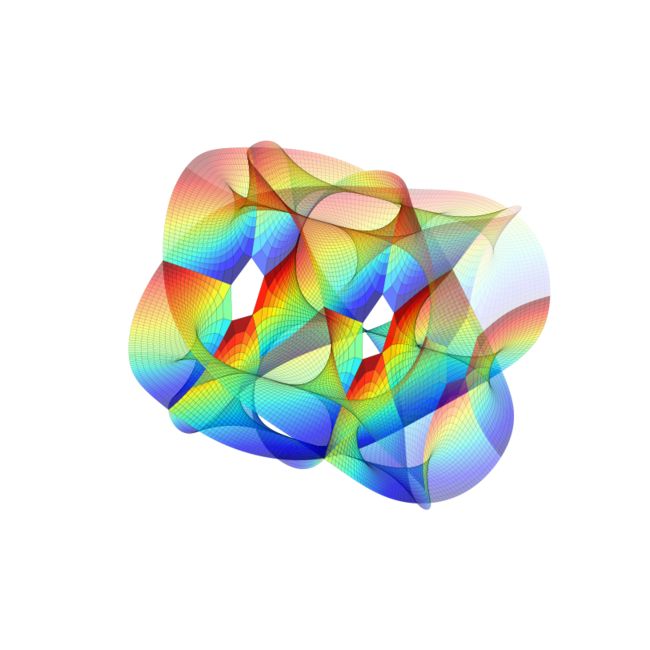Python 绘图/动画程序
本文放一些我写过的 Python 绘图小程序。
Penrose 铺砌
绘图的原理见这里。原代码有瑕疵,我做了修正。对三角形列表中的每个小三角形,都绘制其所在的整个菱形,这个可能是因为精度的原因,否则的话某些三角形拼接的部分会出现一条白线,这个现象用 Asymptote 画也有。
1 #coding = utf-8 2 3 """ 4 菱形版本的彭罗斯铺砌. 5 6 这个算法的关键是搞清楚每次切割后得到的小三角形的类型. 小三角形共分2类4种, 顶角为36度的等腰三角形2种, 顶角为108度的等腰三角形2种. 7 """ 8 import cairo 9 import cmath 10 from math import pi,sqrt 11 12 Width, Height = 600, 600 13 14 a = (sqrt(5)-1)/2 15 16 def subdivide(triangles): 17 result = [] 18 for color, A, B, C in triangles: 19 if color == 0: 20 P = A + (B - A) * a 21 result += [(0, C, P, B), (1, P, C, A)] 22 else: 23 Q = B + (A - B) * a 24 R = B + (C - B) * a 25 result += [(1, R, C, A), (1, Q, R, B), (0, R, Q, A)] 26 return result 27 28 triangles = [] 29 30 for i in xrange(10): 31 B = cmath.rect(1, (2*i - 1) * pi / 10) 32 C = cmath.rect(1, (2*i + 1) * pi / 10) 33 if i%2 == 0: 34 B, C = C, B 35 triangles.append((0,0j,B,C)) 36 37 38 m = input('number of divides: ') 39 40 for i in xrange(m): 41 triangles = subdivide(triangles) 42 43 surface = cairo.ImageSurface(cairo.FORMAT_ARGB32, Width, Height) 44 cr = cairo.Context(surface) 45 cr.translate(Width/2., Height/2.) 46 cr.scale(0.45*Width,0.45*Height) 47 """ 48 要输出图形的矩形区域的话,将上面 cr.scale() 一行注释掉并取消下面两行的注释. 49 """ 50 #WheelRadius = 1.2*sqrt((Width/2.)**2 + (Height/2.)**2) 51 #cr.scale(WheelRadius, WheelRadius) 52 53 color, A, B, C = triangles[0] 54 cr.set_line_width(abs(B - A) / 20.0) 55 cr.set_line_join(cairo.LINE_JOIN_ROUND) 56 57 """ 58 在绘制每个三角形的时候, 可能由于精度之类的原因, 三角形结合的部位会出现一条空白线影响美观, 所以干脆直接绘制整个菱形. 这样会导致每个菱形被绘两次, 但是效果令人满意. 59 """ 60 for color, A, B, C in triangles: 61 D = B + C - A 62 cr.move_to(A.real, A.imag) 63 cr.line_to(B.real, B.imag) 64 cr.line_to(D.real, D.imag) 65 cr.line_to(C.real, C.imag) 66 cr.close_path() 67 if color == 1: 68 cr.set_source_rgb(1.0, 0.078, 0.576) 69 else: 70 cr.set_source_rgb(0, 0.545, 0.545) 71 cr.fill_preserve() 72 cr.set_source_rgb(0.2, 0.2, 0.2) 73 cr.stroke() 74 75 surface.write_to_png('penrose_rhombi_{}.png'.format(m))
Lorenz 吸引子动画演示
程序出自这个博客,作者的代码有些地方写的不太好,我在下面的代码中作了修正。
1 #coding = utf-8 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 3 import numpy as np 4 from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation # 动画演示 5 from scipy.integrate import odeint #解微分方程 6 from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D 7 8 9 # 绘制轨迹的个数 10 N = 20 11 12 # 参数 13 sigma, beta, rho = 10.0, 8/3.0, 28.0 14 def derivative((x,y,z),t0): 15 """返回点 (x,y,z) 处的切方向""" 16 return sigma*(y-x), x*(rho-z)-y, x*y-beta*z 17 18 def solution(x_0,t): 19 """对初始位置 x_0 和时间数组 t, 返回解在 t 的每个元素处的值 20 sicpy.odeint() 函数接受一个函数 f, 一个初始值 x_0 和一个列表 t 为参数, 返回值是 t 对应的解组成的列表. 21 f 应当为 dy/dt = f(y,t) 返回解 y 在 t 时刻的导数值. 