Spring源码学习之IOC实现原理(二)-ApplicationContext
一.Spring核心组件结构
总的来说Spring共有三个核心组件,分别为Core,Context,Bean.三大核心组件的协同工作主要表现在 :Bean是包装我们应用程序自定义对象Object的,Object中存有数据,而Context就是为了这些数据存放提供一个生存环境,保存各个 bean之间的对应关系,并且维护好这些对应关系。Context就是一个Bean关系的集合,也就是我们所谓的IOC容器。Core就是Context 在发现、建立、维护Bean之间关系所需要的一些工具,如资源的加载,资源的抽象等。 (《深入分析Java Web技术内幕》)
1.Bean组件
前面介绍的BeanFactory体系就属于Bean组件,位于org.springframework.beans子包factory包下面。这个包主要解决三个问题,Bean的定义,Bean的创建,Bean的解析。
1. org.springframework.beans, 包含了操作java bean的接口和类。This package contains interfaces and classes for manipulating Java beans. It is used by most other Spring packages. ***
2. org.springframework.beans.annotation, 支持包,提供对java 5注解处理bean样式的支持。 3. org.springframework.beans.factory, 实现spring轻量级IoC容器的核心包。*** 4. org.springframework.beans.factory.access, 定位和获取bean工程的辅助工具类。 5. org.springframework.beans.factory.access.el,从统一样式的EL 获取spring beanFactory的支持类 6. org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation, 配置基于注解驱动的bean的支持包。*** 7. org.springframework.beans.factory.config, bean工厂的SPI接口和配置相关的处理类。 8. org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing, bean definition解析的支持基础类 9. org.springframework.beans.factory.serviceloader, jdk1.6 ServiceLoader基础类的支持包。 10. org.springframework.beans.factory.support,org.springframework.beans.factory包的支持类 11. org.springframework.beans.factory.wiring, 一种决定一个bean实例的元数据的机制。 12. org.springframework.beans.factory.xml, 包含了一个基于xml的beanFactory实现,也包含一个标准的spring-beans的dtd 13. org.springframework.beans.propertyeditors, 属性编辑器,用来将string类型的值转换为object类型,例如:java.util.Properties 14. org.springframework.beans.support,org.springframework.beans的支持包,像:一组bean的排序和保持工具类等
参考资料spring beans源码解读之--总结篇
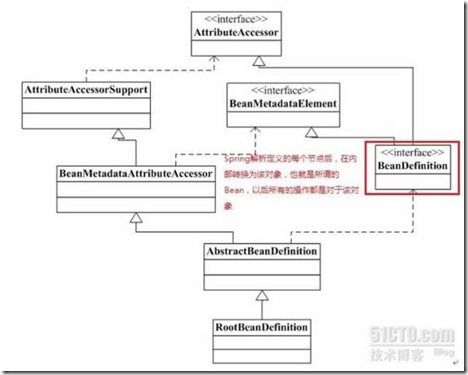
Bean的定义由BeanDefinition抽象出来,也是IOC容器的内部数据结构。BeanDefinition完整的描述了xml文件中关于<bean>节点的所有信息。当Spring解析一个<bean>节点后,在IOC容器内部就会转换为BeanDefinition对象。而最终实例化时,所使用的对象就是RootBeanDefinition对象。
图片引自Spring3.0核心组件的源码简单分析
Bean的创建,采用的是典型的工厂模式,采用的体系即(一)中所说的BeanFactory体系结构。主要的类是DefaultListableBeanFactory,其完整的实现了IOC容器的功能。
Bean的解析,主要就是对于Spring的配置文件进行解析处理,从中解析出相应的信息以用来生成Bean的对象。 其中主要用于解析的实现类就是DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader。
2.Core组件
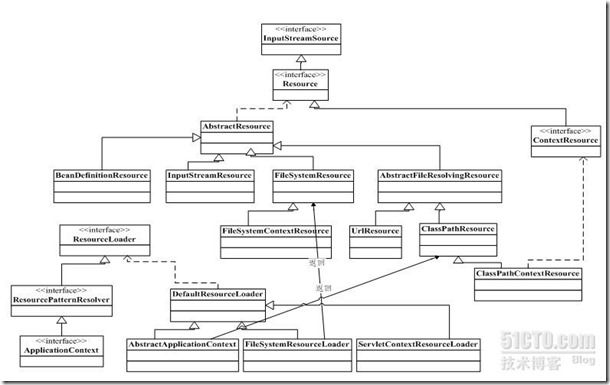
Core组件作为Spring的核心组件,其中包含了很多关键类,一个重要的组成部分就是定义了资源的访问方式。如之前用到的ClassPathResource就是其中的一个典型的资源抽象形式。资源的顶级接口为Resource,它继承自InputStreamSource,实现了其getInputStream方法,返回的是InputStream类。这样所有的资源就是通过该方法来获取输入流的。对于资源的加载,也实现了统一,屏蔽了资源提供者。定义了一个资源加载顶级接口 ResourceLoader ,它默认的加载就是DefaultResourceLoader。
