ROLLUP and CUBE
比较rollup 和 cube的区别
SELECT o.customer_id, oi.product_id, SUM(oi.uni_price*oi.quantity)
"Total" FROM order_items oi JOIN orders oON oi.order_id=o.order_id
GROUP BY ROLLUP (o.customer_id, oi.product_id);
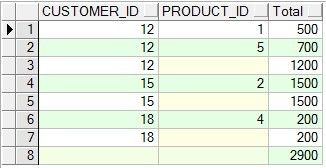
SELECT o.customer_id, oi.product_id, SUM(oi.uni_price*oi.quantity)
"Total" FROM order_items oi JOIN orders o
ON oi.order_id=o.order_id
GROUP BY cube (o.customer_id, oi.product_id);
ROLLUP Extension to GROUP BY
ROLLUP enables a SELECT statement to calculate multiple levels of subtotals across a specified group of dimensions. It also calculates a grand total. ROLLUP is a simple extension to the GROUP BY clause, so its syntax is extremely easy to use. The ROLLUP extension is highly efficient, adding minimal overhead to a query.
The action of ROLLUP is straightforward: it creates subtotals that roll up from the most detailed level to a grand total, following a grouping list specified in theROLLUP clause. ROLLUP takes as its argument an ordered list of grouping columns. First, it calculates the standard aggregate values specified in the GROUP BYclause. Then, it creates progressively higher-level subtotals, moving from right to left through the list of grouping columns. Finally, it creates a grand total.
ROLLUP creates subtotals at n+1 levels, where n is the number of grouping columns. For instance, if a query specifies ROLLUP on grouping columns of time,region, and department(n=3), the result set will include rows at four aggregation levels.
You might want to compress your data when using ROLLUP. This is particularly useful when there are few updates to older partitions.
When to Use ROLLUP
Use the ROLLUP extension in tasks involving subtotals.
-
It is very helpful for subtotaling along a hierarchical dimension such as time or geography. For instance, a query could specify a
ROLLUP(y,m,day)orROLLUP(country,state,city). -
For data warehouse administrators using summary tables,
ROLLUPcan simplify and speed up the maintenance of summary tables.
ROLLUP Syntax
ROLLUP appears in the GROUP BY clause in a SELECT statement. Its form is:
SELECT … GROUP BY ROLLUP(grouping_column_reference_list)
Example 20-2 ROLLUP
This example uses the data in the sh sample schema data, the same data as was used in Figure 20-1. The ROLLUP is across three dimensions.
SELECT channels.channel_desc, calendar_month_desc,
countries.country_iso_code,
TO_CHAR(SUM(amount_sold), '9,999,999,999') SALES$
FROM sales, customers, times, channels, countries
WHERE sales.time_id=times.time_id
AND sales.cust_id=customers.cust_id
AND customers.country_id = countries.country_id
AND sales.channel_id = channels.channel_id
AND channels.channel_desc IN ('Direct Sales', 'Internet')
AND times.calendar_month_desc IN ('2000-09', '2000-10')
AND countries.country_iso_code IN ('GB', 'US')
GROUP BY
ROLLUP(channels.channel_desc, calendar_month_desc, countries.country_iso_code);
CHANNEL_DESC CALENDAR CO SALES$
-------------------- -------- -- --------------
Internet 2000-09 GB 16,569
Internet 2000-09 US 124,224
Internet 2000-09 140,793
Internet 2000-10 GB 14,539
Internet 2000-10 US 137,054
Internet 2000-10 151,593
Internet 292,387
Direct Sales 2000-09 GB 85,223
Direct Sales 2000-09 US 638,201
Direct Sales 2000-09 723,424
Direct Sales 2000-10 GB 91,925
Direct Sales 2000-10 US 682,297
Direct Sales 2000-10 774,222
Direct Sales 1,497,646
1,790,032
Note that results do not always add up due to rounding.
