; j++){
s = cvGet2D(&pI,i,j);
int grayScale = (int)(s.val[0]*0.299 + s.val[1]*0.587 + s.val[2]*0.114);
ptr[i*height+j] = grayScale;
}
}
}
int histogram_Calculate(Mat& mat1, int number){
Mat gray_hist;
int histSize = 255;
float range[] = { 0, 255 } ;
const float* histRange = { range };
bool uniform = true;
bool accumulate = false;
int width, height;
int i, j;
uchar* ptr = mat1.ptr(0);
long int pixel_all = 0, pixel_Calc = 0;
calcHist(&mat1, 1, 0, Mat(), gray_hist, 1, &histSize, &histRange, uniform, accumulate);
width = gray_hist.rows;
height = gray_hist.cols;
for(i=0; i<=width; i++){
pixel_all += ptr[i];
}
for(i=0; i<=width; i++){
pixel_Calc += ptr[255 - i];
if(((pixel_Calc * 100) / pixel_all) > number){
i = 255 - i;
break;
}
}
return i;
}
void pic_Thresholding(Mat& mat1, int threshold){
uchar* ptr = mat1.ptr(0);
int width = mat1.rows;
int height = mat1.cols;
for(int i = 0; i < width; i++){
for(int j=0;j<height;j++){
if(ptr[i*height+j] > 125){
ptr[i*height+j] = 255;
}else{
ptr[i*height+j] = 0;
}
}
}
}
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <math.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <opencv/cv.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "lib/normal.h"
#define DEBUG
#ifdef DEBUG
#define DE(format, ...) printf(format, ## __VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define DE(format, ...) while(0)
#endif
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
int threshold = 0;
Mat img = cv::imread(argv[1]);
double x_beta;
int width = img.rows;
int height = img.cols;
int** selection_1, selection_Number_1;
int** address_1, address_Number_1;
int i, j, color_num, box_flag;
Mat img_3, img_4, img_5;
Mat img_2;
char str[2];
Point s1, s2;
Scalar color = Scalar( 0, 255, 255);
namedWindow("img");
imshow("img",img);
pic_gray(img, img_2);
threshold = histogram_Calculate(img_2, 5);
DE("threshold:%d\n",threshold);
pic_Thresholding(img_2, threshold);
namedWindow("tmp");
imshow("tmp", img_2);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
首先pic_gray来讲源图像img,转化为灰阶图像img_2;接着用histogram_Calculate函数,以5%的比例算出二值化的阀值threshold,最后用pic_Thresholding,
二值化图像。
效果演示如下:
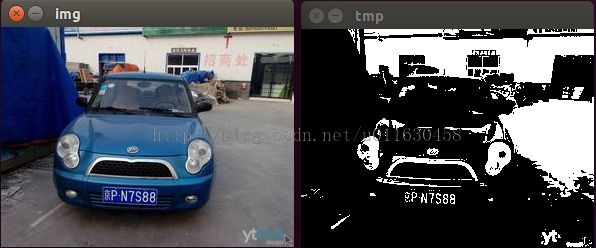
图像分割
车牌是使用是蓝底白字,而这个二值化图像img_2中,蓝色的背景被去除了,留下了白色的字。而根据车牌的特点,每一行中蓝色和白色的交替应该至少是7次。
转化在这个img_2的二值图像中,则表示在车牌所在的行中,像素值的跳变至少是7次。所以根据这个特性,可以将图像中,可能是车牌号所在位置的图像分割出来。
使用的代买如下:
int** selection_Function_1(Mat& mat1, int* number){
int **a, i, j, flag, num = 0, enter_flag = 0;
int width = mat1.rows;
int height = mat1.cols;
uchar* ptr = mat1.ptr(0);
a = (int**)malloc(width * sizeof(int*));
for(i=0; i<width; i++){
flag = 0;
for(j=0; j< height-1; j++){
if(ptr[i*height + j] != ptr[i*height + j +1]){
flag += 1;
}
}
if((flag >= 7) && (enter_flag == 0)){
a[num] = (int* )malloc(2 * sizeof(int));
a[num][0] = i;
enter_flag = 1;
}else if((enter_flag != 0) && (flag < 7)){
if(i - a[num][0] < 8){
continue;
}
a[num][1] = i - 1;
num ++;
enter_flag = 0;
}
}
*number = num;
return a;
}
void pic_cutting(Mat& mat1, Mat& pic_cutting, int** selection, int number){
int real_height = mat1.cols;
IplImage pI_1 = mat1;
IplImage pI_2;
IplImage pI_3;
CvScalar s;
pic_cutting = cv::Mat(selection[number][1] - selection[number][0], real_height, CV_8UC3, 1);
pI_2 = pic_cutting;
for(int i = selection[number][0]; i < selection[number][1]; i++){
for(int j=0; j<real_height; j++){
s = cvGet2D(&pI_1, i, j);
cvSet2D(&pI_2, i-selection[number][0], j, s);
}
}
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
................
