(Caffe,Lenet5)初始化训练网络(三)
本文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/mounty_fsc/article/details/51090306
1. Solver到Net
在SGDSolver的构造函数中详见本系列博文(二),主要执行了其父类Solver的构造函数,接着执行Solver::Init()函数,在Init()中,有两个函数值得注意:InitTrainNet()和InitTestNets()分别初始化训练网络和测试网络。
InitTrainNet
- 首先,
ReadNetParamsFromTextFileOrDie(param_.net(), &net_param)把param_.net()(即examples/mnist/lenet_train_test.prototxt)中的信息读入net_param。 - 其次,
net_.reset(new Net<Dtype>(net_param))重新构建网络,调用Net的构造方法。 - 然后,在构造方法中执行
Net::init(),开始正式创建网络。其主要代码如下:
template <typename Dtype> void Net<Dtype>::Init(const NetParameter& in_param) { ... for (int layer_id = 0; layer_id < param.layer_size(); ++layer_id) { // Setup layer. const LayerParameter& layer_param = param.layer(layer_id); layers_.push_back(LayerRegistry<Dtype>::CreateLayer(layer_param)); // Figure out this layer's input and output for (int bottom_id = 0; bottom_id < layer_param.bottom_size(); ++bottom_id) { const int blob_id = AppendBottom(param, layer_id, bottom_id, &available_blobs, &blob_name_to_idx); // If a blob needs backward, this layer should provide it. need_backward |= blob_need_backward_[blob_id]; } int num_top = layer_param.top_size(); for (int top_id = 0; top_id < num_top; ++top_id) { AppendTop(param, layer_id, top_id, &available_blobs, &blob_name_to_idx); } ... layers_[layer_id]->SetUp(bottom_vecs_[layer_id], top_vecs_[layer_id]); ... } ... }
说明:
- Lenet5在caffe中共有9层,即
param.layer_size() == 5,以上代码每一次for循环创建一个网络层 - 每层网络是通过
LayerRegistry::CreateLayer()创建的,类似与Solver的创建(详见本系列博文(二)) - 14行
Net::AppendBottom(),对于layer_id这层,从Net::blob_中取出blob放入该层对应的bottom_vecs_[layer_id]中 - 20行
Net::AppendTop(),对于layer_id这层,创建blob(未包含数据)并放入Net::blob_中 Layer::SetUp()
- 首先,
InitTestNets
该部分内容见本系列博文:(Caffe,Lenet5)初始化测试网络(四)。
2 训练网络结构
| Layer | layer Type Bottom | Blob Top | Blob Top | Blob Shape |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| minst | Data | data&&label | 64 1 28 28 (50176) && 64 (64) | |
| conv1 | Convolution | data | conv1 | 64 20 24 24 (737280) |
| pool1 | Pooling | conv1 | pool1 | 64 20 12 12 (184320) |
| conv2 | Convolution | pool1 | conv2 | 64 50 8 8 (204800) |
| pool2 | Pooling | conv2 | pool2 | 64 50 4 4 (51200) |
| ip1 | InnerProduct | pool2 | ip1 | 64 500 (32000) |
| relu1 | ReLU | ip1 | ip1(in-place) | 64 500 (32000) |
| ip2 | InnerProduct | ip1 | ip2 | 64 10 (640) |
| loss | SoftmaxWithLoss | ip2&&label | loss | (1) |
注:Top Blob Shape格式为:BatchSize,ChannelSize,Height,Width(Total Count)
3 第一层:Data Layer
3.1 protobuff定义
训练网络的第一层protobuff定义为:
layer { name: "mnist" type: "Data" top: "data" top: "label" include { phase: TRAIN }
transform_param { scale: 0.00390625 }
data_param { source: "examples/mnist/mnist_train_lmdb" batch_size: 64 backend: LMDB }
}3.2 函数LayerRegistry::CreateLayer
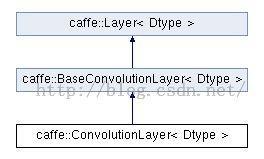
第1节中代码第一次通过调用LayerRegistry::CreateLayer()创建了DataLayer类,DataLayer类的继承关系如下图所示,详见[1]:
由继承图可知,调用DataLayer()的构造函数,依次执行的顺序为其基类构造函数:Layer()、BaseDataLayer()、InternalThread()(详见(Caffe)基本类InternalThread(三) )、BasePrefetchingDataLayer()、及DataLayer()。