22 """ 23 return odeint(derivative,x_0,t) 24 25 x_0 = -15 + 30 * np.random.random((N,3)) # 随机生成 N 个点 26 t = np.linspace(0,4,1001) 27 x_t = np.array([ solution(z,t) for z in x_0]) 28 """ 29 每个点 z 的轨迹是一条空间曲线 z(t), 对区间[0,4]中的 t 计算 z(t), 把这些点连起来, 就得到了轨迹. 30 31 Example: 32 >>> x_t.shape 33 >>> (20,1000,3) 34 """ 35 36 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8,8)) 37 ax = fig.gca(projection='3d',xlim=(-25,25), ylim=(-35,35),zlim=(5,55)) 38 # 不要使用 add_subplot() 函数来构造 3d 实例, 上面的方式是标准的. 39 ax.view_init(30,0) #(初始视角包含 xy 平面的经度和 z 轴的纬度) 40 ax.axis('off') 41 """ 42 接下来把要绘制的轨迹和小球各自放在一个列表中. 首先我们生成轨迹和球的列表, 但是先不给出具体值. 43 这里的 ax.plot() 函数返回的是一个长度为 1 的列表, 所以要用 l,=ax.plot() 的写法. 44 """ 45 colors = plt.cm.jet(np.linspace(0,1,N)) 46 lines = [] 47 points = [] 48 49 for c in colors: 50 l, = ax.plot([],[],'-',c=c) 51 p, = ax.plot([],[],'o',c=c) 52 lines.append(l) 53 points.append(p) 54 55 56 def init(): 57 for line, point in zip(lines,points): 58 line.set_data([],[]) 59 line.set_3d_properties([]) 60 61 point.set_data([],[]) 62 point.set_3d_properties([]) 63 return lines + points 64 65 def animate(i): 66 i = (2*i) % x_t.shape[1] # 调整轨迹运动的速度, 否则太慢了 67 for line, point, x_j in zip(lines,points,x_t): 68 x,y,z = x_j[:i].T 69 70 line.set_data(x,y) 71 line.set_3d_properties(z) 72 73 point.set_data(x[-1:],y[-1:i]) 74 point.set_3d_properties(z[-1:i]) 75 ax.view_init(30, 0.3*i) 76 fig.canvas.draw() 77 return lines + points 78 """ 79 这里要把 x_j 当前的端点画出来, 这个点坐标就是 a,b,c = x_j[i], 因此这里也可以写成 80 point.set_data([a],[b]) 81 point.set_3d_properties([c]) 82 其中 a,b,c 分别是 x_j[i] 的 3 个坐标. 由于 plot() 接受列表为参数, 因此要加 []. 83 试比较 x[-1] 与 x[-1:] 的区别: 84 >>> x =[1,2,3] 85 >>> x[-1] 86 >>> 3 87 >>> x[-1:] 88 >>> [3] 89 """ 90 91 anim = FuncAnimation(fig,animate,init_func=init,frames=500,interval=30,blit=True) 92 #plt.show() 93 anim.save('Lorenz.mp4')
Calabi - Yau 流形
1 #coding=utf-8 2 import numpy as np 3 from numpy import exp, pi, sinh, cosh,sin, cos 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D 6 7 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8,8)) 8 ax = fig.gca(projection='3d',xlim=(-1,1),ylim=(-1,1),zlim=(-1,1),aspect=1) 9 ax.axis('off') 10 11 x = np.linspace(-1,1,30) 12 y = np.linspace(0,0.5*pi,30) 13 X,Y = np.meshgrid(x,y) 14 n = 5 15 alpha = 0.5 * pi 16 17 def CalabiYau(z,k1,k2): 18 z1 = exp(2*pi*1j*k1/n) * cosh(z)**(2.0/n) 19 z2 = exp(2*pi*1j*k2/n) * sinh(z)**(2.0/n) 20 return np.array([z1.real, z2.real, cos(alpha)*z1.imag+sin(alpha)*z2.imag]) 21 22 for k1 in range(n): 23 for k2 in range(n): 24 Z = CalabiYau(X+Y*1j,k1,k2) 25 surface = ax.plot_surface(Z[0],Z[1],Z[2],rstride=1,cstride=1,lw=0.1,cmap='hsv') 26 27 plt.show() 28 #fig.tight_layout() 29 #plt.savefig('Calabi_Yau_Manifold.png')