This query returns the following sets of rows:
-
Regular aggregation rows that would be produced by
GROUPBYwithout usingROLLUP. -
First-level subtotals aggregating across
country_idfor each combination ofchannel_descandcalendar_month. -
Second-level subtotals aggregating across
calendar_month_descandcountry_idfor eachchannel_descvalue. -
A grand total row.
Partial Rollup
You can also roll up so that only some of the sub-totals will be included. This partial rollup uses the following syntax:
GROUP BY expr1, ROLLUP(expr2, expr3);
In this case, the GROUP BY clause creates subtotals at (2+1=3) aggregation levels. That is, at level (expr1, expr2, expr3), (expr1, expr2), and (expr1).
Example 20-3 Partial ROLLUP
SELECT channel_desc, calendar_month_desc, countries.country_iso_code,
TO_CHAR(SUM(amount_sold), '9,999,999,999') SALES$
FROM sales, customers, times, channels, countries
WHERE sales.time_id=times.time_id AND sales.cust_id=customers.cust_id
AND customers.country_id = countries.country_id
AND sales.channel_id= channels.channel_id
AND channels.channel_desc IN ('Direct Sales', 'Internet')
AND times.calendar_month_desc IN ('2000-09', '2000-10')
AND countries.country_iso_code IN ('GB', 'US')
GROUP BY channel_desc, ROLLUP(calendar_month_desc, countries.country_iso_code);
CHANNEL_DESC CALENDAR CO SALES$
-------------------- -------- -- --------------
Internet 2000-09 GB 16,569
Internet 2000-09 US 124,224
Internet 2000-09 140,793
Internet 2000-10 GB 14,539
Internet 2000-10 US 137,054
Internet 2000-10 151,593
Internet 292,387
Direct Sales 2000-09 GB 85,223
Direct Sales 2000-09 US 638,201
Direct Sales 2000-09 723,424
Direct Sales 2000-10 GB 91,925
Direct Sales 2000-10 US 682,297
Direct Sales 2000-10 774,222
Direct Sales 1,497,646
This query returns the following sets of rows:
-
Regular aggregation rows that would be produced by
GROUPBYwithout usingROLLUP. -
First-level subtotals aggregating across
country_idfor each combination ofchannel_descandcalendar_month_desc. -
Second-level subtotals aggregating across
calendar_month_descandcountry_idfor eachchannel_descvalue. -
It does not produce a grand total row.
CUBE Extension to GROUP BY
CUBE takes a specified set of grouping columns and creates subtotals for all of their possible combinations. In terms of multidimensional analysis, CUBEgenerates all the subtotals that could be calculated for a data cube with the specified dimensions. If you have specified CUBE(time, region, department), the result set will include all the values that would be included in an equivalent ROLLUP statement plus additional combinations. For instance, in Figure 20-1, the departmental totals across regions (279,000 and 319,000) would not be calculated by a ROLLUP(time, region, department) clause, but they would be calculated by a CUBE(time, region, department) clause. If n columns are specified for a CUBE, there will be 2 to the n combinations of subtotals returned. Example 20-4gives an example of a three-dimension cube. See Oracle Database SQL Reference for syntax and restrictions.
When to Use CUBE
Consider Using CUBE in any situation requiring cross-tabular reports. The data needed for cross-tabular reports can be generated with a single SELECT usingCUBE. Like ROLLUP, CUBE can be helpful in generating summary tables. Note that population of summary tables is even faster if the CUBE query executes in parallel.
CUBE is typically most suitable in queries that use columns from multiple dimensions rather than columns representing different levels of a single dimension. For instance, a commonly requested cross-tabulation might need subtotals for all the combinations of month, state, and product. These are three independent dimensions, and analysis of all possible subtotal combinations is commonplace. In contrast, a cross-tabulation showing all possible combinations of year, month, and day would have several values of limited interest, because there is a natural hierarchy in the time dimension. Subtotals such as profit by day of month summed across year would be unnecessary in most analyses. Relatively few users need to ask "What were the total sales for the 16th of each month across the year?" See "Hierarchy Handling in ROLLUP and CUBE" for an example of handling rollup calculations efficiently.
