Trie树初探
Trie树
这个其实很简单,看下面这张图大家都能yy出来
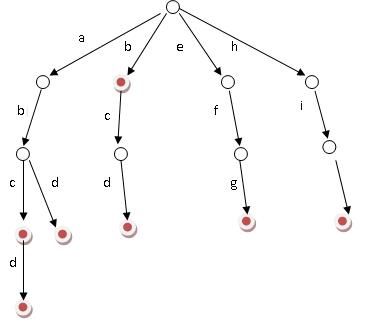
看完这个图我们看几道入门题
[HDOJ 1251] 统计难题
传送门
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1251
题目大意
给定一个字典,对于每个询问回答字典中含该前缀的单词数
题解
用这道题想明白所谓的动态开点即可(以下都由数组模拟指针来实现)
如果我们把所有点都开开,时间复杂度为 O(26lengthmax)
sum表示已开的节点数,每次从源点(定为0)开始向下寻找,如果没建立点就在sum+1的位置开一个点,我们要记录的只是这个点作为前缀所包含的单词数(每次经过+1)以及这个点它带的儿子的位置,由于本题的字符集为26,时间复杂度为 O(26∗sum+sum)
var
x:array[0..1000000]of longint;
y:array[0..1000000,1..26]of longint;
i,j,k,tt,sum:longint;
a,b:string;
function query(a:string):longint;
begin
tt:=0;
for i:=1 to length(a) do
begin
if y[tt,ord(a[i])-96]=0
then exit(0)
else tt:=y[tt,ord(a[i])-96];
end;
exit(x[tt]);
end;
procedure insert(a:string);
begin
tt:=0;
for i:=1 to length(a) do
begin
if y[tt,ord(a[i])-96]=0
then begin inc(sum); y[tt,ord(a[i])-96]:=sum; end;
inc(x[y[tt,ord(a[i])-96]]);
tt:=y[tt,ord(a[i])-96];
end;
end;
begin
sum:=0; fillchar(x,sizeof(x),0);
while not eof do
begin
readln(a);
if a='' then break;
insert(a);
end;
while not eof do
begin
readln(a);
writeln(query(a));
end;
end.
[HDOJ 1671] Phone List
传送门
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1671
题目大意
给定n个串,询问有没有哪个串是其他某个串的子串
[POJ 2001]Shortest Prefixes
传送门
http://poj.org/problem?id=2001
题目大意
求出最短唯一前缀
题解
在Trie树上打标记,每次一个单词经过一个节点,就+1,查询时遇到1它前面的节点就是答案
var
Trie:array[0..100000]of longint;
son:array[0..100000,0..26]of longint;
x:array[0..10000]of string;
i,j,k:longint;
n,sum,tt:Longint;
procedure insert(a:string);
var i:longint;
begin
tt:=0;
for i:=1 to length(a) do
begin
if son[tt,ord(a[i])-96]=0
then begin inc(sum); son[tt,ord(a[i])-96]:=sum; Trie[sum]:=1; end
else inc(Trie[son[tt,ord(a[i])-96]]);
tt:=son[tt,ord(a[i])-96];
end;
end;
function query(a:string):string;
var b:string; i:longint;
begin
b:=''; tt:=son[0,ord(a[1])-96];
for i:=1 to length(a) do
if Trie[tt]=1
then exit(b+a[i])
else begin b:=b+a[i]; if i<>length(a) then tt:=son[tt,ord(a[i+1])-96]; end;
exit(b);
end;
begin
n:=0; sum:=0;
while not eof do
begin
inc(n); readln(x[n]); //if x[n]='' then begin dec(n); break; end;
insert(x[n]);
end;
for i:=1 to n do
writeln(x[i],' ',query(x[i]));
end.POJ 3764
传送门
http://poj.org/problem?id=3764
题目大意
给定一棵树,找一条简单路径,使其边权抑或值最大
题解
xor是Trie树的经典应用
首先(a xor b)xor(a xor c)=b xor c也就是说定义两点间边权抑或f(u,v)=f(1,u) xor f(1,v),O(N)实现
然后原问题就转化为,两点抑或值最大 O(N2) 实现会超时
所以我们把每个值转成二进制倒着插入 Trie 中,也就是说3我们插入的是00000000000000000000000000011,然后枚举每个权值,再在Trie中找与它抑或值最大的
找的时候贪心即可,即找x[i]时,每次x[i]的该位二进制为1能走0就走不能就走1
理论AC,,,,,UOJ自定义测试都能跑起来,交上去就是运行错误,,,,,
const
maxn=100005;
var
w:array[0..4*maxn,1..3]of longint;
s:array[0..5*maxn,1..2]of longint;
x,y:array[0..maxn]of longint;
i,j,k:longint;
n,a,b,c,len,sum,ans:longint;
function max(a,b:longint):Longint;
begin
if a>b then exit(a) else exit(b);
end;
procedure init(a,b,c:longint);
begin
w[len,1]:=b; w[len,2]:=c;
if w[a,3]=0
then w[a,3]:=len else w[w[a,1],3]:=len;
w[a,1]:=len; inc(len);
end;
procedure dfs(a:longint);
var tt:longint;
begin
y[a]:=1; tt:=w[a,3];
while tt<>0 do
begin
if y[w[tt,1]]=0
then begin x[w[tt,1]]:=x[a] xor w[tt,2]; dfs(w[tt,1]); end;
tt:=w[tt,3];
end;
end;
procedure init(a:longint);
var i,tt,b:longint;
begin
tt:=0;
for i:=31 downto 1 do
begin
if (a and (1<<(i-1)))=0
then b:=0 else b:=1;
if s[tt,b]=0
then begin inc(sum); s[tt,b]:=sum; end;
tt:=s[tt,b];
end;
end;
function check(a:longint):longint;
var tt1,tt2,i,b,c,anss:longint;
begin
tt1:=0; tt2:=0; anss:=0;
for i:=31 downto 1 do
begin
if a and(1<<(i-1))=0 then b:=0 else b:=1;
c:=b xor 1;
if s[tt2,c]=0
then tt2:=s[tt2,b]
else begin tt2:=s[tt2,c]; inc(anss,1<<(i-1)); end;
tt1:=s[tt1,b];
end;
exit(anss);
end;
begin
readln(n); len:=n+1;
for i:=1 to n-1 do
begin
readln(a,b,c);
inc(a); inc(b);
init(a,b,c); init(b,a,c);
end;
x[1]:=0;
dfs(1);
sum:=0;
fillchar(s,sizeof(s),0);
for i:=1 to n do
init(x[i]);
ans:=0;
for i:=1 to n do
ans:=max(ans,check(x[i]));
writeln(ans);
end.