XMPP协议实现即时通讯底层书写 (二)-- IOS XMPPFramework Demo+分析
我希望,This is a new day!
在看代码之前,我觉得你还是应该先整理一下心情,来听我说几句:
首先,我希望你是在早上边看这篇blog,然后一边开始动手操作,如果你只是看blog而不去自己对比项目,作用不是很大。一日之计在于晨,所以怀着一颗对技术渴望,激动的,亢奋的心情去学习,你才能有所得。嗯,就拿鄙人当时做项目来说,每天早上起来的第一件事情,就是研究XMPPFramework作者的代码,按照模块来分析和模仿书写,睡觉的时候还在思考,分析,总结...
当然我并不是说每个Dev 都要向我这样,只是希望你能保持一颗积极向上的心态去对待技术,对待你的工作。
that's all。
ResourceURL:https://github.com/robbiehanson/XMPPFramework (如果你还在维护你现有的基于XMPP的产品,那么你需要sometimes 去查看,原作者是否fix 一些bug)
IphoneXMPP Demo
1.AppDelegate.m
a.大概看下头文件,ok,别跳转深入看了,下面我会教快速的看。See this method
有几个地方需要注意:
1)DDLog 用于不用不强求,鄙人喜欢干净清爽的控制台,所以就没用这玩意,因为我并不是很依赖全部打log,而是断点控制台po XXX方法,实时性找出问题修复bug
2)配置XML Stream 流 ,给你的长连接里面增加各种 buff,各种装备,各种属性。ok,不开玩笑了:),这个配置很重要,它决定了你的app需要支持哪些xmpp服务,决定了原作者(罗宾逊)哪些代码功能模块是不需要生效的
3)启动连接,当然对应的也有一个cancel connect
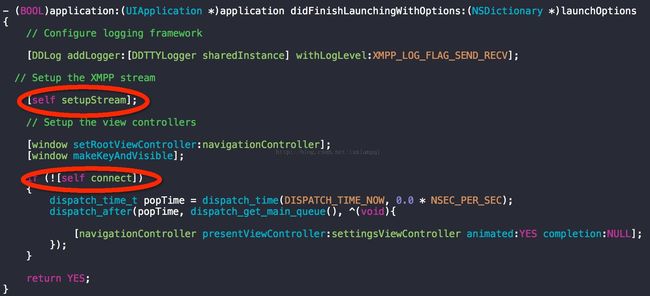
b 设置你的 XML Stream ,开启哪些功能
- (void)setupStream
{
NSAssert(xmppStream == nil, @"Method setupStream invoked multiple times");
// Setup xmpp stream
//
// The XMPPStream is the base class for all activity.
// Everything else plugs into the xmppStream, such as modules/extensions and delegates.
xmppStream = [[XMPPStream alloc] init];
#if !TARGET_IPHONE_SIMULATOR
{
// Want xmpp to run in the background?
//
// P.S. - The simulator doesn't support backgrounding yet.
// When you try to set the associated property on the simulator, it simply fails.
// And when you background an app on the simulator,
// it just queues network traffic til the app is foregrounded again.
// We are patiently waiting for a fix from Apple.
// If you do enableBackgroundingOnSocket on the simulator,
// you will simply see an error message from the xmpp stack when it fails to set the property.
<span style="color:#66ff99;">xmppStream.enableBackgroundingOnSocket = YES;</span>
}
#endif
// Setup reconnect
//
// The XMPPReconnect module monitors for "accidental disconnections" and
// automatically reconnects the stream for you.
// There's a bunch more information in the XMPPReconnect header file.
xmppReconnect = [[XMPPReconnect alloc] init];
// Setup roster
//
// The XMPPRoster handles the xmpp protocol stuff related to the roster.
// The storage for the roster is abstracted.
// So you can use any storage mechanism you want.
// You can store it all in memory, or use core data and store it on disk, or use core data with an in-memory store,
// or setup your own using raw SQLite, or create your own storage mechanism.
// You can do it however you like! It's your application.
// But you do need to provide the roster with some storage facility.
xmppRosterStorage = [[XMPPRosterCoreDataStorage alloc] init];
// xmppRosterStorage = [[XMPPRosterCoreDataStorage alloc] initWithInMemoryStore];
xmppRoster = [[XMPPRoster alloc] initWithRosterStorage:xmppRosterStorage];
xmppRoster.autoFetchRoster = YES;
xmppRoster.autoAcceptKnownPresenceSubscriptionRequests = YES;
// Setup vCard support
//
// The vCard Avatar module works in conjuction with the standard vCard Temp module to download user avatars.
// The XMPPRoster will automatically integrate with XMPPvCardAvatarModule to cache roster photos in the roster.
xmppvCardStorage = [XMPPvCardCoreDataStorage sharedInstance];
xmppvCardTempModule = [[XMPPvCardTempModule alloc] initWithvCardStorage:xmppvCardStorage];
xmppvCardAvatarModule = [[XMPPvCardAvatarModule alloc] initWithvCardTempModule:xmppvCardTempModule];</span>
// Setup capabilities
//
// The XMPPCapabilities module handles all the complex hashing of the caps protocol (XEP-0115).
// Basically, when other clients broadcast their presence on the network
// they include information about what capabilities their client supports (audio, video, file transfer, etc).
