对象池common-pool2策略分析
上一篇:对象池common-pool2分析
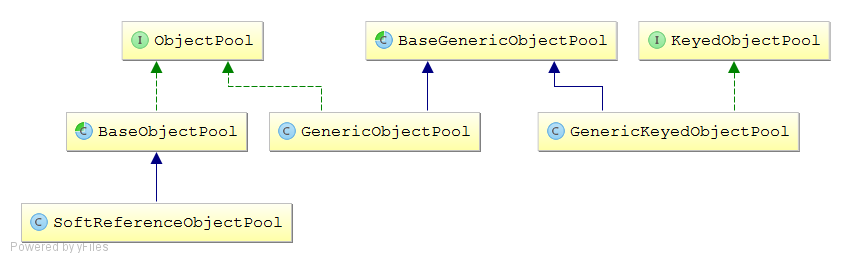
common-pool2策略
上一篇对象池common-pool2分析从三个主要的接口进行分析,这一篇将对源码进行详细的分析,力图找出对象池的管理策略.从之前的分析可以看出ObjectPool定义了对象池需要实现的功能,所以重点分析ObjectPool.
GenericObjectPool:一般对象池
GenericKeyedObjectPool:可以根据key分组的对象池
SoftReferenceObjectPool:软引用对象池.
GenericObjectPool
public GenericObjectPool(PooledObjectFactory<T> factory,
GenericObjectPoolConfig config) {
super(config, ONAME_BASE, config.getJmxNamePrefix());
if (factory == null) {
jmxUnregister(); // tidy up
throw new IllegalArgumentException("factory may not be null");
}
this.factory = factory;
//根据给定的容量和策略创建空闲对象队列,默认容量Integer.MAX_VALUE
//fairness为true时类似FIFO队列
idleObjects = new LinkedBlockingDeque<PooledObject<T>>(config.getFairness());
//设置配置信息
setConfig(config);
//根据给定延迟启动驱逐器
startEvictor(getTimeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis());
}
BaseGenericObjectPool
final void startEvictor(long delay) {
synchronized (evictionLock) {
//如果evictor已经启动则停止
if (null != evictor) {
EvictionTimer.cancel(evictor);
evictor = null;
evictionIterator = null;
}
//当delay即timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis大于0时根据给定的delay启动新的驱逐器
if (delay > 0) {
evictor = new Evictor();
EvictionTimer.schedule(evictor, delay, delay);
}
}
}
BaseGenericObjectPool内部类Evictor
class Evictor extends TimerTask {
/**
* Run pool maintenance. Evict objects qualifying for eviction and then
* ensure that the minimum number of idle instances are available.
* Since the Timer that invokes Evictors is shared for all Pools but
* pools may exist in different class loaders, the Evictor ensures that
* any actions taken are under the class loader of the factory
* associated with the pool.
*/
@Override
public void run() {
ClassLoader savedClassLoader =
Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
try {
if (factoryClassLoader != null) {
// Set the class loader for the factory
ClassLoader cl = factoryClassLoader.get();
if (cl == null) {
// The pool has been dereferenced and the class loader
// GC'd. Cancel this timer so the pool can be GC'd as
// well.
cancel();
return;
}
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(cl);
}
// Evict from the pool
try {
//调用public abstract void evict() throws Exception;此方法由子类实现.
evict();
} catch(Exception e) {
swallowException(e);
} catch(OutOfMemoryError oome) {
// Log problem but give evictor thread a chance to continue
// in case error is recoverable
oome.printStackTrace(System.err);
}
// Re-create idle instances.
try {
//确保对象池中空闲对象数大于等于设置的最小空闲对象数
ensureMinIdle();
} catch (Exception e) {
swallowException(e);
}
} finally {
// Restore the previous CCL
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(savedClassLoader);
}
}
}
GenericObjectPool的方法evict()
public void evict() throws Exception {
assertOpen();//确保连接池是打开的
if (idleObjects.size() > 0) {
PooledObject<T> underTest = null;
//获取驱逐策略
EvictionPolicy<T> evictionPolicy = getEvictionPolicy();
synchronized (evictionLock) {
//驱逐配置
EvictionConfig evictionConfig = new EvictionConfig(
getMinEvictableIdleTimeMillis(),
getSoftMinEvictableIdleTimeMillis(),
getMinIdle());
//空闲时检查
boolean testWhileIdle = getTestWhileIdle();
//getNumTests()获取检测的数量
for (int i = 0, m = getNumTests(); i < m; i++) {
if (evictionIterator == null || !evictionIterator.hasNext()) {
if (getLifo()) {//连接池是否是后进先出
//返回倒序的迭代
evictionIterator = idleObjects.descendingIterator();
} else {
evictionIterator = idleObjects.iterator();
}
}
if (!evictionIterator.hasNext()) {
// Pool exhausted, nothing to do here
return;
}
try {
//获取对象
underTest = evictionIterator.next();
} catch (NoSuchElementException nsee) {
// Object was borrowed in another thread
// Don't count this as an eviction test so reduce i;
i--;
evictionIterator = null;
continue;
}
if (!underTest.startEvictionTest()) {
// Object was borrowed in another thread
// Don't count this as an eviction test so reduce i;
i--;
continue;
}
// User provided eviction policy could throw all sorts of
// crazy exceptions. Protect against such an exception
// killing the eviction thread.
boolean evict;
try {
//检测对象池里的空闲对象是否应该被驱逐
evict = evictionPolicy.evict(evictionConfig, underTest,
idleObjects.size());
} catch (Throwable t) {
// Slightly convoluted as SwallowedExceptionListener
// uses Exception rather than Throwable
PoolUtils.checkRethrow(t);
swallowException(new Exception(t));
// Don't evict on error conditions
evict = false;
}
if (evict) {
destroy(underTest);//销毁
destroyedByEvictorCount.incrementAndGet();
} else {
if (testWhileIdle) {
boolean active = false;
try {
factory.activateObject(underTest);//激活
active = true;
} catch (Exception e) {
destroy(underTest);//激活异常则销毁
destroyedByEvictorCount.incrementAndGet();
}
if (active) {//已经激活
if (!factory.validateObject(underTest)) {//验证不通过则销毁
destroy(underTest);
destroyedByEvictorCount.incrementAndGet();
} else {
try {
factory.passivateObject(underTest);//钝化
} catch (Exception e) {
destroy(underTest);
destroyedByEvictorCount.incrementAndGet();
}
}
}
}
if (!underTest.endEvictionTest(idleObjects)) {
// TODO - May need to add code here once additional
// states are used
}
}
}
}
}
AbandonedConfig ac = this.abandonedConfig;
if (ac != null && ac.getRemoveAbandonedOnMaintenance()) {
removeAbandoned(ac);
}
}
GenericKeyedObjectPool
与GenericObjectPool类似,只是需要遍历key,根据key获取空闲对象.
SoftReferenceObjectPool
如果一个对象只具有软引用,则内存空间足够,垃圾回收器就不会回收它;如果内存空间不足了,就会回收这些对象的内存。SoftReferenceObjectPool没有后台驱逐线程,当内存不足时由虚拟机清除.