2.1InputStreamSource
该接口只有一个抽象方法
public interface InputStreamSource { /** * Return an {@link InputStream}. */ InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException; }
2.2 Resource
作为顶级接口,也是再各个类中调用资源时应用最为广泛的接口,充分体现了面向接口编程的思想。
/** * Interface for a resource descriptor that abstracts from the actual * type of underlying resource, such as a file or class path resource. */ public interface Resource extends InputStreamSource { boolean exists(); boolean isReadable(); boolean isOpen(); URL getURL() throws IOException; URI getURI() throws IOException; File getFile() throws IOException; long contentLength() throws IOException; long lastModified() throws IOException; Resource createRelative(String relativePath) throws IOException; String getFilename(); String getDescription(); }
这就是该接口定义的方法,都是显而易见的方法,同时也是对于资源类来说应用最多的方法。
2.3ClassPathResource
/** * This implementation opens an InputStream for the given class path resource. * @see java.lang.ClassLoader#getResourceAsStream(String) * @see java.lang.Class#getResourceAsStream(String) */ @Override public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException { InputStream is; if (this.clazz != null) { is = this.clazz.getResourceAsStream(this.path); } else if (this.classLoader != null) { is = this.classLoader.getResourceAsStream(this.path); } else { is = ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream(this.path); } if (is == null) { throw new FileNotFoundException(getDescription() + " cannot be opened because it does not exist"); } return is; }
该方法就是ClassPathResource的getInputStream方法,可以发现其主要通过class类或者ClassLoader来返回InputStream。而之前的分析可知,当loadBeanDefinition时,最终应用的是InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);InputSource,属于org.xml.sax包,是一个XML形式的输入流。
3.Context组件
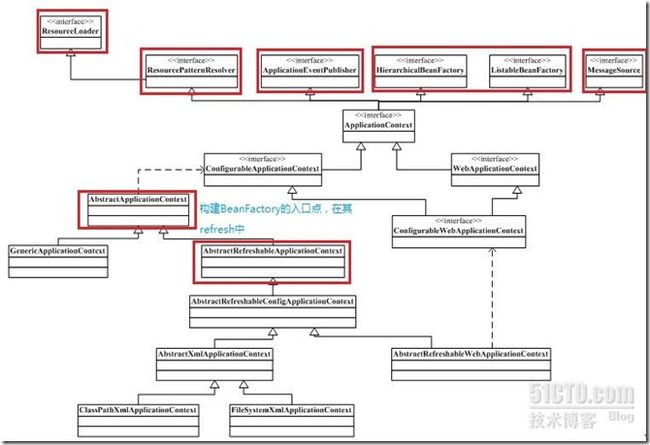
Context组件在Spring的org.springframework.context包下,它的作用主要是给Spring提供一个运行时的环境,用以保证各个对象的状态。其中ApplicationContext是Context的顶级父类接口,它除了继承一个能表示应用环境的基本信息接口外,还继承了5个接口,这5个接口扩展了Context的功能。
public interface ApplicationContext extends EnvironmentCapable, ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory, MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver
可以发现其主要应用子类为ClassPathXmlApplicationContext,FileSystemXmlApplicationContext,以及应用在Web上的XmlWebApplicationContext.
