java基础——网络编程
------ <a href="http://www.itheima.com" target="blank">android培训</a>、<a href="http://www.itheima.comtarget="blank">
java培训</a>、期待与您交流! ---------
<1> 获取本地主机IP地址对象
<pre name="code" class="java"><strong><span style="font-family:Courier New;font-size:14px;">import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
public class NetDemos
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
med1();
}
private static void med1() throws Exception {
// 获取本地主机IP地址对象
InetAddress ip = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
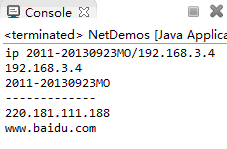
System.out.println("ip "+ip);
System.out.println(ip.getHostAddress());
System.out.println(ip.getHostName());
System.out.println("-------------");
ip = InetAddress.getByName("www.baidu.com");
System.out.println(ip.getHostAddress());
System.out.println(ip.getHostName());
}
}</span></strong>
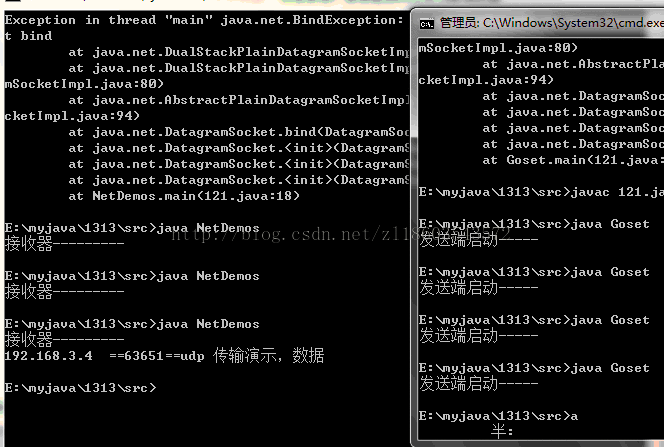
<span style="font-family:Courier New;font-size:14px;"><strong>运行程序,结果显示:</strong></span>
<2> Socket
Socket就是为网络服务提供的一种机制。 通信的两端都有Socket。 网络通信其实就是Socket间的通信。 数据在两个Socket间通过IO传输。<3> UDP传输
DatagramSocket(用来发送和接收数据报包的套接字)与DatagramPacket(数据报包)。 建立发送端,接收端。 建立数据包。 调用Socket的发送接收方法。 关闭Socket。 发送端与接收端是两个独立的运行程序。建立一个UDP的发送端与接收端
<span style="font-family:Courier New;font-size:14px;">import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
class NetDemos
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
// 创建一个UDP接收端
System.out.println("接收器---------");
/*
* 建立UDP接收端的思路
* 建立udp的socket服务,接收数据,所以要明确一个端口
* 创建数据包,用于存储接收的数据,方便用户数据包对象的方法解析
* 使用socket服务的receive方法将接收的数据存储到数'E6��包中
* 通过数据凶的方法解析数据包中的数据
* 关闭资源*/
//建立udpsocket服务
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(10000);
//创建数据包
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buf,buf.length);
//使用接收方法将数据存储到数据包中
ds.receive(dp);
//通过数据包对象的方法,解析其中的数据,
String ip = dp.getAddress().getHostAddress();
//获取的端口是发送端的端口号
int port = dp.getPort();
String text = new String(dp.getData(),0,dp.getLength());
System.out.println(ip+" =="+port + "=="+text);
//关闭资源
ds.close();
}
}
class Goset
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("发送端启动-----");
/*
* 创建UDP传输的发送端
* 1.建立udp的socket服务
* 2.将要发送的数据封装到数据包中
* 3.通过udp的socket服务将数据包发送出去
* 4.关闭socket服务*/
//使用DatagramSocket对象
//如果发送端端口未指定,就会随机分配未被使用的端口
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket();
//将要发送的数据封装到数据包中
String str = "udp 传输演示,数据" ;
//使用DatagramPacket将数据封装3到该对象包中去
byte[] buf = str.getBytes();
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buf,buf.length,InetAddress.getByName("192.168.3.4"),10000);
//通过udp的socket服务将数据凶发送出去产,使用send方法
ds.send(dp);
//关闭资源
ds.close();
}
}</span>
运行程序可以得到:
注:
由于UDP协议传输数据,只管发送数据,而不管接收端是否能够接收到数据。因此,应该首先启动接收端程序,再启动发送端程序。
UDP聊天窗口建立
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
class Goset
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
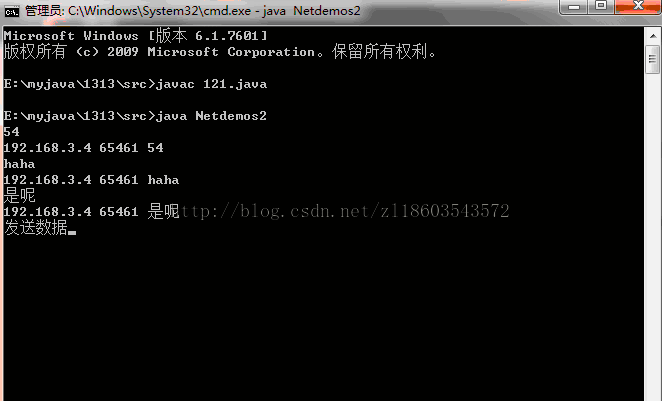
System.out.println("发送消息端程序启动");
//创建一个UDP发送器,建立udpsocket服务
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket();
//创建一个接收数据
BufferedReader bufr = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String line = null;
while((line=bufr.readLine())!=null)
{
byte[] buf =line.getBytes();
//将数据封装
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buf,buf.length,InetAddress.getByName("192.168.3.4"),10102);
ds.send(dp);
if("over".equals(line))
break;
ds.close();
}
}
}
class Recer
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
System.out.println("接收端启动---------");
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(10102);
while(true)
{
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buf,buf.length);
ds.receive(dp);
String ip = dp.getAddress().getHostAddress();
int port = dp.getPort();
String text = new String(dp.getData(),0,dp.getLength());
System.out.println(ip+" "+port+" "+text);
}
}
}
运行程序后可进行操作
UDP 聊天窗口
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
class Netdemos2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try
