如何在进程之间传递文件描述符(file discriptor)
fork的标准用法是master侦听,worker接受和伺服客户端。但是若只能是master侦听和接口并做一些处理后,才能知道该给哪个worker,就必须将client的socket fd传递给worker。可以通过socketpair(很高效的方式),很多服务器都是用它来多进程通信(譬如nginx)。
传递fd,通过sendmsg实现。
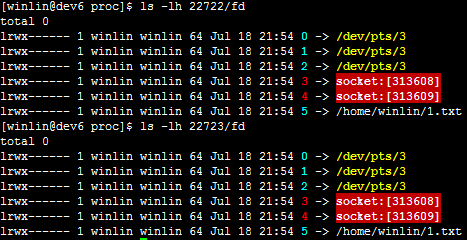
很关键的一点,send的fd和recv的fd不一定一样,而且基本上都不一样!所以不要直接传值。
如何在进程之间传递fd
http://www.myelin.co.nz/post/2003/12/2/If the two processes are communicating over some sort of socket, you can pass the file descriptor between them.
Here's a good explanation, from the postfix archive, of how to actually do it. Basically you use the sendmsg function
with a special flag that lets the kernel know you are sending a file descriptor, and it will duplicate the descriptor
and give it to the target process. Very handy.
===============================================================================================
http://archives.neohapsis.com/archives/postfix/2000-09/1476.html
In BSD, for example, file descriptors are passed through local domain
sockets (AF_LOCAL, formerly AF_UNIX) and the sendmsg() system call with
the cmsg_type field of a "struct cmsghdr" set to SCM_RIGHTS and the data
being an integer value equal to the handle of the file descriptor to be
passed. What in effect happens is the descriptor is duplicated inside
the kernel (as if with dup(2)) and then a reference to the file table
entry that new descriptor refers to is passed through the socket() layer
in a specially tagged internal message buffer. When the message is
"received" the kernel takes it on behalf of the receiving process and
allocates a new descriptor in the receiving process's file descriptor
table and hands back to the user-level code the new integer handle to
that entry. The sender and the receiver now have a descriptor that
refers to the same open file table entry and thus share the same offset
pointer, and by implication the same access rights.
===============================================================================================
《APUE》
17.4. Passing File Descriptors
太多太多了,可惜都很隐晦。所以在centos6下写了个程序:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
// for open
#include <fcntl.h>
// for iov
#include <sys/uio.h>
void send_fd(int sock, int fd)
{
iovec iov[1];
char c = 0;
iov[0].iov_base = &c;
iov[0].iov_len = 1;
int cmsgsize = CMSG_LEN(sizeof(int));
cmsghdr* cmptr = (cmsghdr*)malloc(cmsgsize);
if(cmptr == NULL){
cout << "[send_fd] init cmptr error" << endl;
exit(1);
}
cmptr->cmsg_level = SOL_SOCKET;
cmptr->cmsg_type = SCM_RIGHTS; // we are sending fd.
cmptr->cmsg_len = cmsgsize;
msghdr msg;
msg.msg_iov = iov;
msg.msg_iovlen = 1;
msg.msg_name = NULL;
msg.msg_namelen = 0;
msg.msg_control = cmptr;
msg.msg_controllen = cmsgsize;
*(int *)CMSG_DATA(cmptr) = fd;
int ret = sendmsg(sock, &msg, 0);
free(cmptr);
if (ret == -1){
cout << "[send_fd] sendmsg error" << endl;
exit(1);
}
}
int recv_fd(int sock)
{
int cmsgsize = CMSG_LEN(sizeof(int));
cmsghdr* cmptr = (cmsghdr*)malloc(cmsgsize);
char buf[32]; // the max buf in msg.
iovec iov[1];
iov[0].iov_base = buf;
iov[0].iov_len = sizeof(buf);
msghdr msg;
msg.msg_iov = iov;
msg.msg_iovlen = 1;
msg.msg_name = NULL;
msg.msg_namelen = 0;
msg.msg_control = cmptr;
msg.msg_controllen = cmsgsize;
int ret = recvmsg(sock, &msg, 0);
free(cmptr);
if (ret == -1) {
cout << "[recv_fd] recvmsg error" << endl;
exit(1);
}
int fd = *(int *)CMSG_DATA(cmptr);
return fd;
}
void master_process_cycle(int fds[2]){
cout << "master process #" << getpid() << endl;
// master use fds[0], and close fds[1]
int fd = fds[0];
//close(fds[1]);
//cout << "channel: #" << fds[0] << ", #" << fds[1] << ", fd=#" << fd << endl;
// send file discriptor
system("rm -f /home/winlin/1.txt");
int file = open("/home/winlin/1.txt", O_CREAT|O_TRUNC|O_RDWR);
cout << "[master] dispatch fd to worker process, file=#" << file << endl;
send_fd(fd, file);
close(file);
int status;
waitpid(-1, &status, 0);
exit(0);
}
void worker_process_cycle(int fds[2]){
cout << "worker process #" << getpid() << endl;
// master use fds[1], and close fds[0]
int fd = fds[1];
//close(fds[0]);
//cout << "channel: #" << fds[0] << ", #" << fds[1] << ", fd=#" << fd << endl;
int file = recv_fd(fd);
if(file < 0){
cout << "[worker] invalid fd! " << endl;
exit(1);
}
char msg[] = "child process";
cout << "[worker] write file #" << file << " ret = " << write(file, msg, sizeof(msg)) << endl;
close(file);
exit(0);
}
// <<Unix高级环境编程>> 第17.4节程序
int main(int argc, char** argv){
cout << "current pid: " << getpid() << endl;
int fds[2];
if(socketpair(AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0, fds) == -1){
cout << "failed to create domain socket by socketpair" << endl;
exit(1);
}
cout << "create domain socket by socketpair success" << endl;
cout << "create progress to communicate over domain socket" << endl;
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid == 0){
worker_process_cycle(fds);
}
else{
master_process_cycle(fds);
}
for(;;){
pause();
}
}
[winlin@dev6 2012-7-17-multiple-process]$ rm -f ~/1.txt;./dispatch_fd; echo "result is: " ; sudo cat ~/1.txt; echo ""
current pid: 22722
create domain socket by socketpair success
create progress to communicate over domain socket
master process #22722
worker process #22723
[master] dispatch fd to worker process, file=#5
[worker] write file #5 ret = 14
result is:
child process
有两个关键的地方:
1. cmptr->cmsg_type = SCM_RIGHTS; // we are sending fd. 告诉内核传递的是fd。
2.msg.msg_iov = iov;这个不能为NULL。
另外一个传输固定大小结构体的例子:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
// for open
#include <fcntl.h>
// for iov
#include <sys/uio.h>
#define CMD_FD 1
#define CMD_QUIT 2
struct channel_msg{
int command; // 1: passing fd, 2: quit
int fd; // the fd, set to -1 if no fd.
