python常用模块详解
课程链接:
http://www.cnblogs.com/alex3714/articles/5161349.html
一、os
os.getcwd() 获取当前工作目录,即当前python脚本工作的目录路径
os.chdir("dirname") 改变当前脚本工作目录;相当于shell下cd
os.curdir 返回当前目录: ('.')
os.pardir 获取当前目录的父目录字符串名:('..')
os.makedirs('dirname1/dirname2') 可生成多层递归目录
os.removedirs('dirname1') 若目录为空,则删除,并递归到上一级目录,如若也为空,则删除,依此类推
os.mkdir('dirname') 生成单级目录;相当于shell中mkdir dirname
os.rmdir('dirname') 删除单级空目录,若目录不为空则无法删除,报错;相当于shell中rmdir dirname
os.listdir('dirname') 列出指定目录下的所有文件和子目录,包括隐藏文件,并以列表方式打印
os.remove() 删除一个文件
os.rename("oldname","newname") 重命名文件/目录
os.stat('path/filename') 获取文件/目录信息
os.sep 输出操作系统特定的路径分隔符,win下为"\\",Linux下为"/"
os.linesep 输出当前平台使用的行终止符,win下为"\t\n",Linux下为"\n"
os.pathsep 输出用于分割文件路径的字符串
os.name 输出字符串指示当前使用平台。win->'nt'; Linux->'posix'
os.system("bash command") 运行shell命令,直接显示
os.environ 获取系统环境变量
os.path.abspath(path) 返回path规范化的绝对路径
os.path.split(path) 将path分割成目录和文件名二元组返回
os.path.dirname(path) 返回path的目录。其实就是os.path.split(path)的第一个元素
os.path.basename(path) 返回path最后的文件名。如何path以/或\结尾,那么就会返回空值。即os.path.split(path)的第二个元素
os.path.exists(path) 如果path存在,返回True;如果path不存在,返回False
os.path.isabs(path) 如果path是绝对路径,返回True
os.path.isfile(path) 如果path是一个存在的文件,返回True。否则返回False
os.path.isdir(path) 如果path是一个存在的目录,则返回True。否则返回False
os.path.join(path1[, path2[, ...]]) 将多个路径组合后返回,第一个绝对路径之前的参数将被忽略
os.path.getatime(path) 返回path所指向的文件或者目录的最后存取时间
os.path.getmtime(path) 返回path所指向的文件或者目录的最后修改时间
二、sys
sys.argv 命令行参数List,第一个元素是程序本身路径
sys.exit(n) 退出程序,正常退出时exit(0)
sys.version 获取Python解释程序的版本信息
sys.maxint 最大的Int值
sys.path 返回模块的搜索路径,初始化时使用PYTHONPATH环境变量的值
sys.platform 返回操作系统平台名称
sys.stdout.write('please:')
val = sys.stdin.readline()[:-1]
三、haslib
用于加密相关的操作,代替了md5模块和sha模块,主要提供 SHA1, SHA224, SHA256, SHA384, SHA512 ,MD5 算法
import hashlib # ######## md5 ######## hash = hashlib.md5() hash.update('admin') print hash.hexdigest() # ######## sha1 ######## hash = hashlib.sha1() hash.update('admin') print hash.hexdigest() # ######## sha256 ######## hash = hashlib.sha256() hash.update('admin') print hash.hexdigest() # ######## sha384 ######## hash = hashlib.sha384() hash.update('admin') print hash.hexdigest() # ######## sha512 ######## hash = hashlib.sha512() hash.update('admin') print hash.hexdigest()
以上加密算法虽然依然非常厉害,但时候存在缺陷,即:通过撞库可以反解。所以,有必要对加密算法中添加自定义key再来做加密。
import hashlib # ######## md5 ######## hash = hashlib.md5('898oaFs09f') hash.update('admin') print hash.hexdigest()
python 还有一个 hmac 模块,它内部对我们创建 key 和 内容 再进行处理然后再加密
import hmac h = hmac.new('wueiqi') h.update('hellowo') print h.hexdigest()
四、subprocess
功能:执行系统命令
call
执行命令,返回状态码
|
1
2
|
ret
=
subprocess.call([
"ls"
,
"-l"
], shell
=
False
)
ret
=
subprocess.call(
"ls -l"
, shell
=
True
)
|
shell = True ,允许 shell 命令是字符串形式
check_call
执行命令,如果执行状态码是 0 ,则返回0,否则抛异常
|
1
2
|
subprocess.check_call([
"ls"
,
"-l"
])
subprocess.check_call(
"exit 1"
, shell
=
True
)
|
check_output
执行命令,如果状态码是 0 ,则返回执行结果,否则抛异常
|
1
2
|
subprocess.check_output([
"echo"
,
"Hello World!"
