Libgdx之Texture TextureRegion
Texture是纹理,简单来说就是装载图片的容器。TextureRegion纹理区域,包装了Texture,提供了更多的方法来操作Texture
在介绍类的继承之前,先看看Texture和TextureRegion的坐标系,有时候需要截取图片或者说是只绘制图片的部分,因此知道坐标系就能更好的去绘制图片.

Texture
再介绍示例的时候首先看一下类的继承结构
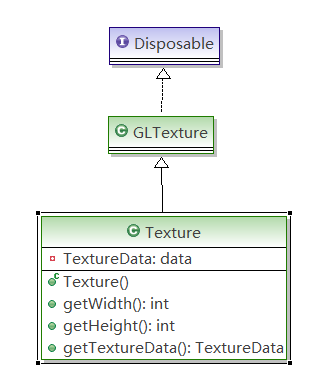
通过类图首先看出Texture继承自Disposable,因此在游戏结束的时候要调用texture.dispose来销毁Texture对象。
由于用的类图工具不能写出函数里的对象,因此把构造函数单独列出来
public Texture (String internalPath) {
this(Gdx.files.internal(internalPath));
}
public Texture (FileHandle file) {
this(file, null, false);
}通过构造函数可以看出可以直接将图片的assets 资源文件夹中的文件的相对路径名创建纹理或者传递一个FileHandle对象来初试化Texture。下面的是部分测试代码
SpriteBatch batch;
Texture tex;
@Override
public void create() {
batch = new SpriteBatch();
tex = new Texture(Gdx.files.internal("badlogic.jpg"));
//tex = new Texture("badlogic.jpg");
}
@Override
public void render() {
Gdx.gl.glClearColor(1, 0, 0, 1);
Gdx.gl.glClear(GL20.GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
batch.begin();
// 将图像全部画出
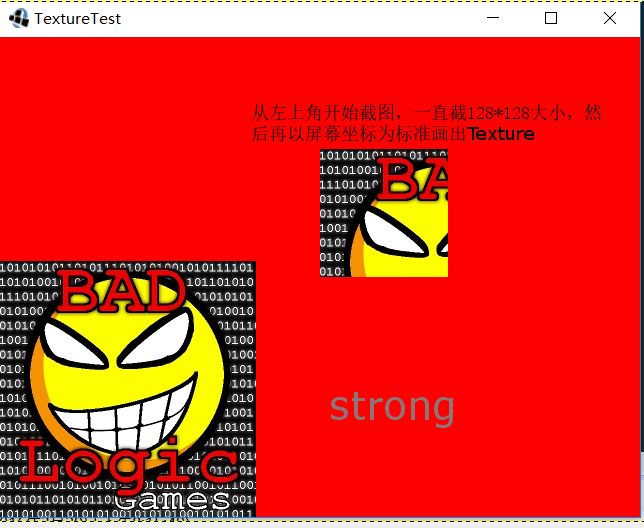
batch.draw(tex, 0, 0);
// 将image同左上角开始截图,截图大小为128*128
batch.draw(tex, 320, 240, 0, 0, 128, 128);
batch.end();
}
@Override
public void dispose() {
batch.dispose();
tex.dispose();
}TextureRegion
通过上面类图可以看出TextureRegion是对Texture的封装,添加了更多的操作方法,上面还有许多方法没有列出,比如对X和对Y的操作都是成对出现的。
到最后还是需要对Texture进行销毁处理,如果是用的内部类的话可以调用下面方法来销毁
textureRegion.getTexture().dispose
下面是几个对TextureRegion初始化常用的方法
/** Constructs a region the size of the specified texture. */
public TextureRegion (Texture texture) {
if (texture == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("texture cannot be null.");
this.texture = texture;
setRegion(0, 0, texture.getWidth(), texture.getHeight());
}
/** @param width The width of the texture region. May be negative to flip the sprite when drawn. * @param height The height of the texture region. May be negative to flip the sprite when drawn. */
public TextureRegion (Texture texture, int width, int height) {
this.texture = texture;
setRegion(0, 0, width, height);
}
/** @param width The width of the texture region. May be negative to flip the sprite when drawn. * @param height The height of the texture region. May be negative to flip the sprite when drawn. */