{
DatagramSocket goset = new DatagramSocket();
DatagramSocket recert = new DatagramSocket(10009);
new Thread(new Goset(goset)).start();
new Thread(new Recert(recert)).start();
}
catch (SocketException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class Recert implements Runnable
{
private DatagramSocket ds;
Recert(DatagramSocket ds)
{
this.ds = ds;
}
public void run()
{
while(true)
{
try
{
byte[] buf= new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buf,buf.length);
ds.receive(dp);
String ip = dp.getAddress().getHostAddress();
int port = dp.getPort();
String txet = new String(dp.getData(),0,dp.getLength());
System.out.println(ip+" "+port+" "+txet);
if(txet.equals("over"));
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
class Goset implements Runnable
{
private DatagramSocket ds ;
public Goset(DatagramSocket ds)
{
this.ds = ds ;
}
public void run()
{
BufferedReader bufr = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String line = null;
try {
while((line=bufr.readLine())!=null)
{
byte[] buf = line.getBytes();
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buf,buf.length,InetAddress.getByName("192.168.3.4"),10009);
ds.send(dp);
if("over".equals(line))
break;
}
ds.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
<4>
TCP协议-客户端&服务端
<1>
客户端(Client)首先与服务端(Server)建立连接,形成通道(其实就是IO流),然后,数据就可以在通道之间进行传输,并且单个Server端可以同时与多个Client端建立连接。
TCP客户端
<1>客户端需要明确服务器的ip地址以及端口,这样才可以去试着建立连接,如果连接失败,会出现异常。<2>连接成功,说明客户端与服务端建立了通道,那么通过IO流就可以进行数据的传输,而Socket对象已经提供了输入流和输出流对象,通过getInputStream(),getOutputStream()获取即可。
<3>与服务端通讯结束后,关闭Socket。
TCP服务端
<1>服务端需要明确它要处理的数据是从哪个端口进入的。<2>当有客户端访问时,要明确是哪个客户端,可通过accept()获取已连接的客户端对象,并通过该对象与客户端通过IO流进行数据传输。
<3>当该客户端访问结束,关闭该客户端。
客户端发送数据到服务端
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
//客户端发送数据到服务端
class NetSerce
{//创建一个TCP服务端
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//服务端接收客户端发送过来的数据,并打印到控制台上。
System.out.println("服务端启动");
//创建服务端的对象
ServerSocket ss;
try {
ss = new ServerSocket(10103);
//接收客户端传输数据
Socket s = ss.accept();
String ip = s.getInetAddress().getHostAddress();
int port = s.getPort();
//读取客户端发过来的数据
InputStream input = s.getInputStream();
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = buf.length;
String text = new String(buf,0,len);
System.out.println(ip+" "+text);
s.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class Netdemos23 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("客户端启动");
try {
// 创建TCP客户端,使用的是scoket对象
Socket s = new Socket("192.168.3.4",10103);
//获取socket中的输出流
OutputStream sOut = s.getOutputStream();
//使用输出流将指定的数据写出去
sOut.write("is my worked".getBytes());
//断开连接,关闭资源
sOut.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}

注意:
TCP协议传输数据必须先开服务端,再开客户端。否则,客户端根本连接不上服务端
Tcp 文本转换器
<span style="font-family:Courier New;font-size:14px;">import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
</span><span style="font-family:KaiTi_GB2312;font-size:14px;color:#ff6666;">//建立一个文本转换服务器,
/*客户端经服务端发送文本,服务端会将文本转成大写在返回给客户端
* 而且客户端可以不断的进行文本转换,当客户端输over时,转换结束</span>
<span style="color: rgb(255, 102, 102); font-family: KaiTi_GB2312;font-size:14px;">*/</span>
<span style="font-family:Courier New;font-size:14px;">
class TransClient
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException, IOException
{
// 创建socket客户端对象
Socket s = new%s0Socket("192.168.3.4",10004);
//定义读取键盘数据的流对象
BufferedReader bufr =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
//定义目的,将数据写入到socket输出流,发给服务端
BufferedWriter bufwout =
new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(s.getOutputStream()));
//定义一个socket 读取流,读取服务端返回的大写信息
BufferedReader bufIn =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream()));
String line = null;
while((line = bufr.readLine())!=null)
{
bufwout.write(line);
bufwout.newLine();
bufwout.flush();
String str = bufIn.readLine();
System.out.println(str);
if("over".equals(line))
break;
}
bufr.close();
s.close();
}
