一 延迟操作
1 延迟操作:就是将某些代码间隔一段时间在执行.时间完全由程序猿自己控制.
2 非多线程的两种延迟操作方法:
2.1 方法调用的代码:
-(void)touchesBegan:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event { //调用需要执行的方法 [self 方法名]; }
2.2 第一种:
-(void)delay
{
NSLog(@"---start----");
[self performSelector:@selector(task:) withObject:nil afterDelay:2.0];
2.3 第二种:定时器
-(void)delay
{
NSLog(@"---start----");
[NSTimer scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:3.0 target:self selector:@selector(task) userInfo:nil repeats:NO];
2.4 第三种: 线程定时
dispatch_after(dispatch_time(DISPATCH_TIME_NOW, (int64_t)(2.0 * NSEC_PER_SEC)), dispatch_get_global_queue(0, 0), ^{
NSLog(@"--GCD----%@",[NSThread currentThread]);
});
二 栅栏函数
1 字面概念: 所谓栅栏函数,字面意思就是在代码的某个地方建立起一座栅栏,不让栅栏后面的代码执行,直到把栅栏拆了,才可以执行后面的代码
2 实际的概念是
01 开始执行之前确保前面的任务都已经执行完毕
02 只有当栅栏函数执行完毕之后,后面的任务才能继续执行
-(void)barrier
{
dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_queue_create("com.download", DISPATCH_QUEUE_CONCURRENT);
dispatch_async(queue, ^{
for (NSInteger i = 0; i<5; i++) {
NSLog(@"download1---%zd--%@",i,[NSThread currentThread]);
}
});
dispatch_async(queue, ^{
for (NSInteger i = 0; i<5; i++) {
NSLog(@"download2---%zd--%@",i,[NSThread currentThread]);
}
});
dispatch_barrier_async(queue, ^{
NSLog(@"+++++++++++++%@",[NSThread currentThread]);
});
dispatch_async(queue, ^{
for (NSInteger i = 0; i<5; i++) {
NSLog(@"download3---%zd--%@",i,[NSThread currentThread]);
}
});
dispatch_async(queue, ^{
for (NSInteger i = 0; i<5; i++) {
NSLog(@"download4---%zd--%@",i,[NSThread currentThread]);
}
});
03 栅栏函数补充:barrier在使用的时候不能使用全局并发队列,如果使用了将失去拦截功能
原因:详见苹果官方文档给出的说明
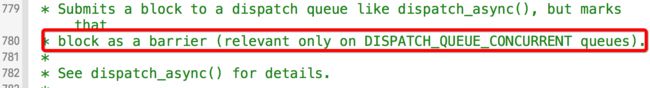
如果是使用了全局并发队列,代码执行的结果是前面的任务并没有执行完毕就开始执行栅栏函数
三 一次性代码
1 概念:
01 整个应用程序只会执行一次
执行一次的原因:static dispatch_once_t 静态变量
02 本身是线性安全的—->相当于加锁的功能
-(void)once
{
NSLog(@"------%s",__func__);
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
NSLog(@"--once---%@",[NSThread currentThread]);
});
}
四 快速迭代
1 概念:循环的意思
2 两种方法:for循环和快速迭代
3 for循环
for (NSInteger i = 0; i<10; i++) {
NSLog(@"%zd---%@",i,[NSThread currentThread]);
}
4 快速迭代
01 并发队列的快速迭代
dispatch_apply(10, dispatch_get_global_queue(0, 0), ^(size_t index) {
NSLog(@"%zd---%@",index,[NSThread currentThread]);
});
02 串行队列快速迭代(和传统的for循环没有区别,都是在主线程中进行)
dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_queue_create("download", DISPATCH_QUEUE_SERIAL);
dispatch_apply(10, queue, ^(size_t index) {
NSLog(@"%zd---%@",index,[NSThread currentThread]);
});
03 传主队列到快速迭代中会出现死锁
死锁原理图:
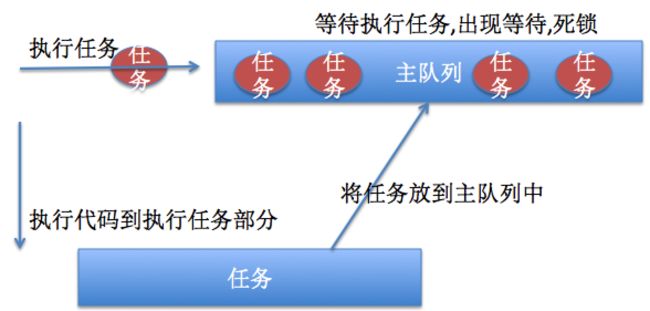
死锁原理:由于快速迭代执行参与的是主线程和子线程,当使用主队列的时候,代码执行到任务,将任务加入到主队列.然后就开始执行主队列的任务,由于所有的任务都是在主队列中执行,会出现等待任务的执行,所有会出现死锁.
五 文件剪切
1 需求:将from中的文件,通过代码剪切到另外一个文件to中
2 思路:运用快速迭代实现剪切文件内容
代码详解
NSString *sourePath = @"/Users/xiaofeng/Desktop/from";
NSString *targetPath = @"/Users/xiaofeng/Desktop/to";
NSArray *subPaths = [[NSFileManager defaultManager] subpathsAtPath:sourePath];
NSLog(@"%@",subPaths);
dispatch_apply(subPaths.count, dispatch_get_global_queue(0, 0), ^(size_t index ) {
NSString *fileName = subPaths[index];
NSLog(@"%@",fileName);
NSString *soureFullpath = [sourePath stringByAppendingPathComponent:fileName];
NSString *targetFullpath = [targetPath stringByAppendingPathComponent:fileName];
[[NSFileManager defaultManager] moveItemAtPath:soureFullpath toPath:targetFullpath error:nil];
NSLog(@"%@----%@----%@",soureFullpath,targetFullpath,[NSThread currentThread]);
});