])
subprocess.check_output(
"exit 1"
, shell
=
True
)
|
subprocess.Popen(...)
用于执行复杂的系统命令
参数:
- args:shell命令,可以是字符串或者序列类型(如:list,元组)
- bufsize:指定缓冲。0 无缓冲,1 行缓冲,其他 缓冲区大小,负值 系统缓冲
- stdin, stdout, stderr:分别表示程序的标准输入、输出、错误句柄
- preexec_fn:只在Unix平台下有效,用于指定一个可执行对象(callable object),它将在子进程运行之前被调用
- close_sfs:在windows平台下,如果close_fds被设置为True,则新创建的子进程将不会继承父进程的输入、输出、错误管道。
所以不能将close_fds设置为True同时重定向子进程的标准输入、输出与错误(stdin, stdout, stderr)。 - shell:同上
- cwd:用于设置子进程的当前目录
- env:用于指定子进程的环境变量。如果env = None,子进程的环境变量将从父进程中继承。
- universal_newlines:不同系统的换行符不同,True -> 同意使用 \n
- startupinfo与createionflags只在windows下有效
将被传递给底层的CreateProcess()函数,用于设置子进程的一些属性,如:主窗口的外观,进程的优先级等等
import subprocess ret1 = subprocess.Popen(["mkdir","t1"]) ret2 = subprocess.Popen("mkdir t2", shell=True)
终端输入的命令分为两种:
- 输入即可得到输出,如:ifconfig
- 输入进行某环境,依赖再输入,如:python
终端输入的命令分为两种:
输入即可得到输出,如:ifconfig
输入进行某环境,依赖再输入,如:python
import subprocess obj = subprocess.Popen(["python"], stdin=subprocess.PIPE, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE) obj.stdin.write('print 1 \n ') obj.stdin.write('print 2 \n ') obj.stdin.write('print 3 \n ') obj.stdin.write('print 4 \n ') obj.stdin.close() cmd_out = obj.stdout.read() obj.stdout.close() cmd_error = obj.stderr.read() obj.stderr.close() print cmd_out print cmd_erro
import subprocess obj = subprocess.Popen(["python"], stdin=subprocess.PIPE, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE) obj.stdin.write('print 1 \n ') obj.stdin.write('print 2 \n ') obj.stdin.write('print 3 \n ') obj.stdin.write('print 4 \n ') out_error_list = obj.communicate() print out_error_list
import subprocess obj = subprocess.Popen(["python"], stdin=subprocess.PIPE, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE) out_error_list = obj.communicate('print "hello"') print out_error_list
五、json和pickle
用于序列化的两个模块
- json,用于字符串 和 python数据类型间进行转换
- pickle,用于python特有的类型 和 python的数据类型间进行转换
Json模块提供了四个功能:dumps、dump、loads、load
pickle模块提供了四个功能:dumps、dump、loads、load
六、shutil
高级的 文件、文件夹、压缩包 处理模块
shutil.copyfileobj(fsrc, fdst[, length])
功能:将文件内容拷贝到另一个文件中,可以部分内容shutil.copyfile(src, dst)
功能:仅拷贝文件shutil.copymode(src, dst)
功能:仅拷贝权限,内容、组、用户均不变shutil.copystat(src, dst)
功能:拷贝状态的信息,包括:mode bits, atime, mtime, flagsshutil.copy(src, dst)
功能:拷贝文件和权限shutil.copy2(src, dst)
功能:拷贝文件和状态信息 1. zipfile 2. tarfile
七、ConfigParser
import configparser #生成文档 #["DEFAULT"]是一个全局模块,对所有的模块生效 ''' config = configparser.ConfigParser() config["DEFAULT"] = {'ServerAliveInterval': '45', 'Compression': 'yes', 'CompressionLevel': '9'} config['bitbucket.org'] = {} config['bitbucket.org']['User'] = 'hg' config['topsecret.server.com'] = {} topsecret = config['topsecret.server.com'] topsecret['Host Port'] = '50022' # mutates the parser topsecret['ForwardX11'] = 'no' # same here config['DEFAULT']['ForwardX11'] = 'yes' with