ELM
1、ELM训练函数elmtrain
function [IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE] = elmtrain(P,T,N,TF,TYPE)
% ELMTRAIN Create and Train a Extreme Learning Machine
% Syntax
% [IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE] = elmtrain(P,T,N,TF,TYPE)
% Description
% Input
% P - Input Matrix of Training Set (R*Q)
% T - Output Matrix of Training Set (S*Q)
% N - Number of Hidden Neurons (default = Q)
% TF - Transfer Function:
% 'sig' for Sigmoidal function (default)
% 'sin' for Sine function
% 'hardlim' for Hardlim function
% TYPE - Regression (0,default) or Classification (1)
% Output
% IW - Input Weight Matrix (N*R)
% B - Bias Matrix (N*1)
% LW - Layer Weight Matrix (N*S)
% Example
% Regression:
% [IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE] = elmtrain(P,T,20,'sig',0)
% Y = elmtrain(P,IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE)
% Classification
% [IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE] = elmtrain(P,T,20,'sig',1)
% Y = elmtrain(P,IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE)
if nargin < 2
error('ELM:Arguments','Not enough input arguments.');
end
if nargin < 3
N = size(P,2);
end
if nargin < 4
TF = 'sig';
end
if nargin < 5
TYPE = 0;
end
if size(P,2) ~= size(T,2)
error('ELM:Arguments','The columns of P and T must be same.');
end
[R,Q] = size(P);
if TYPE == 1
T = ind2vec(T);
end
[S,Q] = size(T);
% Randomly Generate the Input Weight Matrix
IW = rand(N,R) * 2 - 1;
% Randomly Generate the Bias Matrix
B = rand(N,1);
BiasMatrix = repmat(B,1,Q);
% Calculate the Layer Output Matrix H
tempH = IW * P + BiasMatrix;
switch TF
case 'sig'
H = 1 ./ (1 + exp(-tempH));
case 'sin'
H = sin(tempH);
case 'hardlim'
H = hardlim(tempH);
end
% Calculate the Output Weight Matrix
LW = pinv(H') * T';
2、ELM测试函数elmtrain
function Y = elmpredict(P,IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE)
% ELMPREDICT Simulate a Extreme Learning Machine
% Syntax
% Y = elmtrain(P,IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE)
% Description
% Input
% P - Input Matrix of Training Set (R*Q)
% IW - Input Weight Matrix (N*R)
% B - Bias Matrix (N*1)
% LW - Layer Weight Matrix (N*S)
% TF - Transfer Function:
% 'sig' for Sigmoidal function (default)
% 'sin' for Sine function
% 'hardlim' for Hardlim function
% TYPE - Regression (0,default) or Classification (1)
% Output
% Y - Simulate Output Matrix (S*Q)
% Example
% Regression:
% [IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE] = elmtrain(P,T,20,'sig',0)
% Y = elmtrain(P,IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE)
% Classification
% [IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE] = elmtrain(P,T,20,'sig',1)
% Y = elmtrain(P,IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE)
% See also ELMTRAIN
% Yu Lei,11-7-2010
% Copyright www.matlabsky.com
if nargin < 6
error('ELM:Arguments','Not enough input arguments.');
end
% Calculate the Layer Output Matrix H
Q = size(P,2);
BiasMatrix = repmat(B,1,Q);
tempH = IW * P + BiasMatrix;
switch TF
case 'sig'
H = 1 ./ (1 + exp(-tempH));
case 'sin'
