kubernetes源码分析 -- kubelet组件
Kubelet需要在每个minion结点上运行。他负责维护在特定主机上的容器。
Kubelet的代码架构与kube-proxy类似,cmd部分组织代码调用(cmd/kubelet/kubelet.go),kubelet的功能实现在pkg/kubelet包中。
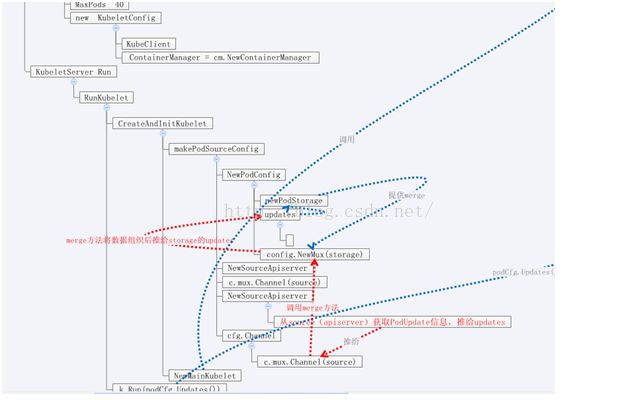
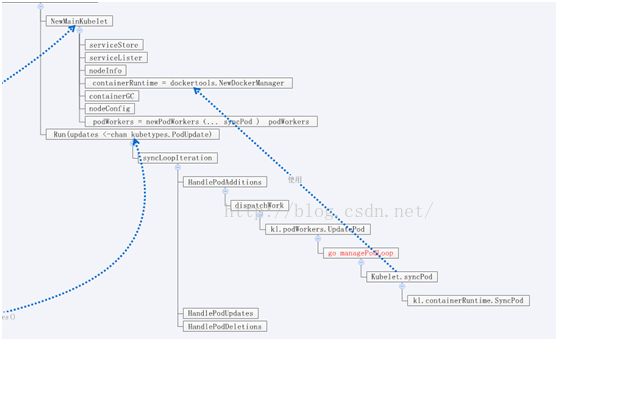
apiServer负责接收server发过来的Pod管理信息,通过channel推送到PodConfig。PodConfig的mux使用Storage的Merge方法,Merge方法又会通过Updates 这个channel将Pod数据推给Kubelet,真正的Pod处理在Kubelet包中。Kubelet通过syncLoop监听channel,收到数据后就执行关于Pod和容器的处理,真正操作容器的方法调用dockertools包中的方法。总体组件图如下:
Kubelet的cmd主函数在cmd/kubelet/kubelet.go文件中。他调用NewKubeletServer函数创建一个server对象并Run起来。其中调用的比较重要函数是RunKubelet,里面的CreateAndInitKubelet创建了管理Pod的Config对象,处理信息的kubelet对象。这些方法都在pkg/kubelet/config包里面。
比较重要的函数有:
func NewPodConfig(mode PodConfigNotificationMode, recorder record.EventRecorder) *PodConfig {
updates := make(chan kubetypes.PodUpdate, 50)
storage := newPodStorage(updates, mode, recorder)
podConfig := &PodConfig{
pods: storage,
mux: config.NewMux(storage),
updates: updates,
sources: sets.String{},
}
return podConfig
}
此函数创建PodConfig对象。他建立起了apiServer到后端kubelet处理消息之间的联系。
Kubelet的Run方法循环监听updates channel上的消息。当收到消息进行处理。以增加一个pod为例,HandlePodAddition的dispatchWork最终会调用到dockertools包中的方法,进行Pod内容器的操作。此处的调用关系比较深,值得注意一下的是看到p. syncPodFn时,其实这个方法就是kubelet.syncPod,避免大家找不到。在这个里面可以看到kubelet操作Pod的过程,比如namespaceMode := fmt.Sprintf("container:%v", podInfraContainerID)看到Pod内的容器的网络模式是通过container模式link到podInfraContainerID的。
这里面的注意函数有syncLoopIteration
func (kl *Kubelet) syncLoopIteration(updates <-chan kubetypes.PodUpdate, handler SyncHandler,
syncCh <-chan time.Time, housekeepingCh <-chan time.Time, plegCh <-chan *pleg.PodLifecycleEvent) bool {
kl.syncLoopMonitor.Store(time.Now())
select {
case u, open := <-updates:
if !open {
glog.Errorf("Update channel is closed. Exiting the sync loop.")
return false
}
kl.addSource(u.Source)
switch u.Op {
case kubetypes.ADD:
glog.V(2).Infof("SyncLoop (ADD, %q): %q", u.Source, format.Pods(u.Pods))
handler.HandlePodAdditions(u.Pods)
case kubetypes.UPDATE:
glog.V(2).Infof("SyncLoop (UPDATE, %q): %q", u.Source, format.Pods(u.Pods))
handler.HandlePodUpdates(u.Pods)
case kubetypes.REMOVE:
。。。
}
以及里面调用到的
func (kl *Kubelet) dispatchWork(pod *api.Pod, syncType kubetypes.SyncPodType, mirrorPod *api.Pod, start time.Time) {
if kl.podIsTerminated(pod) {
return
}
// Run the sync in an async worker.
kl.podWorkers.UpdatePod(pod, mirrorPod, syncType, func() {
metrics.PodWorkerLatency.WithLabelValues(syncType.String()).Observe(metrics.SinceInMicroseconds(start))
})
// Note the number of containers for new pods.
if syncType == kubetypes.SyncPodCreate {
metrics.ContainersPerPodCount.Observe(float64(len(pod.Spec.Containers)))
}
}