【Java.Spring.MVC】DispatcherServlet (及WebApplicationContext部分)
Spring中的DispatcherServlet除了作为处理request的前端控制器,还负责与Spring IOC容器整合并提供Spring的功能。
DispatcherServlet的工作流程
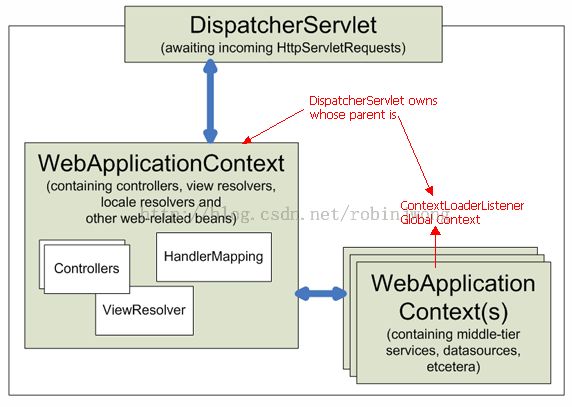
Sping MVC中的Context hierarchy
在Spring MVC中,每个DispatcherServlet拥有其独立的WebApplicationContext,继承了root/global WebApplicationContext中所定义的所有的bean。这些继承的bean可以在DispatcherServlet中被重写;DispatcherServlet也可以定义自己特有的benas。
可以在web.xml中为DispatcherServlet指定一个对应的配置文件,当然也可以选择不指定,那么Servlet的WebApplicationContext将没有特定的benas。
(参考上一节)
获取WebApplicationContext(root的及Servlet的)
- WebApplicationContext被包含到ServletContext中;
- 使用RequestContextUtils中的方法获得DispatcherServlet特定的WebApplicationContext;
- 使用WebApplicationContextUtils中的方法获得root WebApplicationContext for this application;
WebApplicationContext/DispatcherServlet中的特殊的bean type
Spring中的DispatcherServlet使用特定的bean来处理请求和渲染视图。Spring MVC默认会初始化一些默认的bean,而不必手动去配置:
- HandlerMapping - 映射请求到具体的handlers
- HandlerAdapter -
- HandlerExceptionResolver - 异常处理
- ViewResolver - 将view的名称字符串映射为实际的view类型
- LocaleResolver&LocalContextResolver - 本地化处理
- ThemeResolver - 处理应用的主题,例如定制的布局
- MultipartResolver - 解析multi-part request例如处理文件上传
- FlashMapManager -
默认的DispatcherServlet的配置
对于每一个DispatcherServlet都会维护一系列默认的所使用的bean的实现。
这些信息保存在org.springframework.web.servlet 包中的DispatcherServlet.properties文件中。
有时候需要客户化一些bean的属性,例如,重新配置InternalResourceViewResolver中的设置prefix属性。
DispatcherServlet的处理过程
当一个特定的DispatcherServlet收到一条request时:
- 搜索WebApplicationContext并绑定到请求中,默认使用DispatcherServlet.WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE作为键值绑定为request的属性
- 将一个locale resolver绑定到request中
- 绑定theme resolver到request中
- 如果指定了multipart file resolver,那么请求将被视为multipart;如果发现multiparts,request被包装成MultipartHttpServletRequest来进一步处理
- 查找一个适当的handler,如果找到,与该handler相关的处理链将被执行
- 如果返回一个model,将会返回一个view。如果没有model返回,不会渲染view。
DispatcherServlet初始化参数
在web.xml中servlet的声明中可以添加一些初始化参数(init-param 元素):
- contextClass - 实现WebApplicationContext的类,该类将被Servlet初始化;默认使用XMLWebApplicationContext
- contextConfiguration - 指定配置文件的路径;可以包含多个配置路径;如果重复定义了bean,将优先使用最新定义的
- namespace - WebApplicationContext的命名空间;默认为[servlet-name]-servlet
其他
一个web.xml可以配置多个DispatcherServlet,通过其<servlet-mapping>的配置,让每一个DispatcherServlet处理不同的请求(不同的init-params).
与其他的Servlet一样,DispatcherServlet必须在Web应用程序的web.xml文件中进行配置:
<span style="color:#999999;"> <!-- Servelt Configurations -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>default</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:default_servlet.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>default</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping></span>
Spring MVC默认在WEB-INF文件路径下查找一个文件,名为[servlet-name]-servlet.xml(default-servlet.xml在上面的例子中),在此文件中定义beans。该文件包含所有的Spring Web MVC特定的组件(beans)。该文件名/路径可以在Servlet的配置中进行设置。
DispatcherServlet遵循”契约优于配置“的原则,在大多数情况下,无须进行额外的配置,只需按契约行事即可。
对DispatchServlet的默认规则进行调整,可以通过常用的一些配置参数,可以通过<servlet>的<init-param>指定:
- contextConfigLocation —— 如果DispatcherServlet上下文对应的spring配置文件有多个,可以使用该属性按照spring资源路径的方式指定
<url-pattern>的设置:
声明DispatchServlet处理哪些URL,比较常见的匹配模式是*.htm, 、* 或者/app,但这些模式都存在一些问题:
- *.htm —— 隐式声明响应始终是HTML格式的
- /* —— 将其匹配到/*上的话,没有映射特定类型的响应,它表明DispatcherServlet将处理所有的请求。这会在处理图片或css这样的静态资源时带来不必要的麻烦,因为DispatcherServlet默认无法处理静态资源
- /app —— 这样就会在URL中暴露实现的细节
为了不使用这些有缺陷的servlet匹配模式,更倾向于使用匹配下面的DispatcherServlet:
<span style="color:#999999;"><servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>default</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping></span>
通过将DispatcherServlet映射到/,这将会令当前servlet替代容器默认的servlet, 并且会处理所有的请求,包括对静态资源的请求。
Spring mvc命名空间包含了一个新的<mvc:resources>元素,它会为DispatcherServlet增加处理静态资源的功能,所要做的就是在Spring配置文件中对其进行配置。
例如,在上面的default_servlet.xml文件中,添加如下的配置:
<span style="color:#999999;"><?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:jee="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/spring-jee-3.0.xsd">
<!-- To handle static resources -->
<mvc:resources mapping="/resources/**" location="/resources/" />
</beans></span>
通过<mvc:resources>元素来告诉DispatchServlet如何处理这些资源。
<mvc:resources>建立了一个服务于静态资源的处理器。属性mapping被设置为/resources/**,它包含了ANT风格的通配符以表明路径必须以/resources开始,而且也包含它的任意子路径。属性location表明了要服务的文件位置。以上配置表明,所有以/resources路径开头的请求都会自动由应用程序根目录下的/resources目录提供服务。因此,我们的所有图片,样式表,JavaScript以及其他的静态资源都必须放在应用程序的/resources目录下。