H = sin(tempH);
case 'hardlim'
H = hardlim(tempH);
end
% Calculate the Simulate Output
Y = (H' * LW)';
if TYPE == 1
temp_Y = zeros(size(Y));
for i = 1:size(Y,2)
[~,index] = max(Y(:,i));
temp_Y(index,i) = 1;
end
Y = vec2ind(temp_Y);
end
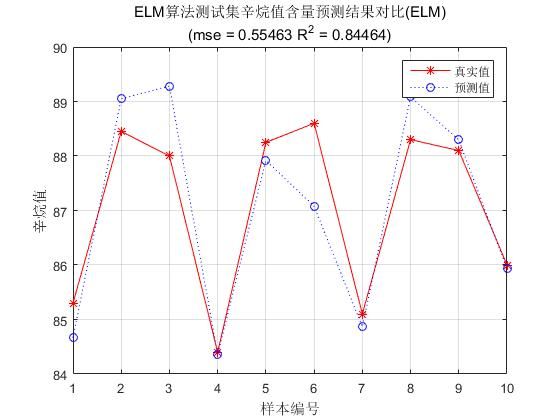
3、使用oil-dataset.mat数据集测试石油辛烷值(回归)
说明:oil_dataset.mat数据集由60个样本,401维属性组成,包含sample属性为60*401矩阵和输出label标签为60*1矩阵。
%% I. 清空环境变量
clear all
clc
%% II. 训练集/测试集产生
%%
% 1. 导入数据
load oil_dataset.mat
%%
% 2. 随机产生训练集和测试集
temp = randperm(size(sample,1));
% 训练集――50个样本
P_train = sample(temp(1:50),:)';
T_train = label(temp(1:50),:)';
% 测试集――10个样本
P_test = sample(temp(51:end),:)';
T_test = label(temp(51:end),:)';
N = size(P_test,2);
%% III. 数据归一化
%%
% 1. 训练集
[p_train,inputps] = mapminmax(P_train);
p_test = mapminmax('apply',P_test,inputps);
%%
% 2. 测试集
[t_train,outputps] = mapminmax(T_train);
t_test = mapminmax('apply',T_test,outputps);
%% IV. ELM创建/训练
[IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE] = elmtrain(p_train,t_train,30,'sig',0);
%% V. ELM仿真测试
t_sim = elmpredict(p_test,IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE);
%%
% 1. 反归一化
T_sim = mapminmax('reverse',t_sim,outputps);
%% VI. 结果对比
result = [T_test' T_sim'];
%%
% 1. 均方误差
E = mse(T_sim - T_test);
%%
% 2. 决定系数
N = length(T_test);
R2=(N*sum(T_sim.*T_test)-sum(T_sim)*sum(T_test))^2/((N*sum((T_sim).^2)-(sum(T_sim))^2)*(N*sum((T_test).^2)-(sum(T_test))^2));
%% VII. 绘图
figure(1)
plot(1:N,T_test,'r-*',1:N,T_sim,'b:o')
grid on
legend('真实值','预测值')
xlabel('样本编号')
ylabel('辛烷值')
string = {'ELM算法测试集辛烷值含量预测结果对比(ELM)';['(mse = ' num2str(E) ' R^2 = ' num2str(R2) ')']};
title(string)
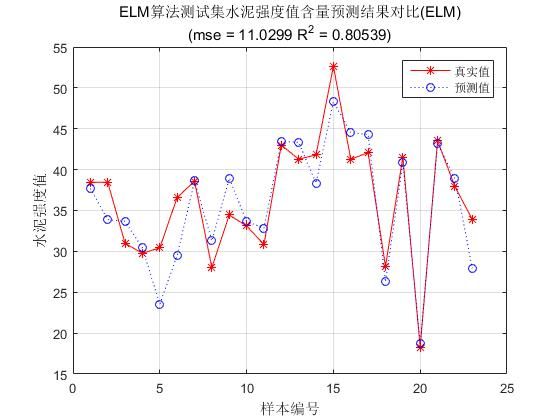
4、使用cement_dataset.mat数据集测试石油辛烷值(回归)
说明:数据集为混凝土抗压强度预测数据集cement_dataset.mat,包含103个样本,属性sample为:103*7矩阵,输出label为:103*1矩阵。
%数据集为混凝土抗压强度预测数据集cement_dataset.mat,将整个数据集中的103个样本随机划分为训练集与测试集,其中训练集包含80个样本,测试集包含23个样本;
%建立极限学习机模型,并训练;利用训练好的极限学习机模型对测试集中的23个样本进行预测;输出结果并绘图(真实值与预测值对比图)
%% I. 清空环境变量
clear all
clc
%% II. 训练集/测试集产生
%%
% 1. 导入水泥样本数据,sample由103个样本个体组成,单个样本为9维属性组成,输出值在out变量中
load cement_dataset.mat
%%
% 2. 随机产生训练集和测试集
temp = randperm(size(sample,1));
% 训练集――80个样本
P_train = sample(temp(1:80),:)';
T_train = label(temp(1:80),:)';
% 测试集――23个样本
P_test = sample(temp(81:end),:)';
T_test = label(temp(81:end),:)';
N = size(P_test,2);
%% III. 数据归一化
%%
% 1. 训练集
[p_train,inputps] = mapminmax(P_train);
p_test = mapminmax('apply',P_test,inputps);
%%
% 2. 测试集
[t_train,outputps] = mapminmax(T_train);
t_test = mapminmax('apply',T_test,outputps);
%% IV. ELM创建/训练
[IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE] = elmtrain(p_train,t_train,7,'sig',0);
%% V. ELM仿真测试
t_sim = elmpredict(p_test,IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE);
%%
% 1. 反归一化
T_sim = mapminmax('reverse',t_sim,outputps);
%% VI. 结果对比
result = [T_test' T_sim'];
%%
% 1. 均方误差
E = mse(T_sim - T_test);
%%
% 2. 决定系数
N = length(T_test);
R2=(N*sum(T_sim.*T_test)-sum(T_sim)*sum(T_test))^2/((N*sum((T_sim).^2)-(sum(T_sim))^2)*(N*sum((T_test).^2)-(sum(T_test))^2));
%% VII. 绘图
figure(1)
