程序员面试的Top10大算法概念
以下是在编程面试中排名前10的算法相关的概念
- String
- Linked List
- Tree
- Graph
- Sorting
- Recursion vs. Iteration (递归 vs. 迭代)
- Dynamic Programming (动态规划)
- Bit Manipulation (位操作)
- Probability (概率问题)
- Combinations and Permutations (排列组合)
1. String
如果你使用的 IDE 没有代码补全功能,下面的方法应该记住:
toCharArray() //get char array of a String
Arrays.sort() //sort an array
Arrays.toString(char[] a) //convert to string
charAt(int x) //get a char at the specific index
length() //string length
length //array size
2. Linked List
在 Java 中,链表的实现很简单,每个节点 Node 都有一个值 val 和指向下个节点的链接 next。
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node(int x) {
val = x;
next = null;
}
}
链表两个著名的应用:栈Stack和队列Queue
Stack
class Stack{
Node top;
public Node peek(){
if(top != null){
return top;
}
return null;
}
public Node pop(){
if(top == null){
return null;
}else{
Node temp = new Node(top.val);
top = top.next;
return temp;
}
}
public void push(Node n){
if(n != null){
n.next = top;
top = n;
}
}
}
Queue:
class Queue{
Node first, last;
public void enqueue(Node n){
if(first == null){
first = n;
last = first;
}else{
last.next = n;
last = n;
}
}
public Node dequeue(){
if(first == null){
return null;
}else{
Node temp = new Node(first.val);
first = first.next;
return temp;
}
}
}
3. Tree
这里的树是指二叉树,每个节点都包含一个左孩子节点和右孩子节点:
class TreeNode{
int value;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
}
4. Graph
图相关的问题主要集中在深度优先搜索(DFS)和广度优先搜索(BFS)。
图广度优先搜索的实现:
1) Define a GraphNode
class GraphNode{
int val;
GraphNode next;
GraphNode[] neighbors;
boolean visited;
GraphNode(int x) {
val = x;
}
GraphNode(int x, GraphNode[] n){
val = x;
neighbors = n;
}
public String toString(){
return "value: "+ this.val;
}
}
2) Define a Queue
class Queue{
GraphNode first, last;
public void enqueue(GraphNode n){
if(first == null){
first = n;
last = first;
}else{
last.next = n;
last = n;
}
}
public GraphNode dequeue(){
if(first == null){
return null;
}else{
GraphNode temp = new GraphNode(first.val, first.neighbors);
first = first.next;
return temp;
}
}
}
3) Breath First Search uses a Queue
public class GraphTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GraphNode n1 = new GraphNode(1);
GraphNode n2 = new GraphNode(2);
GraphNode n3 = new GraphNode(3);
GraphNode n4 = new GraphNode(4);
GraphNode n5 = new GraphNode(5);
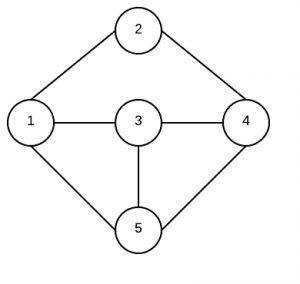
n1.neighbors = new GraphNode[]{n2,n3,n5};
n2.neighbors = new GraphNode[]{n1,n4};
n3.neighbors = new GraphNode[]{n1,n4,n5};
n4.neighbors = new GraphNode[]{n2,n3,n5};
n5.neighbors = new GraphNode[]{n1,n3,n4};
breathFirstSearch(n1, 5);
}
public static void breathFirstSearch(GraphNode root, int x){
if(root.val == x)
System.out.println("find in root");
Queue queue = new Queue();
root.visited = true;
queue.enqueue(root);
while(queue.first != null){
GraphNode c = (GraphNode) queue.dequeue();
for(GraphNode n: c.neighbors){
if(!n.visited){
System.out.print(n + " ");
n.visited = true;
if(n.val == x)
System.out.println("Find "+n);
queue.enqueue(n);
}
}
}
}
}
value: 2 value: 3 value: 5 Find value: 5
value: 4
5. Sorting
不同排序算法的时间复杂度
| Algorithm | Average Time | Worst Time | Space |
| Bubble sort | n^2 | n^2 | 1 |
| Selection sort | n^2 | n^2 | 1 |
| Insertion sort | n^2 | n^2 | |
| Quick sort | n log(n) | n^2 | |
| Merge sort | n log(n) | n log(n) | depends |
6. Recursion vs. Iteration(递归 vs. 迭代)
对程序员来说,递归应该是一个俱有的思想(a built-in thought),Demo:
问题: 有n步台阶,一次只能上1步或2步,共有多少种走法?
Step 1: 找出走完前n步台阶和前n-1步台阶之间的关系
为了走完n步台阶,只有两种方法:从n-1步台阶爬1步走到或从n-2步台阶处爬2步走到。如果f(n)是爬到第n步台阶的方法数,那么f(n) = f(n-1) + f(n-2)
Step 2: 确保开始条件是正确的
f(0) = 0;
f(1) = 1;
public static int f(int n){
if(n <= 2) return n;
int x = f(n-1) + f(n-2);
return x;
}
递归方法的时间复杂度是 n 的指数级,递归过程如下:
f(5)
f(4) + f(3)
f(3) + f(2) + f(2) + f(1)
f(2) + f(1) + f(2) + f(2) + f(1)
将递归转换为迭代:
public static int f(int n) {
if (n <= 2){
return n;
}
int first = 1, second = 2;
int third = 0;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++) {
third = first + second;
first = second;
second = third;
}
return third;
}
7. Dynamic Programming(动态规划)
Dynamic Programming 是可解决具有下面这些性质的问题的技术:
- 一个问题可以通过更小子问题的解决方法来解决。
- 有些子问题的解可能需要计算多次。
- 子问题的解存储在一张表格里,这样每个子问题只用计算一次。
- 需要额外的空间以节省时间。
爬楼梯问题符合具有以上4个性质,可以 Dynamic Programming 来解决
public static int[] A = new int[100];
public static int f3(int n) {
if (n <= 2)
A[n]= n;
if(A[n] > 0)
return A[n];
else
A[n] = f3(n-1) + f3(n-2);//store results so only calculate once!
return A[n];
}
8. Bit Manipulation(位操作)
位操作符:
| OR (|) | AND (&) | XOR (^) | Left Shift (<<) | Right Shift (>>) | Not (~) |
| 1|0=1 | 1&0=0 | 1^0=1 | 0010<<2=1000 | 1100>>2=0011 | ~1=0 |
获得给定数字n的第i位:(i从0计数并从右边开始)
public static boolean getBit(int num, int i){
int result = num & (1 << i);
if(result == 0){
return false;
}else{
return true;
}
}
获得数字10的第二位:
i=1, n=10
1<<1= 10
1010&10=10
10 is not 0, so return true;
9. 概率问题
解决概率相关的问题往往需要很好的分析、了解问题,例子:
一个房间里有 50 个人,那么至少有两个人生日相同的概率是多少?(忽略闰年的事实,也就是一年365天)
计算某些事件的概率很多时候都可以转换成先计算其对立事件的概率:
所以人生日互补相同的概率:P1 = 365/365 * 364/365 * 363/365 * … * (365-49)/365,则至少两个人生日相同的概率:
P = 1 – P1.
public static double caculateProbability(int n){
double x = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
x *= (365.0-i) / 365.0;
}
double pro = Math.round((1 - x) * 100);
return pro/100;
}
calculateProbability(50) = 0.97
10. Combinations and Permutations(排列组合)
排列与组之间的区别在于事件是否排序。