open('example.ini', 'w') as configfile: config.write(configfile) ''' #查询 ''' config = configparser.ConfigParser() config.read('example.ini') print(config.sections()) #['bitbucket.org', 'topsecret.server.com'] if 'bitbucket.org' in config: print('True') print("['bitbucket.org']['User']:",config['bitbucket.org']['User']) print("['bitbucket.org']['Compression']:",config['bitbucket.org']['Compression']) for key in config['bitbucket.org']: print(key) ''' #读 ''' config = configparser.ConfigParser() config.read('example.ini') secs = config.sections() print(secs) #['bitbucket.org', 'topsecret.server.com'] options = config.options('topsecret.server.com') print(options) #['host port', 'forwardx11', 'compression', 'serveraliveinterval', 'compressionlevel'] item_list = config.items('bitbucket.org') print(item_list) #[('compression', 'yes'), ('serveraliveinterval', '45'), ('compressionlevel', '9'), ('forwardx11', 'yes'), ('user', 'hg')] val = config.get('bitbucket.org','compression') print(val) ''' #改写 config = configparser.ConfigParser() config.read('example.ini') #实现从原来的文件中读取,删除[bitbucket.org]模块后将其他内容写到example_new.ini文件中 # sec = config.remove_section('bitbucket.org') # config.write(open('example_new.ini', "w")) #添加[swht]模块 # sec = config.has_section('swht') # sec = config.add_section('swht') # config.write(open('example_new1.ini', "w"))
八、logging
代码示例
#!/usr/local/env python3 import logging # logging.warning("user [swht] is start the systerm!") # logging.critical("server is down!") #创建日志 logger = logging.getLogger('[Test-Log]') logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG) #创建一个控制台的handler并设置日志级别 ch = logging.StreamHandler() ch.setLevel(logging.DEBUG) #创建一个文件的handler并设置日志级别 fh = logging.FileHandler("access.log") fh.setLevel(logging.WARNING) #创建日期格式 fomatter = logging.Formatter('%(asctime)s %(name)s %(levelname)s %(message)s',datefmt='%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S') #add formatter to ch and fh ch.setFormatter(fomatter) fh.setFormatter(fomatter) logger.addHandler(ch) logger.addHandler(fh) # 'application' code logger.debug('debug message') logger.info('info message') logger.warn('warn message') logger.error('error message') logger.critical('critical message') #输出格式: ''' 2016-02-20 16:53:27 [Test-Log] DEBUG debug message 2016-02-20 16:53:27 [Test-Log] INFO info message 2016-02-20 16:53:27 [Test-Log] WARNING warn message 2016-02-20 16:53:27 [Test-Log] ERROR error message 2016-02-20 16:53:27 [Test-Log] CRITICAL critical message
九、time
时间相关的操作,时间有三种表示方式:
- 时间戳 1970年1月1日之后的秒,即:time.time()
- 格式化的字符串 2014-11-11 11:11, 即:time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
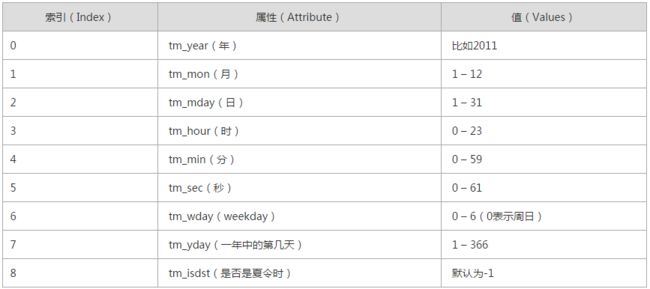
- 结构化时间 元组包含了:年、日、星期等... time.struct_time 即:time.localtime()