plot(1:N,T_test,'r-*',1:N,T_sim,'b:o')
grid on
legend('真实值','预测值')
xlabel('样本编号')
ylabel('水泥强度值')
string = {'ELM算法测试集水泥强度值含量预测结果对比(ELM)';['(mse = ' num2str(E) ' R^2 = ' num2str(R2) ')']};
title(string)
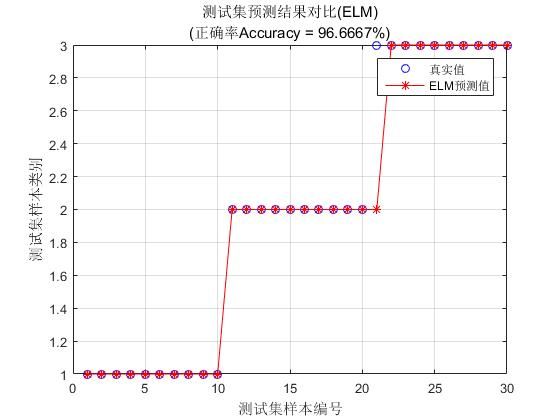
5、使用iris_dataset.mat实现分类
说明:iris以鸢尾花的特征作为数据来源,数据集包含150个数据集,分为3类,每类50个数据,每个数据包含4个属性。三类分别为:setosa, versicolor, virginica。
%% I. 清空环境变量
clear all
clc
%% II. 训练集/测试集产生
%%
% 1. 导入数据
load iris_dataset.mat
%%
% 2. 随机产生训练集和测试集
P_train = [];
T_train = [];
P_test = [];
T_test = [];
for i = 1:3
temp_input = features((i-1)*50+1:i*50,:);
temp_output = classes((i-1)*50+1:i*50,:);
n = randperm(50);
% 训练集――120个样本
P_train = [P_train temp_input(n(1:40),:)'];
T_train = [T_train temp_output(n(1:40),:)'];
% 测试集――30个样本
P_test = [P_test temp_input(n(41:50),:)'];
T_test = [T_test temp_output(n(41:50),:)'];
end
%% III. ELM创建/训练
[IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE] = elmtrain(P_train,T_train,20,'sig',1);
%% IV. ELM仿真测试
T_sim_1 = elmpredict(P_train,IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE);
T_sim_2 = elmpredict(P_test,IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE);
%% V. 结果对比
result_1 = [T_train' T_sim_1'];
result_2 = [T_test' T_sim_2'];
%%
% 1. 训练集正确率
k1 = length(find(T_train == T_sim_1));
n1 = length(T_train);
Accuracy_1 = k1 / n1 * 100;
disp(['训练集正确率Accuracy = ' num2str(Accuracy_1) '%(' num2str(k1) '/' num2str(n1) ')'])
%%
% 2. 测试集正确率
k2 = length(find(T_test == T_sim_2));
n2 = length(T_test);
Accuracy_2 = k2 / n2 * 100;
disp(['测试集正确率Accuracy = ' num2str(Accuracy_2) '%(' num2str(k2) '/' num2str(n2) ')'])
%% VI. 绘图
figure(1)
plot(1:30,T_test,'bo',1:30,T_sim_2,'r-*')
grid on
xlabel('测试集样本编号')
ylabel('测试集样本类别')
string = {'测试集预测结果对比(ELM)';['(正确率Accuracy = ' num2str(Accuracy_2) '%)' ]};
title(string)
legend('真实值','ELM预测值')
训练集正确率Accuracy = 99.1667%(119/120)
测试集正确率Accuracy = 96.6667%(29/30)
附录:官方代码(参考理解,有点�嗦)
训练函数:
function [TrainingTime,TrainingAccuracy] = elm_train(TrainingData_File, Elm_Type, NumberofHiddenNeurons, ActivationFunction)
% Usage: elm_train(TrainingData_File, Elm_Type, NumberofHiddenNeurons, ActivationFunction)
% OR: [TrainingTime, TrainingAccuracy] = elm_train(TrainingData_File, Elm_Type, NumberofHiddenNeurons, ActivationFunction)
%
% Input:
% TrainingData_File - Filename of training data set
% Elm_Type - 0 for regression; 1 for (both binary and multi-classes) classification
% NumberofHiddenNeurons - Number of hidden neurons assigned to the ELM
% ActivationFunction - Type of activation function:
% 'sig' for Sigmoidal function
% 'sin' for Sine function
% 'hardlim' for Hardlim function
%
% Output:
% TrainingTime - Time (seconds) spent on training ELM
% TrainingAccuracy - Training accuracy:
% RMSE for regression or correct classification rate for classification
%
% MULTI-CLASSE CLASSIFICATION: NUMBER OF OUTPUT NEURONS WILL BE AUTOMATICALLY SET EQUAL TO NUMBER OF CLASSES
% FOR EXAMPLE, if there are 7 classes in all, there will have 7 output
% neurons; neuron 5 has the highest output means input belongs to 5-th class
%