其中,值得注意的是DataLayer(),在调用基类构造函数BasePrefetchingDataLayer()之后,对 DataReader reader_ 进行赋值,在该DataLayer对象中维护了一个DataReader对象reader_,其作用是添加读取数据任务至,一个专门读取数据库(examples/mnist/mnist_train_lmdb)的线程(若还不存在该线程,则创建该线程),此处一共取出了4*64个样本至BlockingQueue<Datum*> DataReader::QueuePair::full_。详见(Caffe)基本类DataReader、QueuePair、Body(四)
template <typename Dtype>
DataLayer<Dtype>::DataLayer(const LayerParameter& param)
: BasePrefetchingDataLayer<Dtype>(param),
reader_(param) {
}3.3 函数Layer::SetUp
- 此处按程序执行顺序值得关注的有:
在DataLayer::DataLayerSetUp中根据2.2DataReader中介绍的读取的数据中取出一个样本推测blob的形状 BasePrefetchingDataLayer::LayerSetUp如下代码prefetch_[i].data_.mutable_cpu_data()用到了涉及到gpu、cpu间复制数据的问题,见(Caffe)基本类Blob,Layer,Net(一)1.4SyncedMemory及引用[2]// Before starting the prefetch thread, we make cpu_data and gpu_data // calls so that the prefetch thread does not accidentally make simultaneous // cudaMalloc calls when the main thread is running. In some GPUs this // seems to cause failures if we do not so. for (int i = 0; i < PREFETCH_COUNT; ++i) { prefetch_[i].data_.mutable_cpu_data(); if (this->output_labels_) { prefetch_[i].label_.mutable_cpu_data(); } }BasePrefetchingDataLayer类继承了InternalThread,BasePrefetchingDataLayer<Dtype>::LayerSetUp中通过调用StartInternalThread()开启了一个新线程,从而执行BasePrefetchingDataLayer::InternalThreadEntryBasePrefetchingDataLayer::InternalThreadEntry关键代码如下,其中load_batch(batch)为,从2.2介绍的BlockingQueue<Datum*> DataReader::QueuePair::full_(包含从数据库读出的数据)中读取一个batch_size的数据到BlockingQueue<Batch<Dtype>*> BasePrefetchingDataLayer::prefetch_full_中。由于该线程在prefetch_free_为空时将挂起等待(PREFETCH_COUNT=3),prefetch_full_中用完的Batch将放回prefetch_free_中。该线程何时停止?while (!must_stop()) { Batch<Dtype>* batch = prefetch_free_.pop(); load_batch(batch); #ifndef CPU_ONLY if (Caffe::mode() == Caffe::GPU) { batch->data_.data().get()->async_gpu_push(stream); CUDA_CHECK(cudaStreamSynchronize(stream)); } #endif prefetch_full_.push(batch); }
4 第二层:Convolution Layer
4.1 protobuff定义
layer { name: "conv1" type: "Convolution" bottom: "data" top: "conv1" param { lr_mult: 1 }
param { lr_mult: 2 }
convolution_param { num_output: 20 kernel_size: 5 stride: 1 weight_filler { type: "xavier" }
bias_filler { type: "constant" }
}
}4.2 函数LayerRegistry::CreateLayer
说明:
- 不像DataLayer 直接执行的是构造函数,此时执行的是
GetConvolutuionLayer(),然后调用ConvolutionLayer(),原因如下:
REGISTER_LAYER_CREATOR(Convolution, GetConvolutionLayer);
4.3 Layer::SetUp
在`Layer::SetUp`中,调用了`ConvolutionLayer`的基类`BaseConvolutionLayer`的`LayerSetUp及Reshape`函数,该类的主要成员变量如下:/** * @brief Abstract base class that factors out the BLAS code common to * ConvolutionLayer and DeconvolutionLayer. */
template <typename Dtype>
class BaseConvolutionLayer : public Layer<Dtype> {
public:
explicit BaseConvolutionLayer(const LayerParameter& param)
: Layer<Dtype>(param) {}
virtual void LayerSetUp(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top);
virtual void Reshape(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top);
...
/// @brief The spatial dimensions of a filter kernel.
Blob<int> kernel_shape_;
/// @brief The spatial dimensions of the stride.
Blob<int> stride_;
/// @brief The spatial dimensions of the padding.
Blob<int> pad_;
/// @brief The spatial dimensions of the dilation.
Blob<int> dilation_;
/// @brief The spatial dimensions of the convolution input.
