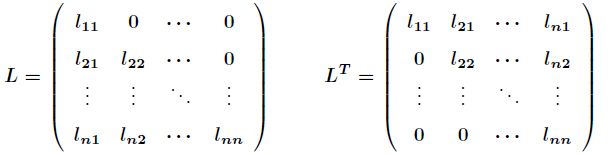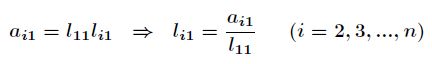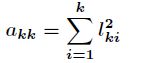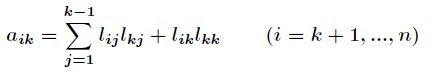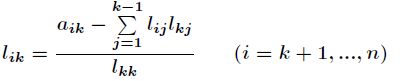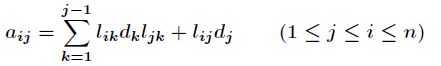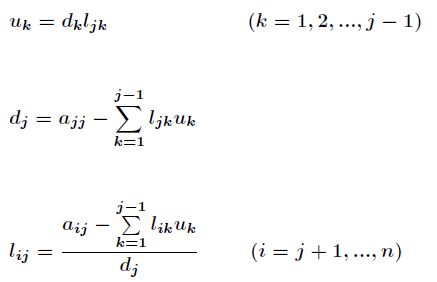Cholesky分解法
Cholesky分解法又叫平方根法,是求解对称正定线性方程组最常用的方法之一。对于一般矩阵,为了消除LU分
解的局限性和误差的过分积累,采用了选主元的方法,但对于对称正定矩阵而言,选主元是不必要的。
定理:若![]() 对称正定,则存在一个对角元为正数的下三角矩阵
对称正定,则存在一个对角元为正数的下三角矩阵![]() ,使得
,使得![]() 成立。
成立。
假设现在要求解线性方程组![]() ,其中
,其中![]() 为对称正定矩阵,那么
为对称正定矩阵,那么![]() 可通过下面步骤求解
可通过下面步骤求解
(1)求![]() 的Cholesky分解,得到
的Cholesky分解,得到![]()
(2)求解![]() ,得到
,得到![]()
(3)求解![]() ,得到
,得到![]()
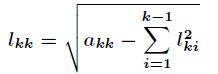
现在的关键问题是对![]() 进行Cholesky分解。假设
进行Cholesky分解。假设
通过![]() 比较两边的关系,首先由
比较两边的关系,首先由![]() ,再由
,再由
这样便得到了矩阵![]() 的第一列元素,假定已经算出了
的第一列元素,假定已经算出了![]() 的前
的前![]() 列元素,通过
列元素,通过
可以得到
进一步再由
最终得到
这样便通过![]() 的前
的前![]() 列求出了第
列求出了第![]() 列,一直递推下去即可求出
列,一直递推下去即可求出![]() ,这种方法称为平方根法。
,这种方法称为平方根法。
代码:
- #include <iostream>
- #include <string.h>
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <vector>
- #include <math.h>
- using namespace std;
- const int N = 1005;
- typedef double Type;
- Type A[N][N], L[N][N];
- /** 分解A得到A = L * L^T */
- void Cholesky(Type A[][N], Type L[][N], int n)
- {
- for(int k = 0; k < n; k++)
- {
- Type sum = 0;
- for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
- sum += L[k][i] * L[k][i];
- sum = A[k][k] - sum;
- L[k][k] = sqrt(sum > 0 ? sum : 0);
- for(int i = k + 1; i < n; i++)
- {
- sum = 0;
- for(int j = 0; j < k; j++)
- sum += L[i][j] * L[k][j];
- L[i][k] = (A[i][k] - sum) / L[k][k];
- }
- for(int j = 0; j < k; j++)
- L[j][k] = 0;
- }
- }
- /** 回带过程 */
- vector<Type> Solve(Type L[][N], vector<Type> X, int n)
- {
- /** LY = B => Y */
- for(int k = 0; k < n; k++)
- {
- for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
- X[k] -= X[i] * L[k][i];
- X[k] /= L[k][k];
- }
- /** L^TX = Y => X */
- for(int k = n - 1; k >= 0; k--)
- {
- for(int i = k + 1; i < n; i++)
- X[k] -= X[i] * L[i][k];
- X[k] /= L[k][k];
- }
- return X;
- }
- void Print(Type L[][N], const vector<Type> B, int n)
- {
- for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
- {
- for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
- cout<<L[i][j]<<" ";
- cout<<endl;
- }
- cout<<endl;
- vector<Type> X = Solve(L, B, n);
- vector<Type>::iterator it;
- for(it = X.begin(); it != X.end(); it++)
- cout<<*it<<" ";
- cout<<endl;
- }
- int main()
- {
- int n;
- cin>>n;
- memset(L, 0, sizeof(L));
- for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
- {
- for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
- cin>>A[i][j];
- }
- vector<Type> B;
- for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
- {
- Type y;
- cin>>y;
- B.push_back(y);
- }
- Cholesky(A, L, n);
- Print(L, B, n);
- return 0;
- }
- /**data**
- 4
- 4 -2 4 2
- -2 10 -2 -7
- 4 -2 8 4
- 2 -7 4 7
- 8 2 16 6
- */
用上述的方法需要进行开方,这有可能损失精度和增加运算量,为了避免开方,Cholesky分解有个改进的版本。
将对称正定矩阵![]() 通过分解成
通过分解成![]() ,其中
,其中![]() 是单位下三角矩阵,
是单位下三角矩阵,![]() 是对角均为正数的对角矩阵。把这
是对角均为正数的对角矩阵。把这
一分解叫做![]() 分解,是Cholesky分解的变形。对应两边的元素,很容易得到
分解,是Cholesky分解的变形。对应两边的元素,很容易得到
由此可以确定计算![]() 和
和![]() 的公式如下
的公式如下
在实际计算时,是将![]() 的严格下三角元素存储在
的严格下三角元素存储在![]() 的对应位置上,而将