二. ApplicationContext源码详解
在ApplicationContext的设计中,一方面可以看到它继承了BeanFactory接口体系结构的ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory,具备了IOC容器的基本功能;另一方面,通过继承MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver这些接口,使得其被赋予了更高级别的特性。
1.java doc
/** * Central interface to provide configuration for an application. * This is read-only while the application is running, but may be * reloaded if the implementation supports this. * * <p>An ApplicationContext provides: * <ul> * <li>Bean factory methods for accessing application components. * Inherited from {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.ListableBeanFactory}. * <li>The ability to load file resources in a generic fashion. * Inherited from the {@link org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader} interface. * <li>The ability to publish events to registered listeners. * Inherited from the {@link ApplicationEventPublisher} interface. * <li>The ability to resolve messages, supporting internationalization. * Inherited from the {@link MessageSource} interface. * <li>Inheritance from a parent context. Definitions in a descendant context * will always take priority. This means, for example, that a single parent * context can be used by an entire web application, while each servlet has * its own child context that is independent of that of any other servlet. * </ul> * * <p>In addition to standard {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory} * lifecycle capabilities, ApplicationContext implementations detect and invoke * {@link ApplicationContextAware} beans as well as {@link ResourceLoaderAware}, * {@link ApplicationEventPublisherAware} and {@link MessageSourceAware} beans. * * @author Rod Johnson * @author Juergen Hoeller * @see ConfigurableApplicationContext * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory * @see org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader */
ApplicationContext添加的功能主要表现在 :
1)可以支持不同的信息源,它扩展了MessageSource,支持国际化。
2)访问资源,主要就是ResourceLoader的继承,这样可以从不同地方得到bean定义的资源。
3)支持应用事件,继承了ApplicationEventPublisher, 这样在上下文中引入了事件机制。
2.源码
public interface ApplicationContext extends EnvironmentCapable, ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory, MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver { /** * Return the unique id of this application context. * @return the unique id of the context, or {@code null} if none *///返回标志Context的Id编号 String getId(); /** * Return a name for the deployed application that this context belongs to. * @return a name for the deployed application, or the empty String by default */ //返回context所属应用名称 String getApplicationName(); /** * Return a friendly name for this context. * @return a display name for this context (never {@code null}) */ String getDisplayName(); /** * Return the timestamp when this context was first loaded. * @return the timestamp (ms) when this context was first loaded */ //返回loaded时间戳 long getStartupDate(); /** * Return the parent context, or {@code null} if there is no parent * and this is the root of the context hierarchy. * @return the parent context, or {@code null} if there is no parent */ //返回双亲ApplicationContext,证明这里是有层次关系的 ApplicationContext getParent(); /** * Expose AutowireCapableBeanFactory functionality for this context. * <p>This is not typically used by application code, except for the purpose of * initializing bean instances that live outside of the application context, * applying the Spring bean lifecycle (fully or partly) to them. * <p>Alternatively, the internal BeanFactory exposed by the * {@link ConfigurableApplicationContext} interface offers access to the * {@link AutowireCapableBeanFactory} interface too. The present method mainly * serves as a convenient, specific facility on the ApplicationContext interface. * <p><b>NOTE: As of 4.2, this method will consistently throw IllegalStateException * after the application context has been closed.</b> In current Spring Framework * versions, only refreshable application contexts behave that way; as of 4.2, * all application context implementations will be required to comply. * @return the AutowireCapableBeanFactory for this context * @throws IllegalStateException if the context does not support the * {@link AutowireCapableBeanFactory} interface, or does not hold an * autowire-capable bean factory yet (e.g. if {@code refresh()} has * never been called), or if the context has been closed already * @see ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh() * @see ConfigurableApplicationContext#getBeanFactory() */ AutowireCapableBeanFactory getAutowireCapableBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException; }
3.*****单步调试ApplicationContext****
仍然采用上一节所使用的例子
ApplicationContext appContext=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); Performer performer=(Performer) appContext.getBean("dancer"); performer.perform();
(1)ApplicationContext appContext=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
调用构造器
/** * Create a new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext, loading the definitions * from the given XML file and automatically refreshing the context. * @param configLocation resource location * @throws BeansException if context creation failed */ public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String configLocation) throws BeansException { this(new String[] {configLocation}, true, null); }
可以看到除了load xml定义文件外,还有自动刷新的作用。
第二个boolean参数,是refresh启动参数。
/** * Create a new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext with the given parent, * loading the definitions from the given XML files. * @param configLocations array of resource locations * @param refresh whether to automatically refresh the context, * loading all bean definitions and creating all singletons. * Alternatively, call refresh manually after further configuring the context. * @param parent the parent context * @throws BeansException if context creation failed * @see #refresh() */ public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException { super(parent); setConfigLocations(configLocations); if (refresh) { refresh(); } }
super(parent),通过逐层向上,最后会到AbstractApplicationContext.
