贪心算法(3)-霍夫曼编码
原文地址 http://www.acmerblog.com/greedy-huffman-coding-5388.html
参考地址 http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/greedy-algorithms-set-3-huffman-coding/
霍夫曼编码是一种无损数据压缩算法。在计算机数据处理中,霍夫曼编码使用变长编码表对源符号(如文件中的一个字母)进行编码,其中变长编码表是通过一种评估来源符号出现机率的方法得到的,出现机率高的字母使用较短的编码,反之出现机率低的则使用较长的编码,这便使编码之后的字符串的平均长度、期望值降低,从而达到无损压缩数据的目的。例如,在英文中,e的出现机率最高,而z的出现概率则最低。当利用霍夫曼编码对一篇英文进行压缩时,e极有可能用一个比特来表示,而z则可能花去25个比特(不是26)。用普通的表示方法时,每个英文字母均占用一个字节(byte),即8个比特。二者相比,e使用了一般编码的1/8的长度,z则使用了3倍多。倘若我们能实现对于英文中各个字母出现概率的较准确的估算,就可以大幅度提高无损压缩的比例。
构建霍夫曼编码主要包括两个部分:
1)根据输入的字符串构建霍夫曼树。
2)便利霍夫曼数并给每个字符分配编码。
哈夫曼树(Huffman Tree),又叫最优二叉树,指的是对于一组具有确定权值的叶子结点的具有最小带权路径长度的二叉树。
构建霍夫曼树的步骤:
算法:输入是没有相同元素的字符数组(长度n)以及字符出现的频率,输出是哈夫曼树。
即假设有n个字符,则构造出得哈夫曼树有n个叶子结点。n个字符的权值(频率)分别设为w1,w2,…,wn,则哈夫曼树的构造规则为:
用一个例子来了解该算法:
1 |
character Frequency |
2 |
a 5 |
3 |
b 9 |
4 |
c 12 |
5 |
d 13 |
6 |
e 16 |
7 |
f 45 |
第1步:将每个元素构造成一个节点,即只有一个元素的树。并构建一个最小堆,包含所有的节点,该算法用了最小堆来作为优先队列。
第2步:选取两个权值最小的节点,并添加一个权值为5+9=14的节点,作为他们的父节点。并更新最小堆,现在最小堆包含5个节点,其中4个树还是原来的节点,权值为5和9的节点合并为一个。
1 |
character Frequency |
2 |
c 12 |
3 |
d 13 |
4 |
内部 节点 14 |
5 |
e 16 |
6 |
f 45 |
重复上面的步骤,直到最小堆只有一个节点。
1 |
character Frequency |
2 |
内部节点 100 |
Now min heap contains 5 nodes where 4 nodes are roots of trees with single element each, and one heap node is root of tree with 3 elements
character Frequency
c 12
d 13
Internal Node 14
e 16
f 45
Step 3: Extract two minimum frequency nodes from heap. Add a new internal node with frequency 12 + 13 = 25
Now min heap contains 4 nodes where 2 nodes are roots of trees with single element each, and two heap nodes are root of tree with more than one nodes.
character Frequency
Internal Node 14
e 16
Internal Node 25
f 45
Step 4: Extract two minimum frequency nodes. Add a new internal node with frequency 14 + 16 = 30
Now min heap contains 3 nodes.
character Frequency
Internal Node 25
Internal Node 30
f 45
Step 5: Extract two minimum frequency nodes. Add a new internal node with frequency 25 + 30 = 55
Now min heap contains 2 nodes.
character Frequency
f 45
Internal Node 55
Step 6: Extract two minimum frequency nodes. Add a new internal node with frequency 45 + 55 = 100
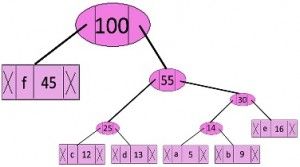
Now min heap contains only one node.
character Frequency Internal Node 100
Since the heap contains only one node, the algorithm stops here.