}
/*
* */
class TransServer
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
//
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10004);
Socket s = ss.accept();
//读取socket流中的数据
BufferedReader bufIn=
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream()));
//目的,socket输出流,将大写数据写入,并发送给客户端
BufferedWriter bufOut =
new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(s.getOutputStream()));
String ip = s.getInetAddress().getHostAddress();
System.out.println(ip);
String line = null;
while((line = bufIn.readLine())!=null)
{
bufOut.write(line.toUpperCase());
bufOut.newLine();
bufOut.flush();
}
s.close();
ss.close();
}
</span>
}
<5>通过TCP上传图片
<span style="font-family:FangSong_GB2312;color:#333333;font-weight: bold;">//通过Tcp上传图片</span><strong><span style="color:#000099;font-family: 'Courier New';">
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
</span><span style="font-family:FangSong_GB2312;color:#333333;"> //客户端</span><span style="color:#000099;font-family: 'Courier New';">
class PicClient
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
//
Socket s = new Socket("192.168.3.4",10006);
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("E:\\10.jpg");
OutputStream out = s.getOutputStream();
byte[] buf= new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len = fis.read(buf))!=-1)
{
out.write(buf,0,len);
}
</span><span style="font-family:FangSong_GB2312;color:#333333;">//提示数据已读完</span><span style="color:#000099;font-family: 'Courier New';">
s.shutdownOutput();
InputStream in = s.getInputStream();
byte[] bufIn = new byte[1024];
int num =in.read(bufIn);
System.out.println(new String(bufIn,0,num));
fis.close();
s.close();
}
}
</span><span style="font-family:FangSong_GB2312;color:#333333;">/*
* 服务端*/</span><span style="color:#000099;font-family: 'Courier New';">
class PicServer
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
//
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10006);
Socket s =ss.accept();
InputStream in = s.getInputStream();
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("111.bmp");
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len = in.read(buf))!=-1)
{
fos.write(buf,0,len);
}
OutputStream out = s.getOutputStream();
out.write("上传成功".getBytes());
fos.close();
s.close();
ss.close();
}
}</span></strong><span style="color:#ff0000;">
</span>实现多个客户端访问服务器
<span style="font-size:18px;">//通过Tcp上传图片
</span><strong><span style="font-family:Courier New;font-size:14px;color:#3333ff;">import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
class Seeyou implements Runnable
{
private Socket s;
Seeyou(Socket s)
{
this.s = s;
}
public void run()
{
try
{
String ip = s.getInetAddress().getHostAddress();
InputStream in = s.getInputStream();
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(ip+"111.bmp");
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len = in.read(buf))!=-1)
{
fos.write(buf,0,len);
}
OutputStream out = s.getOutputStream();
out.write("上传成功".getBytes());
fos.close();
s.close();
}
catch(Exception e)
{
}
}
}
//客户端
class PicClient
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
System.out.println("客户端启动");
//
Socket s = new Socket("192.168.3.4",10006);
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("E:\\10.jpg");
OutputStream out = s.getOutputStream();
byte[] buf= new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len = fis.read(buf))!=-1)
{
out.write(buf,0,len);
}
//提示数据已读完
s.shutdownOutput();
InputStream in = s.getInputStream();
byte[] bufIn = new byte[1024];
int num =in.read(bufIn);
System.out.println(new String(bufIn,0,num));
fis.close();
s.close();
}
}
/*
* 服务端*/
class PicServer
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
System.out.println("服务端启动");
//
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10006);
while(true)
{
Socket s =ss.accept();
new Thread(new Seeyou(s)).start();
}
}
}</span></strong><span style="font-size:18px;">
</span>