回到上面可以看到refresh()方法即为IOC容器初始化的方法,标志着IOC容器的启动。
setConfigLocations(configLocations),设置资源属性数组
/** * Set the config locations for this application context. * <p>If not set, the implementation may use a default as appropriate. */ public void setConfigLocations(String... locations) { if (locations != null) { Assert.noNullElements(locations, "Config locations must not be null"); this.configLocations = new String[locations.length]; for (int i = 0; i < locations.length; i++) { this.configLocations[i] = resolvePath(locations[i]).trim(); } } else { this.configLocations = null; } }
(2)refresh()
该方法属于AbstractApplicationContext,即第一个抽象类。
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. //调用容器准备刷新的方法,获取容器的当时时间,同时给容器设置同步标识 ,log信息也是源自于这个方法 prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context. initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context. initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them. registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event. finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException ex) { logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt", ex); // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag. cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller. throw ex; } } }
2.1 prepareRefresh();
为刷新Context前做准备,设定启动时间,同时Log信息同样源自这个方法。
/** * Prepare this context for refreshing, setting its startup date and * active flag as well as performing any initialization of property sources. */ protected void prepareRefresh() { this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis(); this.active.set(true); if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Refreshing " + this); } // Initialize any placeholder property sources in the context environment initPropertySources(); // Validate that all properties marked as required are resolvable // see ConfigurablePropertyResolver#setRequiredProperties getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties(); }
2.2ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
刷新所有的BeanFactory子容器,同时这里涉及到了解析和载入BeanDefinition的步骤。
下面就分析一下BeanFactory的刷新方法refreshBeanFactory()
这里应用了委派模式,因为refreshBeanFactory()方法属于其子类AbstractRefreshApplicationContext.
/** * This implementation performs an actual refresh of this context's underlying * bean factory, shutting down the previous bean factory (if any) and * initializing a fresh bean factory for the next phase of the context's lifecycle. */ @Override protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException { if (hasBeanFactory()) { destroyBeans(); closeBeanFactory(); } try { DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory(); beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
//对IoC容器进行定制化,如设置启动参数,开启注解的自动装配等
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory); loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory); synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) { this.beanFactory = beanFactory; } } catch (IOException ex) { throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex); } }
1.这里可以看到一个构建DefaultListableBeanFactory容器的过程,先是构造BeanFactory,createBeanFactory()。
2.loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory),这里载入了beanDefinition。
接下来再深入loadBeanDefinition(beanFactory)方法
该方法属于AbstractXmlApplicationContext,又是一个委派模式,让子类来实现。
/** * Loads the bean definitions via an XmlBeanDefinitionReader. * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader * @see #initBeanDefinitionReader * @see #loadBeanDefinitions */ @Override protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException { // Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory. XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory); // Configure the bean definition reader with this context's // resource loading environment. beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment()); beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this); beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this)); // Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader, // then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions. initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader); loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader); }
1.XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory); 这个与(一)中分析的过程一样,同样是创建了一个可以载入BeanDefinition的读写器,同样用DefaultListableBeanFactory作为构造器参数,从而赋予registy属性。
2.调用loadBeanDefinitions()
/** * Load the bean definitions with the given XmlBeanDefinitionReader. * <p>The lifecycle of the bean factory is handled by the {@link #refreshBeanFactory} * method; hence this method is just supposed to load and/or register bean definitions. * @param reader the XmlBeanDefinitionReader to use * @throws BeansException in case of bean registration errors * @throws IOException if the required XML document isn't found * @see #refreshBeanFactory * @see #getConfigLocations * @see #getResources * @see #getResourcePatternResolver */ protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException { Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources(); if (configResources != null) { reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources); } String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations(); if (configLocations != null) { reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations); } }
最终调用reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations);这就又回到了(一)IOC容器初始化的过程。
到这里就完成了BeanDefinition的载入,注册工作。并且最终返回了DefaultListableBeanFactory,所以BeanDefinition持有容器依然是DefaultListableBeanFactory.所以接下来的工作就应该是实例化工作。
2.3 prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
这是在实例化之前进行的工作。
创建好beanFactory后,添加Spring本身需要的工具类。为容器配备了ClassLoader,PropertyEditor和BeanPostProcessor.