// But as you can imagine, this list starts to get pretty big.
// This is where the hashing stuff comes into play.
// Most people running the same version of the same client are going to have the same list of capabilities.
// So the protocol defines a standardized way to hash the list of capabilities.
// Clients then broadcast the tiny hash instead of the big list.
// The XMPPCapabilities protocol automatically handles figuring out what these hashes mean,
// and also persistently storing the hashes so lookups aren't needed in the future.
//
// Similarly to the roster, the storage of the module is abstracted.
// You are strongly encouraged to persist caps information across sessions.
//
// The XMPPCapabilitiesCoreDataStorage is an ideal solution.
// It can also be shared amongst multiple streams to further reduce hash lookups.
xmppCapabilitiesStorage = [XMPPCapabilitiesCoreDataStorage sharedInstance];
xmppCapabilities = [[XMPPCapabilities alloc] initWithCapabilitiesStorage:xmppCapabilitiesStorage];
xmppCapabilities.autoFetchHashedCapabilities = YES;
xmppCapabilities.autoFetchNonHashedCapabilities = NO;
// Activate xmpp modules
[xmppReconnect activate:xmppStream];
[xmppRoster activate:xmppStream];
[xmppvCardTempModule activate:xmppStream];
[xmppvCardAvatarModule activate:xmppStream];
[xmppCapabilities activate:xmppStream];
// Add ourself as a delegate to anything we may be interested in
[xmppStream addDelegate:self delegateQueue:dispatch_get_main_queue()];
[xmppRoster addDelegate:self delegateQueue:dispatch_get_main_queue()];
// Optional:
//
// Replace me with the proper domain and port.
// The example below is setup for a typical google talk account.
//
// If you don't supply a hostName, then it will be automatically resolved using the JID (below).
// For example, if you supply a JID like '[email protected]/rsrc'
// then the xmpp framework will follow the xmpp specification, and do a SRV lookup for quack.com.
//
// If you don't specify a hostPort, then the default (5222) will be used.
// [xmppStream setHostName:@"talk.google.com"];
// [xmppStream setHostPort:5222];
// You may need to alter these settings depending on the server you're connecting to
customCertEvaluation = YES;
}
ok,let's begin.
1)创建一个XML stream 对象,这货是干嘛的呢。打个比喻:货物运输带,上货和下货 都要靠这条带子。谁让这条带子动起来?
长连接
它就是个马达。
那么这里面的货是啥呢?3种货:美版,港版,日版,偶尔带点国行。(*^__^*) 嘻嘻……,哈哈不开玩笑了。有三种货:<iq> <p><message>,偶尔带点其他标签<a><r>什么的。
索达斯内!~斯ko一!~是的,好厉害好棒哒!~发现昨天看得RFC6121有点关系啦。~\(≧▽≦)/~啦啦啦
2)是否开启后台模式---NO,除非你有VOIP需要支持,不然后患无穷,现在github 上后台issue还有一大堆没解决的呢,反正呢很复杂哒,我这菜逼就没支持这货
<span style="color:#66ff99;">xmppStream.enableBackgroundingOnSocket</span>
3)开启重连机制(长连接必备,心跳啥的)
开启roster(两种形式:coreData存储 or 开辟内存--临时对象存储),自动获取服务器上的roster数据?是否自动应答 已经存在订阅出席消息的小伙伴的订阅请求,也就是说是否自动过滤掉已经订阅过的订阅或者是已经形成订阅关系的用户请求啦(难点,后面章节细讲)。开启roster CoreDataStorage,也就是数据库存CoreData储技术。
开启vCard(个人信息详情) module,二次封装vCard Module开启,并且启动 vcard对应的coreData 存储技术
开启capabilitie,和与之的存储技术。这货当初看了好久哒,但是现在真忘记了。。。sorry,这块需要找对应的XEP来进行脑补,不过貌似暂时用不到,就让它默认吧。
原文链接传送门
下面是 XMPPFramework的一个核心:multi delegate (作者独有,膜拜!~)
[xmppStream addDelegate:self delegateQueue:dispatch_get_main_queue()]; [xmppRoster addDelegate:self delegateQueue:dispatch_get_main_queue()];
对roster 进行一个sub delegate回调,在当前Class,主线程队列。
关于multi delegate 技术,建议好好看看里面的具体实现,不要求你会写,大概的核心思想能看懂就成,会return BOOL YES or NO 即可。。。
btw1:鄙人对这个multi delegate再次膜拜,当然他写的很多东西,都是让我膜拜的。。比如socket链接。。。XML解析,DDLog。。。反正好多,好了不说了,说多了都是泪,菜狗只能仰望大神。。
btw2:刷刷刷两个小时过去了,洗洗睡了,写blog真心很累。
btw3:服务器那个水?问你呢,你们环境配好了没,我这边要example测试连接了,快给个账号和密码。劳资效率就是这么高,一天搞定基本的数据连接了。
btw4:经理,我这边还算顺利,约有小成,你看这连接界面,成了,虽然界面丑了点,但是能连上服务端了,真棒。
btw5:啪!你个傻蛋,别说这事demo,怎么有你这种队友。
btw6:下期预告<IOS XMPPFramework --IM底层架构设计+技术准备工作>