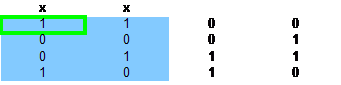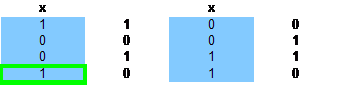简单易懂的Dancing links讲解(3)
Dancing Links除了能解决精确覆盖问题,还能解决重复覆盖问题,这里重点讲重复覆盖
题目:高手做题
描述
SubRaY被布置了n道作业题,可是他一道也不会..但他知道有w位高手,并知道每位高手
会做哪些题,请问SubRaY至少请多少位高手,才能把所有的题都做出来?
输入
第一行两个整数n,w表示有n道作业题和w位高手,作业题以1..n编号.接下来w行,第i+1
行第一个数li表示第i位高手会做的题目的数量,接下来li个数表示第i位高手会做哪
些题目.
3<=n,w<=60,1<=li<=6
输出
一个数,SubRaY至少要请多少位高手.
样例输入
4 4
2 1 2
1 4
3 2 3 4
2 1 3
样例输出
2 代码参考:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_51cea4040100gwpv.html
为了详细讲解Dancing links 重复覆盖的过程,我们先把样例输入转换为如下01矩阵

和精确覆盖一样,先选择含1最少的列,这里选择的1行1列的,选择后,
第1和2列被删除了,第一步, 效果如下:
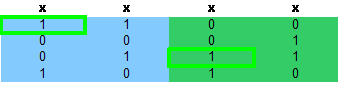
选择3行3列后,第3,4列也被删除了,至此重复覆盖的一个解已经被找到了,即1,3行,
但还不能确定这个解是最优的(可能只需一行就可以把所有列都覆盖),还需要继续搜索,
第二步
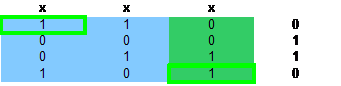
第三步,开始回溯,选择3行3列的兄弟节点4行3列后的效果如下
上图那样不能得到解,继续回溯到如下效果,第四步
第五步
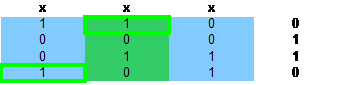
第六步
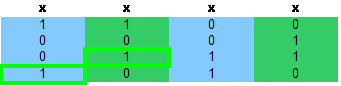
至此重复覆盖的另一个解已经被找到了,即3行和4行,
现在,所有的节点都被遍历过了,这个重复覆盖总共有两个解;1行和3行,3行和4行,每个解都是最优的,都需要两个高手 可供参考的剪枝函数:
- int Hash()
- {
- int ans=0;
- bool hash[maxn]={0};
- for (int c=R[0];c!=0;c=R[c])
- {
- if (!hash[c])
- {
- hash[c]=1;
- ans++;
- for (int i=D[c];i!=c;i=D[i])
- for (int j=R[i];j!=i;j=R[j])
- hash[nCol[j]]=1;
- }
- }
- cout << "Hash =>" << ans << endl;
- return ans;
- }
这个函数实际上是在对当前状态进行重复覆盖,只是覆盖列时,不是删除列,而是把相应列的标志位置1 ,这个函数的目的是,预先估计当前这样选择后,还需要多少行才能覆盖所有列。
函数返回值越大,越可能被剪枝
Dancing links 精确覆盖和重复覆盖的区别
1.精确覆盖更能体现dancing links 的威力,因为在剪枝的时候,精确覆盖不仅对列剪枝,对行也进行了剪枝,
而重复覆盖只对列进行剪枝,要想提高重复覆盖的效率还需要自己写剪枝函数
2.重复覆盖问题一般是求解最优解的,不像精确覆盖找到一个解就算完事,因此重复覆盖需要遍历和考察所有的分支,来找到最优的
全部代码:
- #include<iostream>
- using namespace std;
- const int maxn=20;
- int L[maxn],R[maxn],U[maxn],D[maxn];
- int S[maxn]={0};
- int nCol[maxn];
- int nRow[maxn];
- bool answer[4]={0};
- int n,w;
- int best=INT_MAX;
- int sample[4][4] = {
- {1,1,0,0},
- {0,0,0,1},
- {0,1,1,1},
- {1,0,1,0}
- };
- void init()
- {
- n=4;
- w=4;
- for (int i=0;i<=n;i++)
- {
- L[i]=i-1; R[i]=i+1;
- U[i]=D[i]=i;
- }
- L[0]=n;
- R[n]=0;
- int cnt=n+1;
- for (int i=0;i<w;i++)
- {
- int head=cnt,tail=cnt;
- for (int j=0;j<n;j++)
- {
- int c = j+1;
- if(sample[i][j]==1)
- {
- S[c]++;
- nCol[cnt]=c;
- nRow[cnt]=i;
- U[D[c]]=cnt;
- D[cnt]=D[c];
- U[cnt]=c;
- D[c]=cnt;
- L[cnt]=tail; R[tail]=cnt;
- R[cnt]=head; L[head]=cnt;
- tail=cnt;
- cnt++;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- void Remove(int x)
- {
- cout << "remove=>" << x << endl;
- for (int i=D[x];i!=x;i=D[i])
- {
- L[R[i]]=L[i];
- R[L[i]]=R[i];
- S[nCol[i]]--;
- }
- }
- void Resume(int x)
- {
- cout << "Resume=>" << x << endl;
- for (int i=U[x];i!=x;i=U[i])
- {
- L[R[i]]=R[L[i]]=i;
- S[nCol[i]]++;
- }
- }
- int Hash()
- {
- int ans=0;
- bool hash[maxn]={0};
- for (int c=R[0];c!=0;c=R[c])
- {
- if (!hash[c])
- {
- hash[c]=1;
- ans++;
- for (int i=D[c];i!=c;i=D[i])
- for (int j=R[i];j!=i;j=R[j])
- hash[nCol[j]]=1;
- }
- }
- cout << "Hash =>" << ans << endl;
- return ans;
- }
- void dfs(int ans)
- {
- int best2 = ans + Hash();
- if (best2>=best)
- return;
- if (R[0]==0)
- {
- best=ans;
- for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
- {
- if ( answer[ i ] )
- {
- for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) cout << sample[ i ][ j ] << " ";
- cout << endl;
- }
- }
- return;
- }
- int c,minnum=INT_MAX;
- for (int i=R[0];i!=0;i=R[i])
- {
- if (S[i]==0) return;
- if (S[i]<minnum)
- {
- minnum=S[i];
- c=i;
- }
- }
- for (int i=U[c];i!=c;i=U[i])
- {
- answer[nRow[i]]=true;
- Remove(i);
- for (int j=R[i];j!=i;j=R[j])
- Remove(j);
- dfs(ans+1);
- for (int j=L[i];j!=i;j=L[j])
- Resume(j);
- Resume(i);
- answer[nRow[i]]=false;
- }
- }
- int main()
- {
- // freopen("data.in","r",stdin);
- // freopen("data.out","w",stdout);
- init();
- dfs(0);
- printf("%d\n",best);
- // fclose(stdin);
- // fclose(stdout);
- getchar();
- return 0;
- }