LDD3源码分析之内存映射
转载自http://blog.csdn.net/liuhaoyutz/article/details/7452289
作者:刘昊昱
博客:http://blog.csdn.net/liuhaoyutz
编译环境:Ubuntu 10.10
内核版本:2.6.32-38-generic-pae
LDD3源码路径:examples/simple/
本文分析LDD3第十五章介绍的内存映射模块simple。
一、simple模块编译
在2.6.32-38-generic-pae内核下编译simple模块时,会遇到一些问题,下面列出遇到的问题及解决办法。
执行make编译simple模块,会出现如下错误:
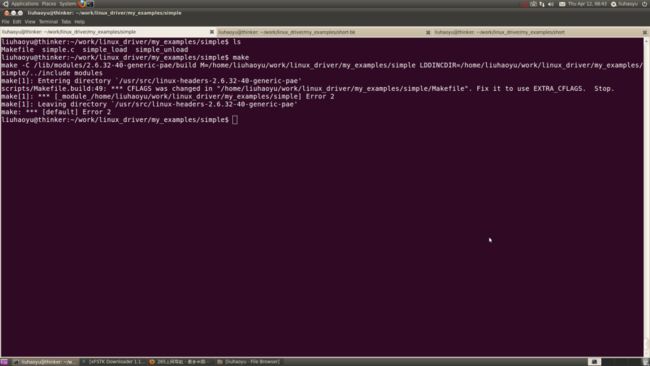
修改Makefile文件,把CFLAGS改为EXTRA_CFLAGS即可解决这个问题。再次编译,出现如下错误:
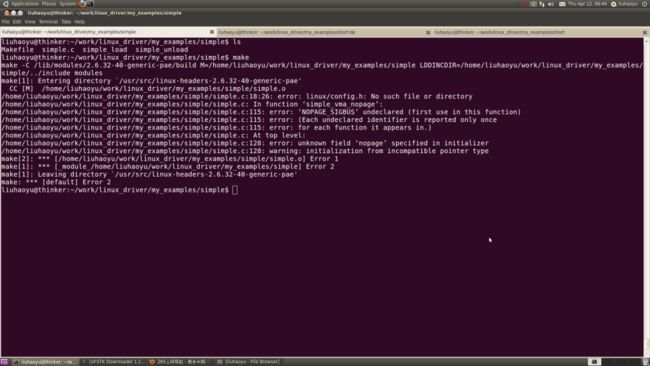
修改simple.c把第18行#include <linux/config.h>屏蔽掉,即可解决第一个错误,再次编译,出现如下错误:

simple.c的第115行,NOPAGE_SIGBUS宏在新的内核中已经不存在了,在2.6.10中该宏被定义为NULL,所以这里把115行改为
再次编译,出现如下错误:
- 115 return 0;
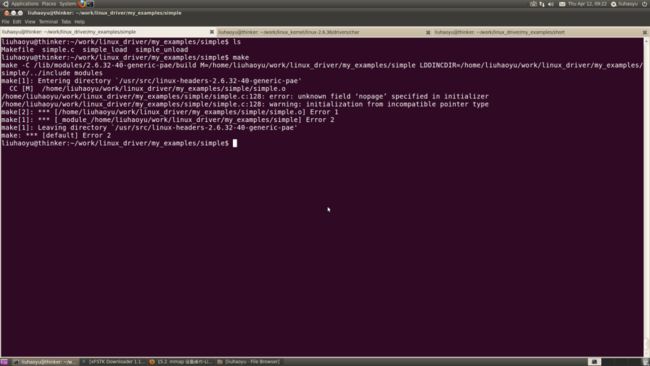
这是因为在新的内核中vm_operations_struct结构体的nopage函数已经被fault函数代替,所以把128行改为:
同时,按照fault的函数原型,重新改写simple_vma_nopage函数如下:
- 128 .fault = simple_vma_nopage,
再次编译,模块编译成功,如下图所示:
- 102int simple_vma_nopage(struct vm_area_struct *vma,
- 103 struct vm_fault *vmf)
- 104{
- 105 struct page *pageptr;
- 106 unsigned long offset = vma->vm_pgoff << PAGE_SHIFT;
- 107 unsigned long physaddr = (unsigned long)vmf->virtual_address - vma->vm_start + offset;
- 108 unsigned long pageframe = physaddr >> PAGE_SHIFT;
- 109
- 110// Eventually remove these printks
- 111 printk (KERN_NOTICE "---- Nopage, off %lx phys %lx\n", offset, physaddr);
- 112 printk (KERN_NOTICE "VA is %p\n", __va (physaddr));
- 113 printk (KERN_NOTICE "Page at %p\n", virt_to_page (__va (physaddr)));
- 114 if (!pfn_valid(pageframe))
- 115 return 0;
- 116 pageptr = pfn_to_page(pageframe);
- 117 printk (KERN_NOTICE "page->index = %ld mapping %p\n", pageptr->index, pageptr->mapping);
- 118 printk (KERN_NOTICE "Page frame %ld\n", pageframe);
