oracle 物化视图
Materialized View Concepts
Oracle uses materialized views (also known as snapshots in prior releases) to replicate data to non-master sites in a replication environment and to cache expensive queries in a data warehouse environment. This chapter, and this Oracle9i Replication manual in general, discusses materialized views for use in a replication environment.
Oracle 物化视图,也被称为快照,通过这种方式可以用于同步数据。
What is a Materialized View?
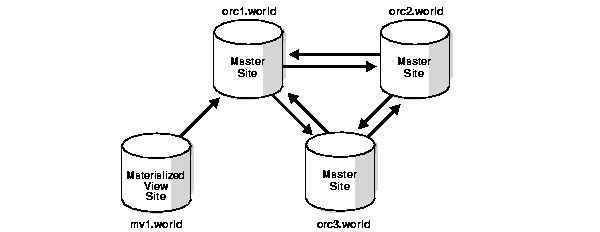
A materialized view is a replica of a target master from a single point in time. The master can be either a master table at a master site or a master materialized view at a materialized view site. Whereas in multimaster replication tables are continuously updated by other master sites, materialized views are updated from one or more masters through individual batch updates, known as a refreshes, from a single master site or master materialized view site, as illustrated in Figure 3-1. The arrows in Figure 3-1 represent database links.
Figure 3-1 Materialized View Connected to a Single Master Site
When a materialized view is fast refreshed, Oracle must examine all of the changes to the master table or master materialized view since the last refresh to see if any apply to the materialized view. Therefore, if any changes where made to the master since the last refresh, then a materialized view refresh takes some time to apply the changes to the materialized view. If, however, no changes at all were made to the master since the last refresh of a materialized view, then the materialized view refresh should be very quick.
当物化视图刷新的时候,Oracle 必须检查主表自从上次刷新以来是否有数据更新变化,如果有变化,将会花一点时间来进行同步,否则没有更新变化,视图刷新将会非常快。
Why Use Materialized Views?
You can use materialized views to achieve one or more of the following goals:
Ease Network Loads
Create a Mass Deployment Environment
Enable Data Subsetting
Enable Disconnected Computing
什么时候可以使用物化视图呢?
Ease Network Loads
If one of your goals is to reduce network loads, then you can use materialized views to distribute your corporate database to regional sites. Instead of the entire company accessing a single database server, user load is distributed across multiple database servers. Through the use of multitier materialized views, you can create materialized views based on other materialized views, which enables you to distribute user load to an even greater extent because clients can access materialized view sites instead of master sites. To decrease the amount of data that is replicated, a materialized view can be a subset of a master table or master materialized view.
设置多个主机,然后物化数据,减轻网络压力。
While multimaster replication also distributes a corporate database among multiple sites, the networking requirements for multimaster replication are greater than those for replicating with materialized views because of the transaction by transaction nature of multimaster replication. Further, the ability of multimaster replication to provide real-time or near real-time replication may result in greater network traffic, and might require a dedicated network link.
Materialized views are updated through an efficient batch process from a single master site or master materialized view site. They have lower network requirements and dependencies than multimaster replication because of the point in time nature of materialized view replication. Whereas multimaster replication requires constant communication over the network, materialized view replication requires only periodic refreshes.
In addition to not requiring a dedicated network connection, replicating data with materialized views increases data availability by providing local access to the target data. These benefits, combined with mass deployment and data subsetting (both of which also reduce network loads), greatly enhance the performance and reliability of your replicated database.
Create a Mass Deployment Environment
Deployment templates allow you to precreate a materialized view environment
locally. You can then use deployment templates to quickly and easily deploy materialized view environments to support sales force automation and other mass deployment environments. Parameters allow you to create custom data sets for individual users without changing the deployment template. This technology enables you to roll out a database infrastructure to hundreds or thousands of users.
Enable Data Subsetting
Materialized views allow you to replicate data based on column- and row-level subsetting, while multimaster replication requires replication of the entire table. Data subsetting enables you to replicate information that pertains only to a particular site. For example, if you have a regional sales office, then you might replicate only the data that is needed in that region, thereby cutting down on unnecessary network traffic.
Enable Disconnected Computing
Materialized views do not require a dedicated network connection. Though you have the option of automating the refresh process by scheduling a job, you can manually refresh your materialized view on-demand, which is an ideal solution for sales applications running on a laptop. For example, a developer can integrate the replication management API for refresh on-demand into the sales application. When the salesperson has completed the day's orders, the salesperson simply dials up the network and uses the integrated mechanism to refresh the database, thus transferring the orders to the main office.
Read-Only, Updatable, and Writeable Materialized Views
A materialized view can be either read-only, updatable, or writeable. Users cannot perform data manipulation language (DML) statements on read-only materialized views, but they can perform DML on updatable and writeable materialized views.