重学数据结构系列之——二叉树基础
1.二叉树
1.定义
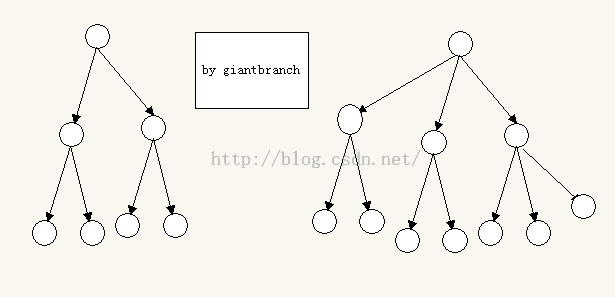
每棵树有且仅有一个树根
左边就是一个二叉树(二叉树的每个结点最多只有两个孩子结点,也就是说每个结点最多有两个子树),右边是不确定是不是叫三叉树
其实我们的计算机的目录结构就像一棵树
2.实现
下面这个是储存int类型的二叉树,既可以int,又可以char请看最底部的代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//结点类
class Node{
public:
//数据
int data;
//左孩子和右孩子
Node *lchild, *rchild;
Node(int _data){
data = _data;
lchild = NULL;
rchild = NULL;
}
~Node(){
if (lchild != NULL) {
delete lchild;
}
if (rchild != NULL) {
delete rchild;
}
}
//先序遍历(先自己再左右,可以看到下面的顺序也是这样)
void preorder(){
//输出当前结点的数据域
cout<<data<<" ";
//左不为空,则递归调用先序遍历
if (lchild != NULL) {
lchild->preorder();
}
//右不为空,也递归调用先序遍历
if (rchild != NULL) {
rchild->preorder();
}
}
//中序遍历(先左,再中,再右)
void inorder(){
if (lchild != NULL) {
lchild->inorder();
}
cout<<data<<" ";
if (rchild != NULL) {
rchild->inorder();
}
}
//后序遍历(先左右,再中间)
void postorder(){
if (lchild != NULL) {
lchild->postorder();
}
if (rchild != NULL) {
rchild->postorder();
}
cout<<data<<" ";
}
//根据先序,中序构建一颗二叉树
//pre_str:先序遍历的字符串(如124536)
//in_str:中序遍历的字符串
//len:(先序)中序遍历的字符串的长度
Node* build(const string &pre_str, const string &in_str, int len){
//先序遍历的第一位(pre_str[0])就是根结点,先构建根结点
//pre_str[0] - '0':因为我们这里用的数据域只是数字0-9,减去字符'0'就是实际的数字,其实就是他们的ASCII相减,你可以输出一下'9'-'0'是不是 9
Node *p = new Node(pre_str[0] - '0');
//查找中序遍历中根节点的位置(根结点左边的都是左子树的,右边的都是右子树)
int pos = in_str.find(pre_str[0]);
//左子树不为空,构建左子树
if (pos > 0) {
//以根结点的左子树作为新的根结点去构建即可
//其中左子树结点有pos个,先序中第一个是根结点,所以substr(1,pos)【表示从索引1开始,截取pos个字符】就是左子树的先序遍历
//in_str.substr(0,pos):从索引0开始,截取pos个字符
p->lchild = build(pre_str.substr(1,pos), in_str.substr(0,pos), pos);
}
//右子树不为空,构建右子树
if (len - pos -1 > 0) {
//其中右子树结点有len - pos -1个,先序中第一个是根结点,跟着是pos个左子树的,所以substr(pos+1)【表示从索引pos+1到字符串的最后】就是右子树先序遍历
//in_str.substr(pos+1):从索引pos+1开始到字符串的最后
p->rchild = build(pre_str.substr(pos+1), in_str.substr(pos+1), len - pos -1);
}
//构建完成,返回二叉树
return p;
}
};
class BinaryTree{
private:
//树的根,就是最上面的结点
Node *root;
public:
//无参构造函数
BinaryTree(){
//一开始是一颗没结点的树--空树
root = NULL;
}
//已知先序,中序遍历的构造函数
BinaryTree(const string &pre_str, const string &in_str, int len){
root = root->build(pre_str, in_str, len);
}
~BinaryTree(){
if (root != NULL) {
delete root;
}
}
//构建一个简单的二叉树以便测试
void build_demo(){
root = new Node(1);
root->lchild = new Node(2);
root->rchild = new Node(3);
root->lchild->lchild = new Node(4);
root->lchild->rchild = new Node(5);
root->rchild->rchild = new Node(6);
}
//先序遍历
void preorder(){
root->preorder();
}
//中序遍历
void inorder(){
root->inorder();
}
//后序遍历
void postorder(){
root->postorder();
}
};
int main(){
BinaryTree binarytree;
binarytree.build_demo();
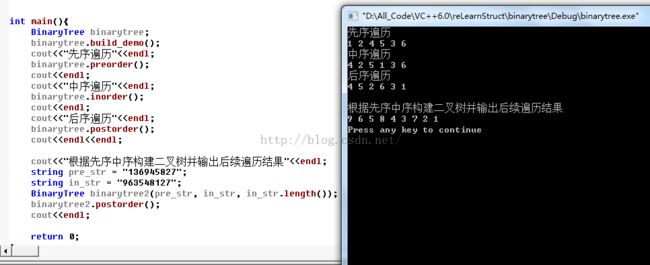
cout<<"先序遍历"<<endl;
binarytree.preorder();
cout<<endl;
cout<<"中序遍历"<<endl;
binarytree.inorder();
cout<<endl;
cout<<"后序遍历"<<endl;
binarytree.postorder();
cout<<endl<<endl;
cout<<"根据先序中序构建二叉树并输出后续遍历结果"<<endl;
string pre_str = "136945827";
string in_str = "963548127";
BinaryTree binarytree2(pre_str, in_str, in_str.length());
binarytree2.postorder();
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
3.运行结果
2.解决一个小问题:二叉树左右对调(镜像)
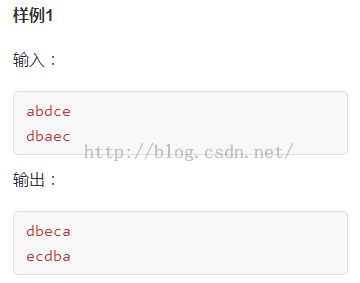
1.描述
已知先序和中序,输出原二叉树的后序和左右对调后(就是镜像)的后序遍历