- 119 get_page(pageptr);
- 120// if (type)
- 121// *type = VM_FAULT_MINOR;
- 122 return VM_FAULT_NOPAGE;
- 123}

二、simple模块分析
首先来看simple模块初始化函数simple_init:
203 - 217行,分配设备编号。
- 197/*
- 198 * Module housekeeping.
- 199 */
- 200static int simple_init(void)
- 201{
- 202 int result;
- 203 dev_t dev = MKDEV(simple_major, 0);
- 204
- 205 /* Figure out our device number. */
- 206 if (simple_major)
- 207 result = register_chrdev_region(dev, 2, "simple");
- 208 else {
- 209 result = alloc_chrdev_region(&dev, 0, 2, "simple");
- 210 simple_major = MAJOR(dev);
- 211 }
- 212 if (result < 0) {
- 213 printk(KERN_WARNING "simple: unable to get major %d\n", simple_major);
- 214 return result;
- 215 }
- 216 if (simple_major == 0)
- 217 simple_major = result;
- 218
- 219 /* Now set up two cdevs. */
- 220 simple_setup_cdev(SimpleDevs, 0, &simple_remap_ops);
- 221 simple_setup_cdev(SimpleDevs + 1, 1, &simple_nopage_ops);
- 222 return 0;
- 223}
220行,创建字符设备,文件操作函数集是simple_remap_ops,使用remap_pfn_range映射内存。
221行,创建字符设备,文件操作函数集是simple_nopage_ops,使用nopage映射内存。
simple_setup_cdev函数定义如下:
simple_setup_cdev函数关联字符设备文件操作函数集,并向内核注册字符设备。
- 145/*
- 146 * Set up the cdev structure for a device.
- 147 */
- 148static void simple_setup_cdev(struct cdev *dev, int minor,
- 149 struct file_operations *fops)
- 150{
- 151 int err, devno = MKDEV(simple_major, minor);
- 152
- 153 cdev_init(dev, fops);
- 154 dev->owner = THIS_MODULE;
- 155 dev->ops = fops;
- 156 err = cdev_add (dev, devno, 1);
- 157 /* Fail gracefully if need be */
- 158 if (err)
- 159 printk (KERN_NOTICE "Error %d adding simple%d", err, minor);
- 160}
下面先来看simple_remap_ops文件操作函数集:
simple_open和simple_release函数的实现都是简单返回0.