/** * Configure the factory's standard context characteristics, * such as the context's ClassLoader and post-processors. * @param beanFactory the BeanFactory to configure */ protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { // Tell the internal bean factory to use the context's class loader etc. beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader()); beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader())); beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment())); // Configure the bean factory with context callbacks. beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this)); //....... }
这里可以看到,ApplicationContextAwareProcessor作为BeanPostProcessor的实现,在这里添加。
其主要作用是当Bean实现了ApplicationContextAware接口后,当该Bean完成实例化依赖注入之后,会通过BeanPostProcessor的方式来给该Bean注入当前的ApplicationContext.从而使得该实例有能力获得ApplicationContext.
2.4 postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
这个方法是预留方法,是用来对BeanFactory进行后处理的方法。
2.5 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
调用所有注册的BeanFactoryPostProcessor的Bean,这里也是针对BeanFactory的后置处理器的调用。
2.6 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
BeanPostProcessor是Bean后置处理器,用于监听容器触发的事件,Bean的后置处理器。Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.这个注册主要是绑定到DefaultListableBeanFactory中取。
后置处理器向容器注册以后,容器中管理的Bean就具备了接收IoC容器事件回调的能力。
BeanPostProcessor是一个接口类,主要有两个方法,一个是postProcessBeforeInitialization,在Bean的初始化前提供回调入口;另一个是postProcessAfterInitialization,在Bean的初始化后提供回调入口。实际上,这两个后置处理器方法是一前一后围绕着Bean定义的init-method方法调用的,都是发生在populateBean()方法之后,即完成依赖注入之后发生的。
上面其实涉及到了两个Spring的扩展点,一个是BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor,他们分别在构建BeanFactory和构建Bean对象时调用,还有就是InitializationBean和DisposableBean,他们分别在Bean实例创建和销毁时被调用。
2.7 initMessageSource()和 initApplicationEventMulticaster();
初始化信息源和事件传播器。
这是由于ApplicationContext分别实现了MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher两个接口。
2.8 finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory)
完成BeanFactory的初始化工作,这里涉及到了对于lazy-init属性的处理。
/** * Finish the initialization of this context's bean factory, * initializing all remaining singleton beans. */ protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { // Initialize conversion service for this context. if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) { beanFactory.setConversionService( beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)); } // Initialize LoadTimeWeaverAware beans early to allow for registering their transformers early. String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false); for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) { getBean(weaverAwareName); } // Stop using the temporary ClassLoader for type matching. beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null); // Allow for caching all bean definition metadata, not expecting further changes. beanFactory.freezeConfiguration(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons(); }
最后一个方法preInstantiateSingletons(),看注释可知实例化所有的单例,non-lazy-init,即lazy-init属性为false,而由于其默认属性就是false,所以这里会实例化所有的单例。
@Override public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException { if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) { this.logger.debug("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this); } // Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions. // While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine. List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<String>(this.beanDefinitionNames); // Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans... for (String beanName : beanNames) { RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName); if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) { if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) { final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName); boolean isEagerInit; if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) { isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Boolean>() { @Override public Boolean run() { return ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit(); } }, getAccessControlContext()); } else { isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean && ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit()); } if (isEagerInit) { getBean(beanName); } } else { getBean(beanName); } } } // Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans... for (String beanName : beanNames) { Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName); if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) { final SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance; if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() { @Override public Object run() { smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated(); return null; } }, getAccessControlContext()); } else { smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated(); } } } }
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()),从这句代码可以看出当BeanDefinition不是抽象类,是单例类,lazyinit属性为false时,则预实例化,其不为FactoryBean时调用getBean()方法。
其BeanDefinition定义如下:Root bean: class [com.wly.source.spring_scoure_inspect.Dancer]; scope=singleton; abstract=false; lazyInit=false; autowireMode=0; dependencyCheck=0; autowireCandidate=true; primary=false; factoryBeanName=null; factoryMethodName=null; initMethodName=null; destroyMethodName=null; defined in class path resource [beans.xml]
所以这里就完成了预实例化的过程。
2.9 finishRefresh()
初始化容器的生命周期事件处理器,并发布容器的生命周期事件。
/** * Finish the refresh of this context, invoking the LifecycleProcessor's * onRefresh() method and publishing the * {@link org.springframework.context.event.ContextRefreshedEvent}. */ protected void finishRefresh() { // Initialize lifecycle processor for this context. initLifecycleProcessor(); // Propagate refresh to lifecycle processor first. getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh(); // Publish the final event. publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this)); // Participate in LiveBeansView MBean, if active. LiveBeansView.registerApplicationContext(this); }