Steps to print codes from Huffman Tree:
Traverse the tree formed starting from the root. Maintain an auxiliary array. While moving to the left child, write 0 to the array. While moving to the right child, write 1 to the array. Print the array when a leaf node is encountered.
C语言实现如下:
001 |
#include <stdio.h> |
002 |
#include <stdlib.h> |
003 |
004 |
#define MAX_TREE_HT 100 |
005 |
006 |
// 一个霍夫曼树节点 |
007 |
struct MinHeapNode |
008 |
{ |
009 |
char data; // 输入的字符数组中的一个字符 |
010 |
unsigned freq; // 字符出现的次数 |
011 |
struct MinHeapNode *left, *right; |
012 |
}; |
013 |
014 |
// 最小堆: 作为优先队列使用 |
015 |
struct MinHeap |
016 |
{ |
017 |
unsigned size; // 最小堆元素的个数 |
018 |
unsigned capacity; //最大容量 |
019 |
struct MinHeapNode **array; |
020 |
}; |
021 |
022 |
//初始化一个最小堆节点 |
023 |
struct MinHeapNode* newNode(char data, unsigned freq) |
024 |
{ |
025 |
struct MinHeapNode* temp = |
026 |
(struct MinHeapNode*) malloc(sizeof(struct MinHeapNode)); |
027 |
temp->left = temp->right = NULL; |
028 |
temp->data = data; |
029 |
temp->freq = freq; |
030 |
return temp; |
031 |
} |
032 |
033 |
// 创建一个容量为capacity 的最小堆 |
034 |
struct MinHeap* createMinHeap(unsigned capacity) |
035 |
{ |
036 |
struct MinHeap* minHeap = |
037 |
(struct MinHeap*) malloc(sizeof(struct MinHeap)); |
038 |
minHeap->size = 0; // current size is 0 |
039 |
minHeap->capacity = capacity; |
040 |
minHeap->array = |
041 |
(struct MinHeapNode**)malloc(minHeap->capacity * sizeof(struct MinHeapNode*)); |
042 |
return minHeap; |
043 |
} |
044 |
045 |
// swap 两个堆节点 |
046 |
void swapMinHeapNode(struct MinHeapNode** a, struct MinHeapNode** b) |
047 |
{ |
048 |
struct MinHeapNode* t = *a; |
049 |
*a = *b; |
050 |
*b = t; |
051 |
} |
052 |
053 |
// 更新最小堆. |
054 |
void minHeapify(struct MinHeap* minHeap, int idx) |
055 |
{ |
056 |
int smallest = idx; |
057 |
int left = 2 * idx + 1; |
058 |
int right = 2 * idx + 2; |
059 |
060 |
if (left < minHeap->size && |
061 |
minHeap->array[left]->freq < minHeap->array[smallest]->freq) |
062 |
smallest = left; |
063 |
064 |
if (right < minHeap->size && |
065 |
minHeap->array[right]->freq < minHeap->array[smallest]->freq) |
066 |
smallest = right; |
067 |
068 |
if (smallest != idx) |
069 |
{ |
070 |
swapMinHeapNode(&minHeap->array[smallest], &minHeap->array[idx]); |
071 |
minHeapify(minHeap, smallest); |
072 |
} |
073 |
} |
074 |
075 |
//检测堆的大小是否为1 |
076 |
int isSizeOne(struct MinHeap* minHeap) |
077 |
{ |
078 |
return (minHeap->size == 1); |
079 |
} |
080 |
081 |
//取得堆中最小的节点 |
082 |
struct MinHeapNode* extractMin(struct MinHeap* minHeap) |
083 |
{ |
084 |
struct MinHeapNode* temp = minHeap->array[0]; |
085 |
minHeap->array[0] = minHeap->array[minHeap->size - 1]; |