2.代码实现
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
//结点类
template<class Type> class Node{
public:
//数据
Type data;
//左孩子和右孩子
Node *lchild, *rchild;
Node(Type _data){
data = _data;
lchild = NULL;
rchild = NULL;
}
~Node(){
if (lchild != NULL) {
delete lchild;
}
if (rchild != NULL) {
delete rchild;
}
}
//先序遍历(先自己再左右,可以看到下面的顺序也是这样)
void preorder(){
//输出当前结点的数据域
cout<<data<<"";
//左不为空,则递归调用先序遍历
if (lchild != NULL) {
lchild->preorder();
}
//右不为空,也递归调用先序遍历
if (rchild != NULL) {
rchild->preorder();
}
}
//中序遍历(先左,再中,再右)
void inorder(){
if (lchild != NULL) {
lchild->inorder();
}
cout<<data<<"";
if (rchild != NULL) {
rchild->inorder();
}
}
//后序遍历(先左右,再中间)
void postorder(){
if (lchild != NULL) {
lchild->postorder();
}
if (rchild != NULL) {
rchild->postorder();
}
cout<<data<<"";
}
//根据先序,中序构建一颗二叉树
//pre_str:先序遍历的字符串(如124536)
//in_str:中序遍历的字符串
//len:(先序)中序遍历的字符串的长度
Node* build(const string &pre_str, const string &in_str, int len){
Node<Type> *p;
//先序遍历的第一位(pre_str[0])就是根结点,先构建根结点
if (pre_str[0]>='0' && pre_str[0]<='9') {
//如果是数字类型
p = new Node<Type>(pre_str[0]-'0');
}else{
p = new Node<Type>(pre_str[0]);
}
//Node<Type> *p = new Node<Type>(pre_str[0]);
//查找中序遍历中根节点的位置(根结点左边的都是左子树的,右边的都是右子树)
int pos = in_str.find(pre_str[0]);
//左子树不为空,构建左子树
if (pos > 0) {
//以根结点的左子树作为新的根结点去构建即可
//其中左子树结点有pos个,先序中第一个是根结点,所以substr(1,pos)【表示从索引1开始,截取pos个字符】就是左子树的先序遍历
//in_str.substr(0,pos):从索引0开始,截取pos个字符
p->lchild = build(pre_str.substr(1,pos), in_str.substr(0,pos), pos);
}
//右子树不为空,构建右子树
if (len - pos -1 > 0) {
//其中右子树结点有len - pos -1个,先序中第一个是根结点,跟着是pos个左子树的,所以substr(pos+1)【表示从索引pos+1到字符串的最后】就是右子树先序遍历
//in_str.substr(pos+1):从索引pos+1开始到字符串的最后
p->rchild = build(pre_str.substr(pos+1), in_str.substr(pos+1), len - pos -1);
}
//构建完成,返回二叉树
return p;
}
Node* buildMirror(const string &pre_str, const string &in_str, int len){
Node<Type> *p;
if (pre_str[0]>='0' && pre_str[0]<='9') {
p = new Node<Type>(pre_str[0]-'0');
}else{
p = new Node<Type>(pre_str[0]);
}
int pos = in_str.find(pre_str[0]);
if (pos > 0) {
p->rchild = buildMirror(pre_str.substr(1,pos), in_str.substr(0,pos), pos);
}
if (len - pos -1 > 0) {
p->lchild = buildMirror(pre_str.substr(pos+1), in_str.substr(pos+1), len - pos -1);
}
return p;
}
};
template<class Type> class BinaryTree{
private:
//树的根,就是最上面的结点
Node<Type> *root;
public:
//无参构造函数
BinaryTree(){
//一开始是一颗没结点的树--空树
root = NULL;
}
//已知先序,中序遍历的构造函数
BinaryTree(const string &pre_str, const string &in_str, int len){
root = root->build(pre_str, in_str, len);
}
~BinaryTree(){
if (root != NULL) {
delete root;
}
}
//先序遍历
void preorder(){
root->preorder();
}
//中序遍历
void inorder(){
root->inorder();
}
//后序遍历
void postorder(){
root->postorder();
}
//构建镜像二叉树
void buildMirror(const string &pre_str, const string &in_str, int len){
root = root->buildMirror(pre_str, in_str, len);
}
};
int main(){
string pre_str;
string in_str;
cin>>pre_str>>in_str;
BinaryTree<char> binarytree(pre_str, in_str, in_str.length());
binarytree.postorder();
cout<<endl;
binarytree.buildMirror(pre_str, in_str, in_str.length());
binarytree.postorder();
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}