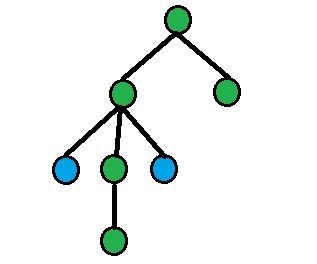
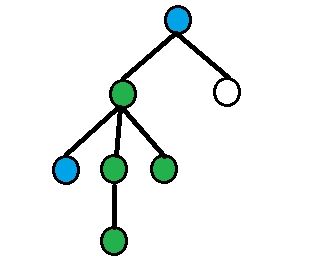
Codeforces 519E - A and B and Lecture Rooms (LCA)
题意:给一棵树,M次询问,每次询问到两个点距离相等的点的个数。
519E - A and B and Lecture Rooms
Author: Bekzhan.Kassenov
In this problem we have to answer to the following queries on tree: for given pairs of vertices your program should output number of eqidistand vertices from them.
Let's denote:
dist(a, b) as distance between vertices a and b.
LCA(a, b) as lowest common ancestor of vertices a and b.
depth[a] as distance between root of the tree and vertex a.
size[a] as size of subtree of vertex a.
On each picture green nodes are equidistant nodes, blue nodes — nodes from query.
Preprocessing: Read edges of tree and build data structure for LCA (it is more convenient to use binary raise, becase we will use it further for other purposes).
Complexity: O(NlogN)
Queries:
We have to consider several cases for each query:
1) a = b. In that case answer is n.
2) dist(a, b) is odd. Then answer is 0.
3) dist(a, l) = dist(b, l), where l = LCA(a, b).
Find children of l, which are ancestors of a and b (let's denote them as aa and bb). Answer will ben - size[aa] - size[bb].
4) All other cases.
Assume that depth[a] > depth[b]. Then using binary raise find dist(a, b) / 2-th ancestor of a (let's denote it as p1),dist(a, b) / 2 - 1-th ancestor of vertex a (denote it as p2). Answer will be size[p1] - size[p2].
Complexity: O(logN) for each query, O(MlogN) for all queries.
Resulting complexity:: O(MlogN + NlogN)
Code: 10083310
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
#define prt(k) cout<<#k" = "<<k<<endl;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 100005;
int n, m, head[N], mm;
struct Edge {
int to, next;
}e[N << 1];
void add(int u, int v)
{
e[mm].to = v;
e[mm].next = head[u];
head[u] = mm++;
}
int sz[N], dep[N];
int f[N][22];
void dfs(int u, int fa)
{
dep[u] = dep[fa] + 1;
f[u][0] = fa;
sz[u] = 1;
for (int i=head[u];~i;i=e[i].next)
{
int v = e[i].to;
if (v != fa)
{
dfs(v, u);
sz[u] += sz[v];
}
}
}
int maxh;
void gao()
{
int j;
for (j=1;(1<<j)<n;j++)
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
f[i][j] = f[f[i][j-1]][j-1];
maxh = j - 1;
}
int swim(int x, int k)
{
for (int i=0;i<=maxh;i++)
if (k >> i & 1)
x = f[x][i];
return x;
}
int LCA(int x, int y)
{
if (dep[x] > dep[y]) swap(x, y); ///dep[x] <= dep[y];
y = swim(y, dep[y] - dep[x]);
if (x == y) return y;
for (int i=maxh; i>=0; i--) {
if (f[x][i] != f[y][i])
x = f[x][i], y = f[y][i];
}
return f[x][0];
}
int main()
{
dep[0] = 1;
cin >> n ;
mm = 0;
memset(head, -1, sizeof head);
for (int i=1;i<n;i++)
{
int u, v;
scanf("%d%d", &u, &v);
add(u, v); add(v, u);
}
dfs(1, 0);
gao();
/** prt(maxh);
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<=maxh;j++)
{
printf("f[%d][%d] = %d\n", i,j,f[i][j]);
}
}
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=i+1;j<=n;j++)
printf("LCA(%d, %d) = %d\n", i,j,LCA(i,j)); */
cin >> m;
for (int i=0;i<m;i++) {
int x, y;
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
if (x == y) {
printf("%d\n", n);
continue;
}
if (dep[x] < dep[y])
swap(x, y);
int z = LCA(x, y);
int dist = dep[x] + dep[y] - dep[z] - dep[z];
if (dist & 1) {
printf("0\n");
continue;
}
dist /= 2;
int da = dep[x] - dep[z];
int db = dep[y] - dep[z];
if (da == db) {
int aa = swim(x, da-1);
int bb = swim(y, db - 1);
int ans = n - sz[aa] - sz[bb];
printf("%d\n", ans);
continue;
}
int p1 = swim(x, dist);
int p2 = swim(x, dist-1);
int ans = sz[p1] - sz[p2];
printf("%d\n", ans);
}
}