Android中级第五讲--GPRS定位的实现
博客出自:http://blog.csdn.net/liuxian13183,转载注明出处! All Rights Reserved !
前段时间在弄GPRS定位的问题,使用google的地图定位,大家也都知道,google现在在中国境内有很多限制,而且国外刷机严重,难免将google的各种服务给刷掉,所以最终采用百度的定位系统,完美实现。现在有时间了,给大家讲一讲,代码并不多。
我还是先说说google的定位吧,说不定有些仁兄需要的呢!
首先判断机器的GPRS模块是否正常,如果不正常,那没办法了,哪家的定位系统都不能用。
LocationManager alm = (LocationManager) this
.getSystemService(Context.LOCATION_SERVICE);
if (alm.isProviderEnabled(android.location.LocationManager.GPS_PROVIDER)) {
Toast.makeText(this, "GPS模块正常", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return;
}设置开启GPRS页面
Toast.makeText(this, "请开启GPS!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); Intent intent = new Intent(Settings.ACTION_SECURITY_SETTINGS); startActivityForResult(intent, 0); // 此为设置完成后返回到获取界面
设置省电模式,获得最好的定位方式
locationManager = (LocationManager) getSystemService(Context.LOCATION_SERVICE); gprs_view = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.gprs_view); Criteria criteria = new Criteria(); // 获得最好的定位效果 criteria.setAccuracy(Criteria.ACCURACY_COARSE); criteria.setAltitudeRequired(false); criteria.setBearingRequired(false); criteria.setCostAllowed(false); // 使用省电模式 criteria.setPowerRequirement(Criteria.POWER_LOW); // 获得当前的位置提供者 provider = locationManager.getBestProvider(criteria, false); ser.append(provider); locationManager.requestLocationUpdates(provider, 2000, 10, this);
获得上次location对象
// 使用网络定位,获得上次定位的location对象
if (location == null) {
location = locationManager
.getLastKnownLocation(LocationManager.NETWORK_PROVIDER);
provider = LocationManager.NETWORK_PROVIDER;
}
然后定位
String latLongString;
if (location != null) {
double lat = location.getLatitude();
double lng = location.getLongitude();
latLongString = "纬度:" + lat + "\n经度:" + lng;
Geocoder gc = new Geocoder(context);
List<Address> addresses = null;
try {
addresses = gc.getFromLocation(location.getLatitude(),
location.getLongitude(), 1);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
ser.append("\n" + addresses.get(0).getCountryName());
} else {
latLongString = "无法获取地理信息";
}
ser.append("\n" + "您当前的位置是:\n" + latLongString);
实现LocationListener接口,并在onLocationChanged和onProviderDisabled方法中实现updateWithNewLocation方法
以期待在未获得location对象时,不断获取直到取到为止
private void updateWithNewLocation(Location location) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if (location == null) {
locationManager.requestLocationUpdates(provider, 2000, (float) 0.1,
this);
}
}
以上是我弄到的关于用google开发服务的资料,实际上次定位的位置很难得到,实现定位,比较困难,也许是笔者使用的是水货,刷过机的原因吧。
下面是百度的定位,可以说都能实现吧
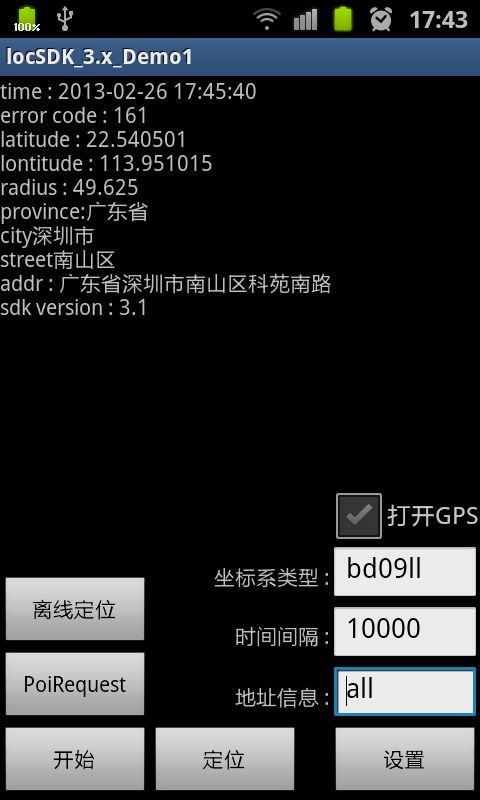
首先请大家看效果图,是实现了的!PS:朝鲜金胖子,看到我的经纬度乱来啊!