- 166/* Device 0 uses remap_pfn_range */
- 167static struct file_operations simple_remap_ops = {
- 168 .owner = THIS_MODULE,
- 169 .open = simple_open,
- 170 .release = simple_release,
- 171 .mmap = simple_remap_mmap,
- 172};
simple_remap_mmap函数的实现如下:
- 43static int simple_open (struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
- 44{
- 45 return 0;
- 46}
- 52static int simple_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
- 53{
- 54 return 0;
- 55}
这里我们要介绍一下,当用户空间调用mmap执行内存映射时,file_operations结构的mmap函数被调用,其函数原型是:
- 85static int simple_remap_mmap(struct file *filp, struct vm_area_struct *vma)
- 86{
- 87 if (remap_pfn_range(vma, vma->vm_start, vma->vm_pgoff,
- 88 vma->vm_end - vma->vm_start,
- 89 vma->vm_page_prot))
- 90 return -EAGAIN;
- 91
- 92 vma->vm_ops = &simple_remap_vm_ops;
- 93 simple_vma_open(vma);
- 94 return 0;
- 95}
其中vma包含了用于访问设备的虚拟地址信息。vma中vm_area_struct结构体类型,该结构体用于描述一个虚拟内存区,在2.6.10上,其定义如下:
- int (*mmap)(struct file *filp, struct vm_area_struct *vma);
vm_area_struct结构体描述的虚拟内存区介于vm_start和vm_end之间,vm_ops成员指向这个VMA的操作函数集,其类型为vm_operations_struct结构体,定义如下:
- 55/*
- 56 * This struct defines a memory VMM memory area. There is one of these
- 57 * per VM-area/task. A VM area is any part of the process virtual memory
- 58 * space that has a special rule for the page-fault handlers (ie a shared
- 59 * library, the executable area etc).
- 60 */
- 61struct vm_area_struct {
- 62 struct mm_struct * vm_mm; /* The address space we belong to. */
- 63 unsigned long vm_start; /* Our start address within vm_mm. */
- 64 unsigned long vm_end; /* The first byte after our end address
- 65 within vm_mm. */
- 66
- 67 /* linked list of VM areas per task, sorted by address */
- 68 struct vm_area_struct *vm_next;
- 69
- 70 pgprot_t vm_page_prot; /* Access permissions of this VMA. */
- 71 unsigned long vm_flags; /* Flags, listed below. */
- 72
- 73 struct rb_node vm_rb;
- 74
- 75 /*
- 76 * For areas with an address space and backing store,
- 77 * linkage into the address_space->i_mmap prio tree, or
- 78 * linkage to the list of like vmas hanging off its node, or
- 79 * linkage of vma in the address_space->i_mmap_nonlinear list.
- 80 */
- 81 union {
- 82 struct {
- 83 struct list_head list;
- 84 void *parent; /* aligns with prio_tree_node parent */
- 85 struct vm_area_struct *head;
- 86 } vm_set;
- 87
- 88 struct prio_tree_node prio_tree_node;
- 89 } shared;
- 90
- 91 /*
- 92 * A file's MAP_PRIVATE vma can be in both i_mmap tree and anon_vma
- 93 * list, after a COW of one of the file pages. A MAP_SHARED vma
- 94 * can only be in the i_mmap tree. An anonymous MAP_PRIVATE, stack
- 95 * or brk vma (with NULL file) can only be in an anon_vma list.
- 96 */
- 97 struct list_head anon_vma_node; /* Serialized by anon_vma->lock */
- 98 struct anon_vma *anon_vma; /* Serialized by page_table_lock */
- 99
- 100 /* Function pointers to deal with this struct. */
- 101 struct vm_operations_struct * vm_ops;
- 102
- 103 /* Information about our backing store: */
- 104 unsigned long vm_pgoff; /* Offset (within vm_file) in PAGE_SIZE
- 105 units, *not* PAGE_CACHE_SIZE */
- 106 struct file * vm_file; /* File we map to (can be NULL). */
- 107 void * vm_private_data; /* was vm_pte (shared mem) */
- 108
- 109#ifdef CONFIG_NUMA
- 110 struct mempolicy *vm_policy; /* NUMA policy for the VMA */
- 111#endif
- 112};
当用户调用mmap系统调用时,内核会进行如下处理:
- 170/*
- 171 * These are the virtual MM functions - opening of an area, closing and
- 172 * unmapping it (needed to keep files on disk up-to-date etc), pointer
- 173 * to the functions called when a no-page or a wp-page exception occurs.
