android之线程池深度剖析
1.线程池的引入
引入的好处
1)提升性能(创建和消耗对象费时费CPU资源);2)防止内存过度消耗(控制活动线程的数量,防止并发线程过多);
使用条件
在Android中当同时并发多个网络线程时,引入线程池技术会极大地提高APP的性能。
例如:多线程下载,点一个下载一个(假设允许最多同时下载五个),当点到第六个的时候开始等待,这就涉及到线程的管理
2.封装线程池管理者
1)jdk自身带有线程池的实现类ThreadPoolExecutor
2)ThreadPoolManager是基于ThreadPoolExecutor进行了封装的类
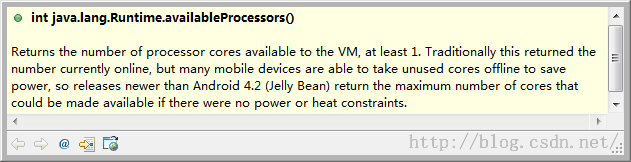
其中,获取当前可用的处理器核心数我们用Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(),我们来看它的注释:
package com.example.threadpooldemo;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* 线程池管理
* 管理整个项目中所有的线程,所以不能有多个实例对象
*/
public class ThreadPoolManager {
/**
* 单例设计模式(饿汉式)
* 单例首先私有化构造方法,然后饿汉式一开始就开始创建,并提供get方法
*/
private static ThreadPoolManager mInstance = new ThreadPoolManager();
public static ThreadPoolManager getInstance() {
return mInstance;
}
private int corePoolSize;//核心线程池的数量,同时能够执行的线程数量
private int maximumPoolSize;//最大线程池数量,表示当缓冲队列满的时候能继续容纳的等待任务的数量
private long keepAliveTime = 1;//存活时间
private TimeUnit unit = TimeUnit.HOURS;
private ThreadPoolExecutor executor;
private ThreadPoolManager() {
/**
* 给corePoolSize赋值:当前设备可用处理器核心数*2 + 1,能够让cpu的效率得到最大程度执行(有研究论证的)
*/
corePoolSize = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()*2+1;
maximumPoolSize = corePoolSize;//虽然maximumPoolSize用不到,但是需要赋值,否则报错
executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
corePoolSize, //当某个核心任务执行完毕,会依次从缓冲队列中取出等待任务
maximumPoolSize, //5,先corePoolSize,然后new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(),然后maximumPoolSize,但是它的数量是包含了corePoolSize的
keepAliveTime,//表示的是maximumPoolSize当中等待任务的存活时间
unit,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(),//缓冲队列,用于存放等待任务,Linked的先进先出
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),//创建线程的工厂
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy()//用来对超出maximumPoolSize的任务的处理策略
);
}
/**
* 执行任务
*/
public void execute(Runnable runnable){
if(runnable==null)return;
executor.execute(runnable);
}
/**
* 从线程池中移除任务
*/
public void remove(Runnable runnable){
if(runnable==null)return;
executor.remove(runnable);
}
}
1>ThreadPoolExecutor说明文档:
ThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue, threadFactory, handler)
corePoolSize: 核心线程数,能够同时执行的任务数量;
maximumPoolSize:除去缓冲队列中等待的任务,最大能容纳的任务数(其实是包括了核心线程池数量);
keepAliveTime:超出workQueue的等待任务的存活时间,就是指maximumPoolSize里面的等待任务的存活时间;
unit:时间单位;
workQueue:阻塞等待线程的队列,一般使用new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()这个,如果不指定容量,会一直往里边添加,没有限制,workQueue永远不会满;
threadFactory:创建线程的工厂,使用系统默认的类;
handler:当任务数超过maximumPoolSize时,对任务的处理策略,默认策略是拒绝添加;
2>执行流程:
当线程数小于corePoolSize时,每添加一个任务,则立即开启线程执行;当corePoolSize满的时候,后面添加的任务将放入缓冲队列workQueue等待;当workQueue也满的时候,看是否超过maximumPoolSize线程数,如果超过,默认拒绝执行。
3>举例说明:
假如corePoolSize=2,maximumPoolSize=3,workQueue容量为8;最开始,执行的任务A,B,此时corePoolSize已用完,再次执行任务C,则C将被放入缓冲队列workQueue中等待着,如果后来又添加了7个任务,此时workQueue已满,则后面再来的任务将会和maximumPoolSize比较,由于maximumPoolSize为3,所以只能容纳1个了,因为有2个在corePoolSize中运行了,所以后面来的任务默认都会被拒绝。
Runnable只是一个接口,它的源码如下,而线程是真正开启系统资源去执行任务,他们两个,线程是真正消耗系统资源的
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package java.lang;
/**
* Represents a command that can be executed. Often used to run code in a
* different {@link Thread}.
*/
public interface Runnable {
/**
* Starts executing the active part of the class' code. This method is
* called when a thread is started that has been created with a class which
* implements {@code Runnable}.
*/
public void run();
}
3.线程池例子
下面是一个线程池的例子(演示多线程执行任务),以加深对原理的理解
1)引入我们封装好的ThreadPoolManager.java
2)演示功能
package com.example.threadpooldemo;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.SystemClock;
import android.util.Log;
/**
* 演示线程池
*
*/
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
/**
* 创建九个任务
*/
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
ThreadPoolManager.getInstance().execute(new DownloadTask(i));
}
}
/**
* 模仿下载任务,实现Runnable
*/
class DownloadTask implements Runnable{
private int num;
public DownloadTask(int num) {
super();
this.num = num;
Log.d("JAVA", "task - "+num + " 等待中...");
}
@Override
public void run() {
Log.d("JAVA", "task - "+num + " 开始执行了...开始执行了...");
SystemClock.sleep(5000); //模拟延时执行的时间
Log.e("JAVA", "task - "+num + " 结束了...");
}
}
}
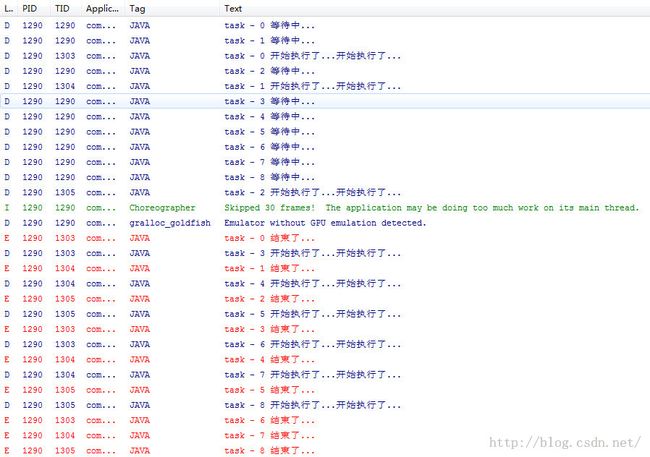
打印结果如下:
项目源码,点击下载