};
void write_channel(int sock, channel_msg* data, int size)
{
msghdr msg;
// init msg_control
if(data->fd == -1){
msg.msg_control = NULL;
msg.msg_controllen = 0;
}
else{
union {
struct cmsghdr cm;
char space[CMSG_SPACE(sizeof(int))];
} cmsg;
memset(&cmsg, 0, sizeof(cmsg));
cmsg.cm.cmsg_level = SOL_SOCKET;
cmsg.cm.cmsg_type = SCM_RIGHTS; // we are sending fd.
cmsg.cm.cmsg_len = CMSG_LEN(sizeof(int));
msg.msg_control = (cmsghdr*)&cmsg;
msg.msg_controllen = sizeof(cmsg);
*(int *)CMSG_DATA(&cmsg.cm) = data->fd;
}
// init msg_iov
iovec iov[1];
iov[0].iov_base = data;
iov[0].iov_len = size;
msg.msg_iov = iov;
msg.msg_iovlen = 1;
// init msg_name
msg.msg_name = NULL;
msg.msg_namelen = 0;
if (sendmsg(sock, &msg, 0) == -1){
cout << "[write_channel] sendmsg error" << endl;
exit(1);
}
}
void read_channel(int sock, channel_msg* data, int size)
{
msghdr msg;
// msg_iov
iovec iov[1];
iov[0].iov_base = data;
iov[0].iov_len = size;
msg.msg_iov = iov;
msg.msg_iovlen = 1;
// msg_name
msg.msg_name = NULL;
msg.msg_namelen = 0;
// msg_control
union { // union to create a 8B aligned memory.
struct cmsghdr cm; // 16B = 8+4+4
char space[CMSG_SPACE(sizeof(int))]; // 24B = 16+4+4
} cmsg;
memset(&cmsg, 0, sizeof(cmsg));
msg.msg_control = (cmsghdr*)&cmsg;
msg.msg_controllen = sizeof(cmsg);
if (recvmsg(sock, &msg, 0) == -1) {
cout << "[read_channel] recvmsg error" << endl;
exit(1);
}
data->fd = *(int *)CMSG_DATA(&cmsg.cm);
}
void master_process_cycle(int fds[2]){
cout << "master process #" << getpid() << endl;
// master use fds[0], and close fds[1]
int fd = fds[0];
//close(fds[1]);
//cout << "channel: #" << fds[0] << ", #" << fds[1] << ", fd=#" << fd << endl;
// send file discriptor
system("rm -f /home/winlin/1.txt");
int file = open("/home/winlin/1.txt", O_CREAT|O_TRUNC|O_RDWR);
cout << "[master] dispatch fd to worker process, file=#" << file << endl;
channel_msg data = {CMD_FD, file};
write_channel(fd, &data, sizeof(channel_msg));
close(file);
read_channel(fd, &data, sizeof(channel_msg));
if(CMD_QUIT == data.command){
cout << "[master] worker process exited" << endl;
}
int status;
waitpid(-1, &status, 0);
exit(0);
}
void worker_process_cycle(int fds[2]){
cout << "worker process #" << getpid() << endl;
// master use fds[1], and close fds[0]
int fd = fds[1];
//close(fds[0]);
//cout << "channel: #" << fds[0] << ", #" << fds[1] << ", fd=#" << fd << endl;
channel_msg data;
read_channel(fd, &data, sizeof(channel_msg));
int file = data.fd;
if(file < 0){
cout << "[worker] invalid fd! " << endl;
exit(1);
}
char msg[] = "child process";
cout << "[worker] write file #" << file << " ret = " << write(file, msg, sizeof(msg)) << endl;
close(file);
sleep(3);
data.command = CMD_QUIT;
data.fd = -1;
write_channel(fd, &data, sizeof(channel_msg));
exit(0);
}
// <<Unix高级环境编程>> 第17.4节程序
int main(int argc, char** argv){
cout << "current pid: " << getpid() << endl;
int fds[2];
if(socketpair(AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0, fds) == -1){
cout << "failed to create domain socket by socketpair" << endl;
exit(1);
}
cout << "create domain socket by socketpair success" << endl;
cout << "create progress to communicate over domain socket" << endl;
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid == 0){
worker_process_cycle(fds);
}
else{
master_process_cycle(fds);
}
for(;;){
pause();
}
}