理解radiance irradiance
<2015.6 Update> 重新整理成的文档,有渲染方程的推导:理解 radiance 和 irradiance,用了Etendue的思路,结合维基百科自己想的咯。
<2015.10 Update> 也可以看做光粒、用通量的思路,请参考:
Chapter 2 Rendering Concepts, Radiosity and Realistic Image Synthesis 有关于 点光源 和 Mirror BRDF 的数学形式(Dirac delta function)及相应的渲染方程。
有关 线光源 等其它delta分布,可以用delta函数与普通函数的复合描述:比如单位圆上的分布 δ(x^2+y^2-1).
和
《计算机真实感图形的算法基础》 第二章中 一个统一的光照模型
<Before 2015.6 Update>:
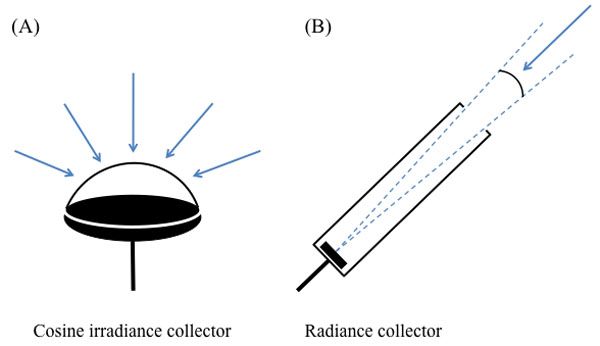
来自http://sites.sinauer.com/animalcommunication2e/chapter04.02.html,这个图可以帮助我们理解:
irradiance,就是单位面积上的功率(出射时叫radiant exitance)。
是来自环境周围四面八方的,定义成半球形,如(A)。[ 有一种变体定义成球形,叫做 scalar irradiance ]
radiance :给(A)罩上一个圆柱侧面,侧面的高从零逐渐增加,微小面积的基础上又逐渐形成了微小的立体角,就变成了上图中的(B),
面积 和 立体角 同时趋向于0,极限情况下就是 radiance。
如果接受面是倾斜的,就要乘以cos(θ)。
通过Etendue定义的 radiance:
“From the source point of view, it is the product of the area of the source and the solid angle that the system's entrance pupil subtends as seen from the source. Equivalently, from the system point of view, the etendue equals the area of the entrance pupil times the solid angle the source subtends as seen from the pupil. These definitions must be applied for infinitesimally small "elements" of area and solid angle ... The radiance of an optical system is equal to the derivative of the radiant flux with respect to the etendue.”
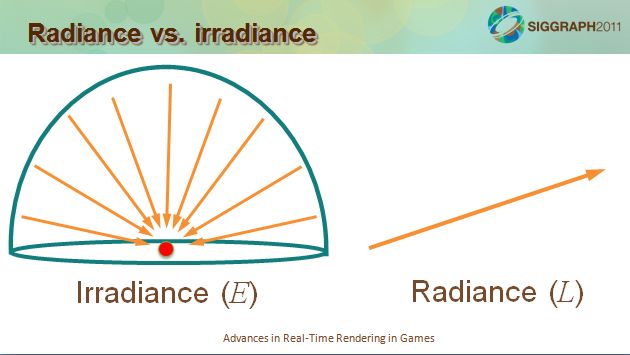
下图表示 极限情况下的 irradiance 和 radiance http://www.fseraph.com/?p=230