% Sample1 regression: [TrainingTime, TrainingAccuracy, TestingAccuracy] = elm_train('sinc_train', 0, 20, 'sig')
% Sample2 classification: elm_train('diabetes_train', 1, 20, 'sig')
%
%%%% Authors: MR QIN-YU ZHU AND DR GUANG-BIN HUANG
%%%% NANYANG TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY, SINGAPORE
%%%% EMAIL: [email protected]; [email protected]
%%%% WEBSITE: http://www.ntu.edu.sg/eee/icis/cv/egbhuang.htm
%%%% DATE: APRIL 2004
%%%%%%%%%%% Macro definition
REGRESSION=0;
CLASSIFIER=1;
%%%%%%%%%%% Load training dataset
train_data=load(TrainingData_File);
%训练集输出
T=train_data(:,1)';
%训练集输入
P=train_data(:,2:size(train_data,2))';
clear train_data; % Release raw training data array
%训练样本个数
NumberofTrainingData=size(P,2);
%输入神经元个数
NumberofInputNeurons=size(P,1);
%若是分类,进行处理,否则跳出
if Elm_Type~=REGRESSION
%统计分类类别个数,并将分类结果的不同类别值存储在label中,label中元素个数即为分类的类别数
sorted_target=sort(T,2);
label=zeros(1,1);
label(1,1)=sorted_target(1,1);
j=1;
for i = 2:NumberofTrainingData
if sorted_target(1,i) ~= label(1,j)
j=j+1;
label(1,j) = sorted_target(1,i);
end
end
number_class=j;
NumberofOutputNeurons=number_class;
%将所有训练样本单一输出值转换为矩阵输出,例如有两类输出,则神经元输出结果为[1;0]或[0;1]
temp_T=zeros(NumberofOutputNeurons, NumberofTrainingData);
for i = 1:NumberofTrainingData
for j = 1:number_class
if label(1,j) == T(1,i)
break;
end
end
temp_T(j,i)=1;
end
T=temp_T*2-1;
end
% Calculate weights & biases
start_time_train=cputime;
% Random generate input weights InputWeight (w_i) and biases BiasofHiddenNeurons (b_i) of hidden neurons
InputWeight=rand(NumberofHiddenNeurons,NumberofInputNeurons)*2-1;
BiasofHiddenNeurons=rand(NumberofHiddenNeurons,1);
tempH=InputWeight*P;
clear P; % Release input of training data
ind=ones(1,NumberofTrainingData);
BiasMatrix=BiasofHiddenNeurons(:,ind); % Extend the bias matrix BiasofHiddenNeurons to match the demention of H
tempH=tempH+BiasMatrix;
%%%%%%%%%%% Calculate hidden neuron output matrix H
switch lower(ActivationFunction)
case {'sig','sigmoid'}
%%%%%%%% Sigmoid
H = 1 ./ (1 + exp(-tempH));
case {'sin','sine'}
%%%%%%%% Sine
H = sin(tempH);
case {'hardlim'}
%%%%%%%% Hard Limit
H = hardlim(tempH);
%%%%%%%% More activation functions can be added here
end
clear tempH; % Release the temparary array for calculation of hidden neuron output matrix H
%%%%%%%%%%% Calculate output weights OutputWeight (beta_i)
OutputWeight=pinv(H') * T';
end_time_train=cputime;
TrainingTime=end_time_train-start_time_train % Calculate CPU time (seconds) spent for training ELM
%%%%%%%%%%% Calculate the training accuracy
Y=(H' * OutputWeight)'; % Y: the actual output of the training data
if Elm_Type == REGRESSION
TrainingAccuracy=sqrt(mse(T - Y)) % Calculate training accuracy (RMSE) for regression case
output=Y;
end
clear H;
if Elm_Type == CLASSIFIER
%%%%%%%%%% Calculate training & testing classification accuracy
MissClassificationRate_Training=0;
for i = 1 : size(T, 2)
[x, label_index_expected]=max(T(:,i));
[x, label_index_actual]=max(Y(:,i));
output(i)=label(label_index_actual);
if label_index_actual~=label_index_expected
MissClassificationRate_Training=MissClassificationRate_Training+1;