的对应位置上,而将![]() 的对角元存储在
的对角元存储在![]() 的对应的对角位置上。
的对应的对角位置上。
类似地求解线性方程组![]() 的解步骤如下
的解步骤如下
(1)对矩阵![]() 进行分解得到
进行分解得到![]()
(2)求解![]() ,得到
,得到![]()
(3)求解![]() ,得到
,得到![]()
代码:
- #include <iostream>
- #include <string.h>
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <vector>
- #include <math.h>
- using namespace std;
- const int N = 1005;
- typedef double Type;
- Type A[N][N], L[N][N], D[N][N];
- /** 分解A得到A = LDL^T */
- void Cholesky(Type A[][N], Type L[][N], Type D[][N], int n)
- {
- for(int k = 0; k < n; k++)
- {
- for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
- A[k][k] -= A[i][i] * A[k][i] * A[k][i];
- for(int j = k + 1; j < n; j++)
- {
- for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
- A[j][k] -= A[j][i] * A[i][i] * A[k][i];
- A[j][k] /= A[k][k];
- }
- }
- memset(L, 0, sizeof(L));
- memset(D, 0, sizeof(D));
- for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
- {
- D[i][i] = A[i][i];
- L[i][i] = 1;
- }
- for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
- {
- for(int j = 0; j < i; j++)
- L[i][j] = A[i][j];
- }
- }
- void Transposition(Type L[][N], int n)
- {
- for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
- {
- for(int j = 0; j < i; j++)
- swap(L[i][j], L[j][i]);
- }
- }
- void Multi(Type A[][N], Type B[][N], int n)
- {
- Type **C = new Type*[n];
- for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
- C[i] = new Type[n];
- for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
- {
- for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
- {
- C[i][j] = 0;
- for(int k = 0; k < n; k++)
- C[i][j] += A[i][k] * B[k][j];
- }
- }
- for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
- {
- for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
- B[i][j] = C[i][j];
- }
- for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
- {
- delete[] C[i];
- C[i] = NULL;
- }
- delete C;
- C = NULL;
- }
- /** 回带过程 */
- vector<Type> Solve(Type L[][N], Type D[][N], vector<Type> X, int n)
- {
- /** LY = B => Y */
- for(int k = 0; k < n; k++)
- {
- for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
- X[k] -= X[i] * L[k][i];
- X[k] /= L[k][k];
- }
- /** DL^TX = Y => X */
- Transposition(L, n);
- Multi(D, L, n);
- for(int k = n - 1; k >= 0; k--)
- {
- for(int i = k + 1; i < n; i++)
- X[k] -= X[i] * L[k][i];
- X[k] /= L[k][k];
- }
- return X;
- }
- void Print(Type L[][N], Type D[][N], const vector<Type> B, int n)
- {
- for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
- {
- for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
- cout<<L[i][j]<<" ";
- cout<<endl;
- }
- cout<<endl;
- vector<Type> X = Solve(L, D, B, n);
- vector<Type>::iterator it;
- for(it = X.begin(); it != X.end(); it++)
- cout<<*it<<" ";
- cout<<endl;
- }
- int main()
- {
- int n;
- cin>>n;
- memset(L, 0, sizeof(L));
- for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
- {
- for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
- cin>>A[i][j];
- }
- vector<Type> B;
- for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
- {
- Type y;
- cin>>y;
- B.push_back(y);
- }
- Cholesky(A, L, D, n);
- Print(L, D, B, n);
- return 0;
- }
- /**data**
- 4
- 4 -2 4 2
- -2 10 -2 -7
- 4 -2 8 4
- 2 -7 4 7
- 8 2 16 6
- */
参考资料:http://class.htu.cn/nla/cha1/sect3.htm