public TextureRegion (Texture texture, int x, int y, int width, int height) {
this.texture = texture;
setRegion(x, y, width, height);
}测试代码
private final String TAG = TextureRegionTest.class.getSimpleName();
SpriteBatch batch;
TextureRegion region, region2, region3, region4;
@Override
public void create() {
batch = new SpriteBatch();
// 加载全部图像
region = new TextureRegion(new Texture(Gdx.files.internal("badlogic.jpg")));
// 加载图像,从坐标(0,0)开始截取到width=128, height=128之间的图像,以Texture坐标系为准
region2 = new TextureRegion(new Texture(Gdx.files.internal("badlogic.jpg")), 128, 128);
// 加载图像,从坐标(128,128)开始截取width=256, height=256之间的图像,以Texture坐标系为准,不足的地方以乱码补充
region3 = new TextureRegion(new Texture(Gdx.files.internal("badlogic.jpg")), 128, 128, 256, 128);
// 加载图像,从坐标(128,128)开始截取width=128, height=128之间的图像,以Texture坐标系为准
region4 = new TextureRegion(new Texture(Gdx.files.internal("badlogic.jpg")), 128, 128, 128, 128);
Gdx.app.log(TAG, "region2 regionX=" + region2.getRegionX() + " regionY=" + region2.getRegionY());
Gdx.app.log(TAG, "region2 width=" + region2.getRegionWidth() + " height=" + region2.getRegionHeight());
Gdx.app.log(TAG, "region3 regionX=" + region3.getRegionX() + " regionY=" + region3.getRegionY());
Gdx.app.log(TAG, "region3 width=" + region3.getRegionWidth() + " height=" + region3.getRegionHeight());
Gdx.app.log(TAG, "region4 regionX=" + region4.getRegionX() + " regionY=" + region4.getRegionY());
Gdx.app.log(TAG, "region4 width=" + region4.getRegionWidth() + " height=" + region4.getRegionHeight());
}
@Override
public void render() {
Gdx.gl.glClearColor(1, 0, 0, 1);
Gdx.gl.glClear(GL20.GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
batch.begin();
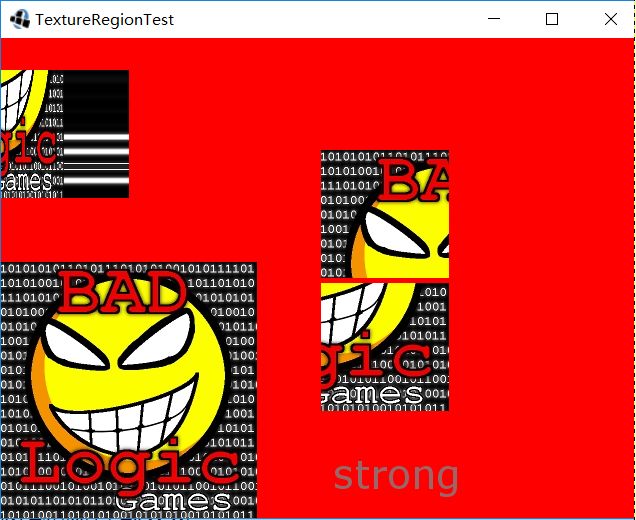
// 将region全部画出
batch.draw(region, 0, 0);
batch.draw(region2, 320, 240);
batch.draw(region3, 0, 320, 128, 128);
batch.draw(region4, 320, 240-128-5, 128, 128);
batch.end();
}
@Override
public void dispose() {
batch.dispose();
region.getTexture().dispose();
region2.getTexture().dispose();
region3.getTexture().dispose();
}