end
end
TrainingAccuracy=1-MissClassificationRate_Training/NumberofTrainingData
end
if Elm_Type~=REGRESSION
save('elm_model', 'NumberofInputNeurons', 'NumberofOutputNeurons', 'InputWeight', 'BiasofHiddenNeurons', 'OutputWeight', 'ActivationFunction', 'label', 'Elm_Type');
else
save('elm_model', 'InputWeight', 'BiasofHiddenNeurons', 'OutputWeight', 'ActivationFunction', 'Elm_Type');
end
测试函数:
function [TestingTime, TestingAccuracy] = elm_predict(TestingData_File)
% Usage: elm_predict(TestingData_File)
% OR: [TestingTime, TestingAccuracy] = elm_predict(TestingData_File)
%
% Input:
% TestingData_File - Filename of testing data set
%
% Output:
% TestingTime - Time (seconds) spent on predicting ALL testing data
% TestingAccuracy - Testing accuracy:
% RMSE for regression or correct classification rate for classification
%
% MULTI-CLASSE CLASSIFICATION: NUMBER OF OUTPUT NEURONS WILL BE AUTOMATICALLY SET EQUAL TO NUMBER OF CLASSES
% FOR EXAMPLE, if there are 7 classes in all, there will have 7 output
% neurons; neuron 5 has the highest output means input belongs to 5-th class
%
% Sample1 regression: [TestingTime, TestingAccuracy] = elm_predict('sinc_test')
% Sample2 classification: elm_predict('diabetes_test')
%
%%%% Authors: MR QIN-YU ZHU AND DR GUANG-BIN HUANG
%%%% NANYANG TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY, SINGAPORE
%%%% EMAIL: [email protected]; [email protected]
%%%% WEBSITE: http://www.ntu.edu.sg/eee/icis/cv/egbhuang.htm
%%%% DATE: APRIL 2004
%%%%%%%%%%% Macro definition
REGRESSION=0;
CLASSIFIER=1;
%%%%%%%%%%% Load testing dataset
test_data=load(TestingData_File);
TV.T=test_data(:,1)';
TV.P=test_data(:,2:size(test_data,2))';
clear test_data; % Release raw testing data array
NumberofTestingData=size(TV.P,2);
load elm_model.mat;
if Elm_Type~=REGRESSION
%%%%%%%%%% Processing the targets of testing
temp_TV_T=zeros(NumberofOutputNeurons, NumberofTestingData);
for i = 1:NumberofTestingData
for j = 1:size(label,2)
if label(1,j) == TV.T(1,i)
break;
end
end
temp_TV_T(j,i)=1;
end
TV.T=temp_TV_T*2-1;
end % end if of Elm_Type
%%%%%%%%%%% Calculate the output of testing input
start_time_test=cputime;
tempH_test=InputWeight*TV.P;
clear TV.P; % Release input of testing data
ind=ones(1,NumberofTestingData);
BiasMatrix=BiasofHiddenNeurons(:,ind); % Extend the bias matrix BiasofHiddenNeurons to match the demention of H
tempH_test=tempH_test + BiasMatrix;
switch lower(ActivationFunction)
case {'sig','sigmoid'}
%%%%%%%% Sigmoid
H_test = 1 ./ (1 + exp(-tempH_test));
case {'sin','sine'}
%%%%%%%% Sine
H_test = sin(tempH_test);
case {'hardlim'}
%%%%%%%% Hard Limit
H_test = hardlim(tempH_test);
%%%%%%%% More activation functions can be added here
end
TY=(H_test' * OutputWeight)'; % TY: the actual output of the testing data
end_time_test=cputime;
TestingTime=end_time_test-start_time_test % Calculate CPU time (seconds) spent by ELM predicting the whole testing data
if Elm_Type == REGRESSION
TestingAccuracy=sqrt(mse(TV.T - TY)) % Calculate testing accuracy (RMSE) for regression case