CUBE Syntax
CUBE appears in the GROUP BY clause in a SELECT statement. Its form is:
SELECT … GROUP BY CUBE (grouping_column_reference_list)
Example 20-4 CUBE
SELECT channel_desc, calendar_month_desc, countries.country_iso_code,
TO_CHAR(SUM(amount_sold), '9,999,999,999') SALES$
FROM sales, customers, times, channels, countries
WHERE sales.time_id=times.time_id AND sales.cust_id=customers.cust_id AND
sales.channel_id= channels.channel_id
AND customers.country_id = countries.country_id
AND channels.channel_desc IN
('Direct Sales', 'Internet') AND times.calendar_month_desc IN
('2000-09', '2000-10') AND countries.country_iso_code IN ('GB', 'US')
GROUP BY CUBE(channel_desc, calendar_month_desc, countries.country_iso_code);
CHANNEL_DESC CALENDAR CO SALES$
-------------------- -------- -- --------------
1,790,032
GB 208,257
US 1,581,775
2000-09 864,217
2000-09 GB 101,792
2000-09 US 762,425
2000-10 925,815
2000-10 GB 106,465
2000-10 US 819,351
Internet 292,387
Internet GB 31,109
Internet US 261,278
Internet 2000-09 140,793
Internet 2000-09 GB 16,569
Internet 2000-09 US 124,224
Internet 2000-10 151,593
Internet 2000-10 GB 14,539
Internet 2000-10 US 137,054
Direct Sales 1,497,646
Direct Sales GB 177,148
Direct Sales US 1,320,497
Direct Sales 2000-09 723,424
Direct Sales 2000-09 GB 85,223
Direct Sales 2000-09 US 638,201
Direct Sales 2000-10 774,222
Direct Sales 2000-10 GB 91,925
Direct Sales 2000-10 US 682,297
This query illustrates CUBE aggregation across three dimensions.
Partial CUBE
Partial CUBE resembles partial ROLLUP in that you can limit it to certain dimensions and precede it with columns outside the CUBE operator. In this case, subtotals of all possible combinations are limited to the dimensions within the cube list (in parentheses), and they are combined with the preceding items in the GROUP BYlist.
The syntax for partial CUBE is as follows:
GROUP BY expr1, CUBE(expr2, expr3)
This syntax example calculates 2*2, or 4, subtotals. That is:
-
(
expr1,expr2,expr3) -
(
expr1,expr2) -
(
expr1,expr3) -
(
expr1)
Example 20-5 Partial CUBE
Using the sales database, you can issue the following statement:
SELECT channel_desc, calendar_month_desc, countries.country_iso_code,
TO_CHAR(SUM(amount_sold), '9,999,999,999') SALES$
FROM sales, customers, times, channels, countries
WHERE sales.time_id = times.time_id
AND sales.cust_id = customers.cust_id
AND customers.country_id=countries.country_id
AND sales.channel_id = channels.channel_id
AND channels.channel_desc IN ('Direct Sales', 'Internet')
AND times.calendar_month_desc IN ('2000-09', '2000-10')
AND countries.country_iso_code IN ('GB', 'US')
GROUP BY channel_desc, CUBE(calendar_month_desc, countries.country_iso_code);
CHANNEL_DESC CALENDAR CO SALES$
-------------------- -------- -- --------------
Internet 292,387
Internet GB 31,109
Internet US 261,278
Internet 2000-09 140,793
Internet 2000-09 GB 16,569
Internet 2000-09 US 124,224
Internet 2000-10 151,593
Internet 2000-10 GB 14,539
Internet 2000-10 US 137,054
Direct Sales 1,497,646
Direct Sales GB 177,148
Direct Sales US 1,320,497
Direct Sales 2000-09 723,424
Direct Sales 2000-09 GB 85,223
Direct Sales 2000-09 US 638,201
Direct Sales 2000-10 774,222
Direct Sales 2000-10 GB 91,925
Direct Sales 2000-10 US 682,297