SQLiteDataBase(通过测试类测试写好的SQLite的相关数据库操作)
SQLiteDataBase(通过测试类测试写好的SQLite的相关数据库操作)
1.首先,创建数据库:
创建一个DbHelper.java的类
package com.example.sqldatabase;
import android.content.Context;
import android.database.DatabaseErrorHandler;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase.CursorFactory;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteOpenHelper;
/**
* @author 郑明亮
* @date 2015-11-13 下午8:02:27
* @version 1.0
* 测试看com.example.sqldatabase.test.StudentTest.java
*/
public class DbHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
/**
* @param context
*/
public DbHelper(Context context) {
//四个参数分别为:上下文,数据库的名字,Cursor工厂,数据库的版本号(最低从1开始)
super(context,"data.db", null, 1);
}
@Override
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase arg0) {
//创建数据库的一个表
String sql = "create table student(_id integer primary key autoincrement,name varchar(20),age integer,score float)";
arg0.execSQL(sql);
}
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase arg0, int arg1, int arg2) {
// 只有当数据库的版本号改变时才会调用的方法
}
}
2.然后写对数据库的增删改查:写一个dao层;
StudentDao.java
package com.example.entity.dao;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import android.content.Context;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import com.example.entity.Student;
import com.example.sqldatabase.DbHelper;
/**
* @author 郑明亮
* @date 2015-11-13 下午8:50:03
* @version 1.0
*/
public class StudentDao {
DbHelper helper = null;
public StudentDao(Context context) {
//在构造方法中实例化的好处是,
//当实例化StudentDao时,数据库DbHelper也进行了实例化
helper = new DbHelper(context);
}
/**
* @param name 学生姓名
* @param age 年龄
* @param score 分数
* 增加一个学生
*/
public void add(String name, int age, float score) {
SQLiteDatabase db = helper.getWritableDatabase();
db.execSQL("insert into student(name,age,score) values(?,?,?)",
new Object[] { name, age, score });
db.close();
}
/**
* @param id
* 通过id删除一个学生
*/
public void delete(int id) {
SQLiteDatabase db = helper.getWritableDatabase();
db.execSQL("delete from student where _id=?", new Object[] { id });
db.close();
}
/**
* @param id
* @param name
* @param age
* @param score
* 通过id更新一个学生的基本信息
*/
public void update(int id, String name, int age, float score) {
SQLiteDatabase db = helper.getWritableDatabase();
db.execSQL("update student set name=? ,age=? ,score=? where _id=?",
new Object[] { name, age, score, id });
db.close();
}
/**
* @param id
* @return 返回一个学生对象;
* 通过id返回一个学生的信息;
*/
public Student findByName(int id) {
Student student=null;
SQLiteDatabase db = helper.getReadableDatabase();
Cursor cursor = db.rawQuery("select * from student where _id=?",
new String[] { ""+id});
if(cursor.moveToFirst()){
String name = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("name"));
int age = cursor.getInt(cursor.getColumnIndex("age"));
float score = cursor.getFloat(cursor.getColumnIndex("score"));
student = new Student();
student.setName(name);
student.setAge(age);
student.setScore(score);}
return student;
}
/**
* @return 返回所有的学生信息
*/
public List<Student> findAll() {
List<Student> list = new ArrayList<Student>();
SQLiteDatabase db = helper.getReadableDatabase();
Cursor cursor = db.rawQuery("select * from student ", null);
while (cursor.moveToNext()) {
int id = cursor.getInt(cursor.getColumnIndex("_id"));
String name = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("name"));
int age = cursor.getInt(cursor.getColumnIndex("age"));
float score = cursor.getFloat(cursor.getColumnIndex("score"));
Student student = new Student(id, name, age, score);
list.add(student);
}
db.close();
return list;
}
}
3.在创建dao层时,用到了一个学生类,创建一个学生类:
Student.java
package com.example.entity;
/**
* @author 郑明亮
* @date 2015-11-13 下午8:47:48
* @version 1.0
*/
public class Student {
int id;
public Student() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Student(int id, String name, int age, float score) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.score = score;
}
String name;
int age;
float score;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public float getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(float score) {
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return "Id:"+id+",Name:"+name+",age:"+age+",score:"+score;
}
}
4.准备工作做好之后,该测试写的增删改查是不是正确了,
创建一个测试类StudentTest.java:
package com.example.sqldatabase.test;
import java.util.List;
import android.test.AndroidTestCase;
import android.util.Log;
import com.example.entity.Student;
import com.example.entity.dao.StudentDao;
/**
* @author 郑明亮
* @date 2015-11-13 下午8:12:04
* @version 1.0
*/
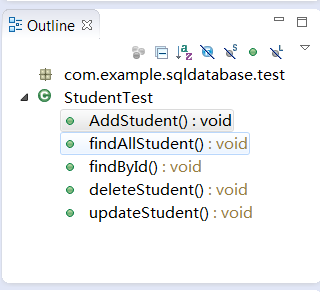
public class StudentTest extends AndroidTestCase {
/**
* 增加一名学生
*/
public void AddStudent() throws Exception {
StudentDao studentdao = new StudentDao(getContext());
studentdao.add("小明", 27, 91);
}
/**
* 查询所有的学生
*/
public void findAllStudent() throws Exception {
StudentDao studentdao = new StudentDao(getContext());
List<Student> list = studentdao.findAll();
for (Student s : list)
Log.e("Student",s.toString());
}
/**
* 通过id查找学生信息
*/
public void findById(){
StudentDao studentdao = new StudentDao(getContext());
Student student=studentdao.findByName(1);
System.out.println(student.toString());
}
/**通过id删除学生信息
*
*/
public void deleteStudent(){
StudentDao studentdao = new StudentDao(getContext());
studentdao.delete(1);
}
/**
*通过id更新学生的基本信息
*/
public void updateStudent(){
StudentDao studentdao = new StudentDao(getContext());
studentdao.update(2, "郑明亮修改", 100, 100);
}
}
目录结构:
所有的测试都在测试类中进行即可,不太懂使用测试类(Android Junit Test),请继续往下看,
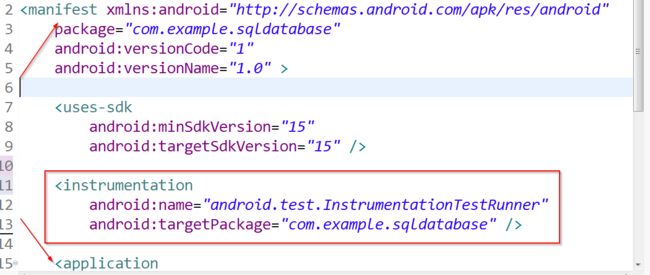
直接这样执行还是不行的,肯定会保存的,需要在AndroidManifest.xml中加两条配置,声明一下
项目下载地址:http://download.csdn.net/detail/zml_2015/9269019