Blob<int> conv_input_shape_;
/// @brief The spatial dimensions of the col_buffer.
vector<int> col_buffer_shape_;
/// @brief The spatial dimensions of the output.
vector<int> output_shape_;
const vector<int>* bottom_shape_;
...
};- LayerSetUp函数中,主要是初始化了kernel_shape_、stride_、pad_、dilation_以及初始化网络参数,并存放与Layer::blobs_中。
- Reshape函数中,conv_input_shape_、bottom_shape_等
5 第三层:Pooling Layer
5.1 protobuff定义
layer { name: "pool1" type: "Pooling" bottom: "conv1" top: "pool1" pooling_param { pool: MAX kernel_size: 2 stride: 2 }
}5.2 Layer::SetUp
通过调用虚函数LayerSetUp及Reshape对以下成员变量进行初始化
/** * @brief Pools the input image by taking the max, average, etc. within regions. * * TODO(dox): thorough documentation for Forward, Backward, and proto params. */
template <typename Dtype>
class PoolingLayer : public Layer<Dtype> {
....
int kernel_h_, kernel_w_;
int stride_h_, stride_w_;
int pad_h_, pad_w_;
int channels_;
int height_, width_;
int pooled_height_, pooled_width_;
bool global_pooling_;
Blob<Dtype> rand_idx_;
Blob<int> max_idx_;
};6 第四层、第五层
基本同第二层、第三层
7 第六层:InnerProduct Layer
7.1 protobuff定义
layer { name: "ip1" type: "InnerProduct" bottom: "pool2" top: "ip1" param { lr_mult: 1 }
param { lr_mult: 2 }
inner_product_param { num_output: 500 weight_filler { type: "xavier" }
bias_filler { type: "constant" }
}
}7.2 Layer::SetUp
/** * @brief Also known as a "fully-connected" layer, computes an inner product * with a set of learned weights, and (optionally) adds biases. * * TODO(dox): thorough documentation for Forward, Backward, and proto params. */
template <typename Dtype>
class InnerProductLayer : public Layer<Dtype> {
...
int M_;
int K_;
int N_;
bool bias_term_;
Blob<Dtype> bias_multiplier_;
};说明:
- N_为输出大小,即等于
protobuff中定义的num_output - K_为输入大小,对于该层
Bottom Blob形状为(N, C, H, W),N为batch_size,K_=C*H*W(Caffe)基本类Blob,Layer,Net(一),M_=N。其中只有C、H、W跟内积相关
8 第七层:ReLU Layer
8.1 protobuff定义
layer { name: "relu1" type: "ReLU" bottom: "ip1" top: "ip1" }8.2 说明
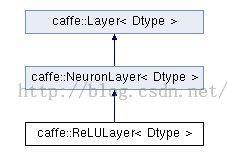
ReLULayer主要是用来做计算的,其继承关系如下,详细参加[4]、[5]
9 第八层:InnerProduct Layer
参见第7节
10 第九层:SoftmaxWithLoss Layer
10.1 protobuff定义
layer { name: "loss" type: "SoftmaxWithLoss" bottom: "ip2" bottom: "label" top: "loss" }10.2 LayerRegistry::CreateLayer
10.3 Layer::SetUp
值得注意的是:
在
SoftmaxWithLossLayer<Dtype>::LayerSetUp中,为SoftmaxWithLossLayer定义softmax_layer赋值,softmax_layer_ = LayerRegistry<Dtype>::CreateLayer(softmax_param),其类型为SoftmaxLayer。那么SoftmaxWithLossLayer与SoftmaxLayer的作用是?/// The internal SoftmaxLayer used to map predictions to a distribution. shared_ptr<Layer<Dtype> > softmax_layer_;此函数内调用Layer::SetLossWeights初始化了该层的Top Blob(loss)
11 剩余的工作
至此,训练网络基本创建完毕,接下来剩下的工作主要有:
- 反向检查一次网络,看哪些blobs会对loss产生影响,在LeNet5中,前面的9层均有影响
- 初始化权值共享
[1].http://caffe.berkeleyvision.org/doxygen/classcaffe_1_1BasePrefetchingDataLayer.html
[2].http://caffe.berkeleyvision.org/tutorial/net_layer_blob.html Implementation Details
[3].http://caffe.berkeleyvision.org/doxygen/classcaffe_1_1ConvolutionLayer.html
[4].http://caffe.berkeleyvision.org/doxygen/classcaffe_1_1ReLULayer.html
[5].http://caffe.berkeleyvision.org/tutorial/layers.html ReLU / Rectified-Linear and Leaky-ReLU