print time.time() print time.mktime(time.localtime()) print time.gmtime() #可加时间戳参数 print time.localtime() #可加时间戳参数 print time.strptime('2014-11-11', '%Y-%m-%d') print time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d') #默认当前时间 print time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d',time.localtime()) #默认当前时间 print time.asctime() print time.asctime(time.localtime()) print time.ctime(time.time()) import datetime ''' datetime.date:表示日期的类。常用的属性有year, month, day datetime.time:表示时间的类。常用的属性有hour, minute, second, microsecond datetime.datetime:表示日期时间 datetime.timedelta:表示时间间隔,即两个时间点之间的长度 timedelta([days[, seconds[, microseconds[, milliseconds[, minutes[, hours[, weeks]]]]]]]) strftime("%Y-%m-%d") ''' import datetime print datetime.datetime.now() print datetime.datetime.now() - datetime.timedelta(days=5)
十、random
随机数使用
import random print random.random() print random.randint(1,2) print random.randrange(1,10)
使用示例
import random checkcode = '' for i in range(4): current = random.randrange(0,4) if current != i: temp = chr(random.randint(65,90)) else: temp = random.randint(0,9) checkcode += str(temp) print checkcode
十一、paramiko
paramiko是一个用于做远程控制的模块,使用该模块可以对远程服务器进行命令或文件操作,值得一说的是,fabric和ansible内部的远程管理就是使用的paramiko来现实。
#!/usr/bin/env python #coding:utf-8 import paramiko ssh = paramiko.SSHClient() ssh.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy()) ssh.connect('192.168.1.108', 22, 'alex', '123') stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh.exec_command('df') print stdout.read() ssh.close();
import os,sys import paramiko t = paramiko.Transport(('182.92.219.86',22)) t.connect(username='wupeiqi',password='123') sftp = paramiko.SFTPClient.from_transport(t) sftp.put('/tmp/test.py','/tmp/test.py') t.close()
import paramiko pravie_key_path = '/home/auto/.ssh/id_rsa' key = paramiko.RSAKey.from_private_key_file(pravie_key_path) t = paramiko.Transport(('182.92.219.86',22)) t.connect(username='wupeiqi',pkey=key) sftp = paramiko.SFTPClient.from_transport(t) sftp.put('/tmp/test3.py','/tmp/test3.py') t.close() import paramiko pravie_key_path = '/home/auto/.ssh/id_rsa' key = paramiko.RSAKey.from_private_key_file(pravie_key_path) t = paramiko.Transport(('182.92.219.86',22)) t.connect(username='wupeiqi',pkey=key) sftp = paramiko.SFTPClient.from_transport(t) sftp.get('/tmp/test3.py','/tmp/test4.py') t.close(
十二、shelve
#!/usr/local/env python3 import shelve name = ['swht','shen','test'] class Test(object): def __init__(self,n): self.n = n t1 = Test(1234) t2 = Test(123456) #存数据 # shelve_file = shelve.open('ret.txt') # shelve_file['use'] = name # shelve_file['t1'] = t1 # shelve_file['t2'] = t2 # shelve_file.close() #取数据 shelve_load = shelve.open('ret.txt') a = shelve_load.get('use') print(a) b = shelve_load.get('t1') print(b.n) c = shelve_load.get('t2') print(c.n) shelve_load.close()