selection_1 = selection_Function_1(img_2, &selection_Number_1);
for(i=0; i< selection_Number_1; i++){
DE("selection_1[%d]:%d, %d\n", i, selection_1[i][0], selection_1[i][1]);
}
for(i=0; i<selection_Number_1; i++){
pic_cutting(img, img_3, selection_1, i);
sprintf(str, "%d", i);
namedWindow(str);
imshow(str, img_3);
}
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
首先使用函数selection_Function_1,将二值图像img_2中连续出现了至少七次跳变行的图像行开始位置与结束位置保存到二维数组selection_1,img_2中一共有
多少次出现满足连续出现至少七次跳变行图像的统计保存在selection_Number_1中。
接着函数pic_cutting用img源图像长度作为新图像长度,用selection_1中保存的行开始,结束位置作为新图像宽度,从源图像中将对应位置的图像复制到img_3
中。显示效果如下:

从显示效果途中,我们看到原图像被分割为了6张图片,车牌在第五张图片中。
图片筛选
从车牌号特性知道,车牌的背景为蓝色。这里就是检测分割出来的图片中,蓝色占的数量,将不满足要求的图片抛弃掉。
接着将筛选出来的图片,再一次灰阶、二值化。
代码如下:
int choice_Color(Mat& mat1, int color_Start, int color_End){
int width = mat1.rows;
int height = mat1.cols;
uchar* ptr = mat1.ptr(0);
IplImage pI_1;
int flag[width];
int num, i, j, num_width = 0;
CvScalar s;
pI_1 = mat1;
cvCvtColor(&pI_1, &pI_1, CV_BGR2HSV);
for(i=0; i<width; i++){
num = 0;
for(j=0; j<height; j++){
s = cvGet2D(&pI_1, i, j);
if((s.val[0] >= color_Start) && (s.val[0] <= color_End)){
num += 1;
}
}
if(num > 20){
flag[i] = 1;
num_width += 1;
}else{
flag[i] = 0;
}
num = 0;
}
return num_width;
}
int main(int ragc, char** argv){
..........
for(i=0; i<selection_Number_1; i++){
pic_cutting(img, img_3, selection_1, i);
color_num = choice_Color(img_3, 110, 120); //蓝色为H:110--120
DE("color_num:%d\n", color_num);
if(color_num > 5){
IplImage pI_1 = img_3;
cvCvtColor(&pI_1, &pI_1, CV_HSV2BGR);
pic_gray(img_3, img_3);
threshold = histogram_Calculate(img_3, 3);
pic_Thresholding(img_3, threshold);
sprintf(str, "%d", i);
namedWindow(str);
imshow(str, img_3);
}
}
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
使用choice_Color将分割出来的每张图片img_3都依次转化为HSV,然后根据H来检测出图像中蓝色像素超过20的行数,并将该数据返回到color_num中。
接着判断如果color_num 大于了5行就表示该图像不能抛弃。
演示效果如下:

因为该图像中,蓝色干扰背景相当多,所以该步骤,只筛选丢弃了最后一张图片。