- 174 */
- 175struct vm_operations_struct {
- 176 void (*open)(struct vm_area_struct * area);
- 177 void (*close)(struct vm_area_struct * area);
- 178 struct page * (*nopage)(struct vm_area_struct * area, unsigned long address, int *type);
- 179 int (*populate)(struct vm_area_struct * area, unsigned long address, unsigned long len, pgprot_t prot, unsigned long pgoff, int nonblock);
- 180#ifdef CONFIG_NUMA
- 181 int (*set_policy)(struct vm_area_struct *vma, struct mempolicy *new);
- 182 struct mempolicy *(*get_policy)(struct vm_area_struct *vma,
- 183 unsigned long addr);
- 184#endif
- 185};
1.在进程的虚拟空间查找一块VMA.
2.将这块VMA进行映射.
3.如果设备驱动程序中定义了mmap函数,则调用它.
4.将这个VMA插入到进程的VMA链表中.
内存映射工作大部分由内核完成,驱动程序中的mmap函数只需要为该地址范围建立合适的页表,并将vma->vm_ops替换为一系列的新操作就可以了。有两种建立页表的方法,一是使用remap_pfn_range函数一次全部建立,或者通过nopage方法每次建立一个页表。
simple_remap_mmap函数使用remap_pfn_range函数一次建立全部页表,remap_pfn_range函数原型如下:
vma代表虚拟内存区域。
- int remap_pfn_range(struct vm_area_struct *vma, unsigned long virt_addr, unsigned long pfn, unsigned long size, pgprot_t prot);
virt_addr代表要建立页表的用户虚拟地址的起始地址,remap_pfn_range函数为处于virt_addr和virt_addr+size之间的虚拟地址建立页表。
pfn是与物理内存起始地址对应的页帧号,虚拟内存将要被映射到该物理内存上。页帧号只是将物理地址右移PAGE_SHIFT位。在大多数情况下,VMA结构中的vm_pgoff赋值给pfn即可。remap_pfn_range函数建立页表,对应的物理地址是pfn<<PAGE_SHIFT到pfn<<(PAGE_SHIFT)+size。
size代表虚拟内存区域大小。
port是VMA要求的protection属性,驱动程序只要使用vma->vm_page_prot中的值即可。
在simple_remap_mmap函数中,
87 - 90行,调用remap_pfn_range函数建立页表:
可对比上面对remap_pfn_range函数的参数的解释来理解。
- remap_pfn_range(vma, vma->vm_start, vma->vm_pgoff,
- vma->vm_end - vma->vm_start,
- vma->vm_page_prot)
92行,vma->vm_ops是struct vm_operations_struct类型变量,代表内核操作虚拟内存区的函数集,这里赋值为simple_remap_vm_ops,其定义如下:
这里仅仅实现了open和close函数,其它函数由内核提供。当进程打开或关闭VMA时,就会调用这两个函数,当fork进程或者创建一个新的对VMA引用时,也会调用open函数。实际的打开和关闭工作由内核完成,这里实现的open和close函数不必重复内核所做的工作,只要根据驱动程序的需要处理其他必要的事情。对于simple这样的简单驱动程序,simple_vma_open和simple_vma_close函数仅仅是打印相关信息:
- 80static struct vm_operations_struct simple_remap_vm_ops = {
- 81 .open = simple_vma_open,
- 82 .close = simple_vma_close,
- 83};
回到simple_remap_mmap函数:
- 63void simple_vma_open(struct vm_area_struct *vma)
- 64{
- 65 printk(KERN_NOTICE "Simple VMA open, virt %lx, phys %lx\n",
- 66 vma->vm_start, vma->vm_pgoff << PAGE_SHIFT);
- 67}
- 68
- 69void simple_vma_close(struct vm_area_struct *vma)
- 70{
- 71 printk(KERN_NOTICE "Simple VMA close.\n");
- 72}
93行,显式调用simple_vma_open(vma),这里要注意,必须显示调用该函数,因为open函数还没有注册到系统。
至此,Device 0的相关代码就分析完了。
