PowerShell 学习_Part1_Introduction to Toolmaking
PowerShell 简介
Windows PowerShell™ 是一种基于任务的命令行 shell 和脚本语言,专门用于管理系统。 Windows PowerShell™ 构建于 .NET Framework 之上,能够帮助 IT 专业人员和高级用户控制和自动管理 Windows 操作系统以及在 Windows 上运行的应用程序。
内置 Windows PowerShell 命令(称为 cmdlet)可用于通过命令行管理企业中的计算机。使用 Windows PowerShell™ Provider,您可以像访问文件系统那样轻松地访问数据存储,如注册表和证书存储。 此外,Windows PowerShell™ 还具有一个功能丰富的表达式分析程序和一种经过充分开发的脚本语言。
Windows PowerShell™ 具有以下特性:
• 用于执行常见系统管理任务的 cmdlet,这些任务包括管理注册表、服务、进程和事件日志,以及使用 Windows Management Instrumentation 等。
• 基于任务的脚本语言,以及对现有脚本和命令行工具的支持。
• 一致性设计。 由于 cmdlet 和系统数据存储使用通用语法和命名约定,因此可以轻松地共享数据,并且还可以将来自一个 cmdlet 的输出用作另一个 cmdlet 的输入,而无需重新设置格式或进行处理。
• 简化且基于命令的操作系统导航,允许用户使用与文件系统导航相同的技术来导航注册表和其他数据存储。
• 强大的对象操纵功能。 可以直接操纵对象,或将对象发送到其他工具或数据库。
• 可扩展的接口。 独立软件供应商和企业开发人员可以构建自定义工具和实用程序来管理其软件。
PowerShell’s scripting language
PowerShell’s
scripting languagePowerShell’s
scripting languagePowerShell’s
scripting language
变量(引用内容要添加$在变量名前):
$var = 'hello'
$number = 1
$numbers = 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9(用法:$numbers[0]代表第一个,$numbers[-1]代表最后一个,$numbers[-2]代表倒数第二个)
说明:
1。获取变量操作的命令:Get-Command –noun variable
2。PowerShell不需要事先声明
3。声明字符串一般用‘’,用“”的情况如下:
a 拼接两个字符串
$name = 'Don'
$prompt = "My name is $name"
输出:My name is Don
b 转义字符
$debug = "`$computer contains $computer" #the first $ is escaped
$head = "Column`tColumn`tColumn" #`t is the tab character
c 字符串包含单引号
$filter1 = "name='BITS'"
$computer = 'BITS'
$filter2 = "name='$computer'"
对象成员及变量
很著名的一句话,在PowerShell里也适用:Everything in PowerShell is an object
即使一个字符串'name',也是System.String的对象,我们可以通过Get-Member来获取成员:
$var = 'Hello'
$var | Get-Member
我们可以用“.(点)" 来获取成员变量
$svc = Get-Service
$svc[0].name #get the first object's name property
$name = $svc[1].name
$name.length #get the length property
$name.ToUpper() #invoke the ToUpper method
逻辑结构:if switch
If ($this -eq $that) {
# commands
} elseif ($those -ne $them) {
# commands
} elseif ($we -gt $they) {
# commands
} else {
# commands
}
Switch ($status) {
0 { $status_text = 'ok' }
1 { $status_text = 'error' }
2 { $status_text = 'jammed' }
3 { $status_text = 'overheated' }
4 { $status_text = 'empty' }
default { $status_text = 'unknown' }
}
循环结构:
Do {
# commands
} While ($this -eq $that)
$services = Get-Service
ForEach ($service in $services) {
$service.Stop()
}
For ($i=0;$i –lt 5;$i++) {
#do something
}
Break and Continue in constructs
简单的Script和函数
举例(首先要在测试机上运行:Enable-PSRemoting)
#提供参数的智能提示
Param(
[string]$computerName='localhost'
)
Get-CimInstance -ClassName Win32_OperatingSystem -ComputerName $computerName
调用方法:
.\Get-OSInfo –computerName SERVER2
.\Get-OSInfo –comp SERVER2
.\Get-OSInfo SERVER2
.\Get-OSInfo
封装到一个函数里:
function Get-OSInfo
{
#提供参数的智能提示
Param(
[string]$computerName='localhost'
)
Get-CimInstance -ClassName Win32_OperatingSystem -ComputerName $computerName
}
测试函数的方法:
1. Dot sourcing . .\tools.ps1------Get-OSInfo(注意:这种方法,即使shell退出,Get-OSInfo依然在内存;而且每次保存后要重新运行)
2. 在函数定义后添加调用语句:Get-OSInfo –computername SERVER2
3. A better way ahead: modules
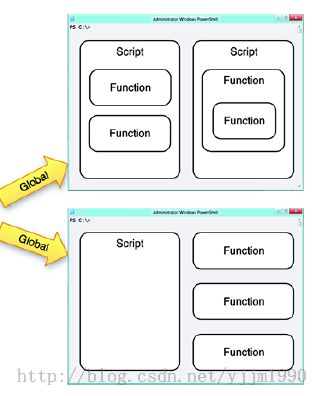
Scope
Scope就像我们C#里的namespace。
和Scope有关的PowerShell元素包括:
*变量
*函数
*别名
*PSDrives
*PSSnapins
一个Shell就是最外层的Scope(global),每一个新开的PowerShell窗口就是一个新的,单独的global Scope,和其他的PowerShell窗口是相互隔离的。ISE可以开多个PowerShell窗口:(文件——新的PowerShell标签)
说明:比如在script里定义了一个变量,那么这个变量就属于Script的范围(在这个script里面的函数等是可以访问到这个变量的,但是global看不到)。
我们看一段代码,就更加明白了:
$var="hello"
function My_Function
{
Write-Host "In the function, var contains '$var'"
$var="Goodbye"
Write-Host "In the function, the var is now '$var'"
}
Write-Host "In the script, var is '$var'"
Write-Host "Running the script"
My_Function
Write-Host "Function is done!"
Write-Host "In the script, the var is now '$var'"
输出:
查找顺序:
现在自己的scope里查找,如果找不到,就到父scope里查找,如果到global还找不到,那么就error
PowerShell的out-of-scope
1. 长格式
和scope有关的参数:-scope,用来指定scope,两种设定方法:
a. 值类型:0:当前scope。1:当前的父scope,以此类推
b. 字符类型:local:当前scope;Script:距离当前最近的scope(在scope嵌套中);global:代表shell级别。
默认值:0或者local
举例:New-Variable –Name Color –Value Purple –Scope 1 (会定义在父script里面)
2. 短格式
$global:color = 'purple'(无论这个变量在那里调用,都是在操作最高层的(global scope))