百度的定位相对来说要简单的多,为什么呢,因为它只有两三个方法,一般国内的手机GPS功能有被“阉割”的可能,所以一般GPS定位取不到位置,通用的还是GPRS网络定位功能。
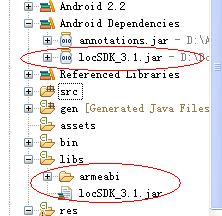
如图,导入项目所需包
然后在manifest.xml中加入权限,以及定义Service
<application
android:name="com.baidu.locSDK.test.Location"
android:icon="@drawable/icon"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<activity
android:name="mainActivity"
android:configChanges="orientation|keyboardHidden"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<service
android:name="com.baidu.location.f"
android:enabled="true"
android:process=":remote" >
</service>
</application>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_WIFI_STATE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CHANGE_WIFI_STATE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_PHONE_STATE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.MOUNT_UNMOUNT_FILESYSTEMS" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_LOGS" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.VIBRATE" />
主要代码如下,但要先打开网络
mStartBtn.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
if (!mIsStart) {
setLocationOption();
mLocClient.start();
mStartBtn.setText("开始");
mIsStart = true;
} else {
mLocClient.stop();
mIsStart = false;
mStartBtn.setText("结束");
}
Log.d("locSDK_Demo1",
"... mStartBtn onClick... pid=" + Process.myPid()
+ " count=" + count++);
}
});
private void setLocationOption() {
LocationClientOption option = new LocationClientOption();
option.setOpenGps(mGpsCheck.isChecked()); // gps
option.setCoorType(mCoorEdit.getText().toString());
option.setAddrType(mAddrEdit.getText().toString());
option.setScanSpan(Integer.parseInt(mSpanEdit.getText().toString()));
mLocClient.setLocOption(option);
}
最终展示出来
public void logMsg(String str) {
try {
mData = str;
if ( mTv != null )
mTv.setText(mData);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public class MyLocationListenner implements BDLocationListener {
@Override
public void onReceiveLocation(BDLocation location) {
if (location == null)
return ;
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(256);
sb.append("time : ");
sb.append(location.getTime());
sb.append("\nerror code : ");
sb.append(location.getLocType());
sb.append("\nlatitude : ");
sb.append(location.getLatitude());
sb.append("\nlontitude : ");
sb.append(location.getLongitude());
sb.append("\nradius : ");
sb.append(location.getRadius());
if (location.getLocType() == BDLocation.TypeGpsLocation){
sb.append("\nspeed : ");
sb.append(location.getSpeed());
sb.append("\nsatellite : ");
sb.append(location.getSatelliteNumber());
} else if (location.getLocType() == BDLocation.TypeNetWorkLocation){
sb.append("\nprovince:");
sb.append(location.getProvince());
sb.append("\ncity");
sb.append(location.getCity());
sb.append("\nstreet");
sb.append(location.getDistrict());
sb.append("\naddr : ");
sb.append(location.getAddrStr());
}
sb.append("\nsdk version : ");
sb.append(mLocationClient.getVersion());
logMsg(sb.toString());
}
public void onReceivePoi(BDLocation poiLocation) {
if (poiLocation == null){
return ;
}
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(256);
sb.append("Poi time : ");
sb.append(poiLocation.getTime());
sb.append("\nerror code : ");
sb.append(poiLocation.getLocType());
sb.append("\nlatitude : ");
sb.append(poiLocation.getLatitude());
sb.append("\nlontitude : ");
sb.append(poiLocation.getLongitude());
sb.append("\nradius : ");
sb.append(poiLocation.getRadius());
if (poiLocation.getLocType() == BDLocation.TypeNetWorkLocation){
sb.append("\naddr : ");
sb.append(poiLocation.getAddrStr());
}
if(poiLocation.hasPoi()){
sb.append("\nPoi:");
sb.append(poiLocation.getPoi());
}else{
sb.append("noPoi information");
}
logMsg(sb.toString());
}
}
就是这样,一个麻烦至极的定位功能完成了!源码下载地址: http://download.csdn.net/detail/liuxian13183/5088512