除了remap_pfn_range函数外,在驱动程序中实现nopage函数通常可以为设备提供更加灵活的内存映射途径。当访问的页面不在内存,即发生缺页中断时,nopage就会被调用。这是因为,当发生缺页中断时,系统会经过如下处理过程:
1.找到缺页的虚拟地址所在的VMA。
2.如果必要,分配中间页目录表和页表。
3.如果页表项对应的物理页面不存在,则调用nopage函数,它返回物理页面的页描述符。
4.将物理页面的地址填充到页表中。
下面我们看Device 1的相关代码,其文件操作函数集如下:
与Device 0相比,只有mmap的实现不一样,我们看simple_nopage_mmap:
- 174/* Device 1 uses nopage */
- 175static struct file_operations simple_nopage_ops = {
- 176 .owner = THIS_MODULE,
- 177 .open = simple_open,
- 178 .release = simple_release,
- 179 .mmap = simple_nopage_mmap,
- 180};
135 - 137行,设置vma->vm_flags标志。
- 131static int simple_nopage_mmap(struct file *filp, struct vm_area_struct *vma)
- 132{
- 133 unsigned long offset = vma->vm_pgoff << PAGE_SHIFT;
- 134
- 135 if (offset >= __pa(high_memory) || (filp->f_flags & O_SYNC))
- 136 vma->vm_flags |= VM_IO;
- 137 vma->vm_flags |= VM_RESERVED;
- 138
- 139 vma->vm_ops = &simple_nopage_vm_ops;
- 140 simple_vma_open(vma);
- 141 return 0;
- 142}
139行,指定vma->vm_ops为simple_nopage_vm_ops。
140行,显式调用simple_vma_open函数。
simple_nopage_vm_ops结构定义如下:
这个结构体中,需要分析的是simple_vma_nopage函数:
- 125static struct vm_operations_struct simple_nopage_vm_ops = {
- 126 .open = simple_vma_open,
- 127 .close = simple_vma_close,
- 128 .nopage = simple_vma_nopage,
- 129};
106行,得到起始物理地址保存在offset中。
- 102struct page *simple_vma_nopage(struct vm_area_struct *vma,
- 103 unsigned long address, int *type)
- 104{
- 105 struct page *pageptr;
- 106 unsigned long offset = vma->vm_pgoff << PAGE_SHIFT;
- 107 unsigned long physaddr = address - vma->vm_start + offset;
- 108 unsigned long pageframe = physaddr >> PAGE_SHIFT;
- 109
- 110// Eventually remove these printks
- 111 printk (KERN_NOTICE "---- Nopage, off %lx phys %lx\n", offset, physaddr);
- 112 printk (KERN_NOTICE "VA is %p\n", __va (physaddr));
- 113 printk (KERN_NOTICE "Page at %p\n", virt_to_page (__va (physaddr)));
- 114 if (!pfn_valid(pageframe))
- 115 return NOPAGE_SIGBUS;
- 116 pageptr = pfn_to_page(pageframe);
- 117 printk (KERN_NOTICE "page->index = %ld mapping %p\n", pageptr->index, pageptr->mapping);
- 118 printk (KERN_NOTICE "Page frame %ld\n", pageframe);
- 119 get_page(pageptr);
- 120 if (type)
- 121 *type = VM_FAULT_MINOR;
- 122 return pageptr;
- 123}
107行,得到address参数对应的物理地址,保存在physaddr中。
108行,得到address的物理地址对应的页帧号,保存在pageframe中。
116行,使用pfn_to_page函数,由页帧号返回对应的page结构指针保存在pageptr中。
119行,调用get_page增加pageptr指向页面的引用计数。
至此,simple模块的代码我们就分析完了。