086 |
--minHeap->size; |
087 |
minHeapify(minHeap, 0); |
088 |
return temp; |
089 |
} |
090 |
091 |
// 想最小堆中插入一个节点 |
092 |
void insertMinHeap(struct MinHeap* minHeap, struct MinHeapNode* minHeapNode) |
093 |
{ |
094 |
++minHeap->size; |
095 |
int i = minHeap->size - 1; |
096 |
while (i && minHeapNode->freq < minHeap->array[(i - 1)/2]->freq) |
097 |
{ |
098 |
minHeap->array[i] = minHeap->array[(i - 1)/2]; |
099 |
i = (i - 1)/2; |
100 |
} |
101 |
minHeap->array[i] = minHeapNode; |
102 |
} |
103 |
104 |
//构建一个最小堆 |
105 |
void buildMinHeap(struct MinHeap* minHeap) |
106 |
{ |
107 |
int n = minHeap->size - 1; |
108 |
int i; |
109 |
for (i = (n - 1) / 2; i >= 0; --i) |
110 |
minHeapify(minHeap, i); |
111 |
} |
112 |
113 |
void printArr(int arr[], int n) |
114 |
{ |
115 |
int i; |
116 |
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) |
117 |
printf("%d", arr[i]); |
118 |
printf("\n"); |
119 |
} |
120 |
121 |
// 检测是否是叶子节点 |
122 |
int isLeaf(struct MinHeapNode* root) |
123 |
{ |
124 |
return !(root->left) && !(root->right) ; |
125 |
} |
126 |
127 |
// 创建一个容量为 size的最小堆,并插入 data[] 中的元素到最小堆 |
128 |
struct MinHeap* createAndBuildMinHeap(char data[], int freq[], int size) |
129 |
{ |
130 |
struct MinHeap* minHeap = createMinHeap(size); |
131 |
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) |
132 |
minHeap->array[i] = newNode(data[i], freq[i]); |
133 |
minHeap->size = size; |
134 |
buildMinHeap(minHeap); |
135 |
return minHeap; |
136 |
} |
137 |
138 |
// 构建霍夫曼树 |
139 |
struct MinHeapNode* buildHuffmanTree(char data[], int freq[], int size) |
140 |
{ |
141 |
struct MinHeapNode *left, *right, *top; |
142 |
143 |
// 第 1步 : 创建最小堆. |
144 |
struct MinHeap* minHeap = createAndBuildMinHeap(data, freq, size); |
145 |
146 |
//知道最小堆只有一个元素 |
147 |
while (!isSizeOne(minHeap)) |
148 |
{ |
149 |
// 第二步: 取到最小的两个元素 |
150 |
left = extractMin(minHeap); |
151 |
right = extractMin(minHeap); |
152 |
153 |
// Step 3: 根据两个最小的节点,来创建一个新的内部节点 |
154 |
// '$' 只是对内部节点的一个特殊标记,没有使用 |
155 |
top = newNode('$', left->freq + right->freq); |
156 |
top->left = left; |
157 |
top->right = right; |
158 |
insertMinHeap(minHeap, top); |
159 |
} |
160 |
161 |
// 第4步: 最后剩下的一个节点即为跟节点 |
162 |
return extractMin(minHeap); |
163 |
} |
164 |
165 |
// 打印霍夫曼编码 |
166 |
void printCodes(struct MinHeapNode* root, int arr[], int top) |
167 |
{ |
168 |
if (root->left) |
169 |
{ |
170 |
arr[top] = 0; |
171 |
printCodes(root->left, arr, top + 1); |
172 |
} |
173 |
174 |
if (root->right) |
175 |
{ |
176 |
arr[top] = 1; |
177 |
printCodes(root->right, arr, top + 1); |
178 |
} |
179 |
180 |
// 如果是叶子节点就打印 |
181 |
if (isLeaf(root)) |
182 |
{ |
183 |
printf("%c: " |