output=TY;
end
if Elm_Type == CLASSIFIER
%%%%%%%%%% Calculate training & testing classification accuracy
MissClassificationRate_Testing=0;
for i = 1 : size(TV.T, 2)
[x, label_index_expected]=max(TV.T(:,i));
[x, label_index_actual]=max(TY(:,i));
output(i)=label(label_index_actual);
if label_index_actual~=label_index_expected
MissClassificationRate_Testing=MissClassificationRate_Testing+1;
end
end
TestingAccuracy=1-MissClassificationRate_Testing/NumberofTestingData
end
save('elm_output','output');
训练和测试在一起:
function [TrainingTime, TestingTime, TrainingAccuracy, TestingAccuracy] = elm(TrainingData_File, TestingData_File, Elm_Type, NumberofHiddenNeurons, ActivationFunction)
% Usage: elm(TrainingData_File, TestingData_File, Elm_Type, NumberofHiddenNeurons, ActivationFunction)
% OR: [TrainingTime, TestingTime, TrainingAccuracy, TestingAccuracy] = elm(TrainingData_File, TestingData_File, Elm_Type, NumberofHiddenNeurons, ActivationFunction)
%
% Input:
% TrainingData_File - Filename of training data set
% TestingData_File - Filename of testing data set
% Elm_Type - 0 for regression; 1 for (both binary and multi-classes) classification
% NumberofHiddenNeurons - Number of hidden neurons assigned to the ELM
% ActivationFunction - Type of activation function:
% 'sig' for Sigmoidal function
% 'sin' for Sine function
% 'hardlim' for Hardlim function
% 'tribas' for Triangular basis function
% 'radbas' for Radial basis function (for additive type of SLFNs instead of RBF type of SLFNs)
%
% Output:
% TrainingTime - Time (seconds) spent on training ELM
% TestingTime - Time (seconds) spent on predicting ALL testing data
% TrainingAccuracy - Training accuracy:
% RMSE for regression or correct classification rate for classification
% TestingAccuracy - Testing accuracy:
% RMSE for regression or correct classification rate for classification
%
% MULTI-CLASSE CLASSIFICATION: NUMBER OF OUTPUT NEURONS WILL BE AUTOMATICALLY SET EQUAL TO NUMBER OF CLASSES
% FOR EXAMPLE, if there are 7 classes in all, there will have 7 output
% neurons; neuron 5 has the highest output means input belongs to 5-th class
%
% Sample1 regression: [TrainingTime, TestingTime, TrainingAccuracy, TestingAccuracy] = ELM('sinc_train', 'sinc_test', 0, 20, 'sig')
% Sample2 classification: elm('diabetes_train', 'diabetes_test', 1, 20, 'sig')
%
%%%% Authors: MR QIN-YU ZHU AND DR GUANG-BIN HUANG
%%%% NANYANG TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY, SINGAPORE
%%%% EMAIL: [email protected]; [email protected]
%%%% WEBSITE: http://www.ntu.edu.sg/eee/icis/cv/egbhuang.htm
%%%% DATE: APRIL 2004
%%%%%%%%%%% Macro definition
REGRESSION=0;
CLASSIFIER=1;
%%%%%%%%%%% Load training dataset
train_data=load(TrainingData_File);
%训练集输出
T=train_data(:,1)';
%训练集输入
P=train_data(:,2:size(train_data,2))';
clear train_data; % Release raw training data array
%%%%%%%%%%% Load testing dataset
test_data=load(TestingData_File);
%测试集输出
TV.T=test_data(:,1)';
%测试集输入
TV.P=test_data(:,2:size(test_data,2))';
clear test_data; % Release raw testing data array
%训练样本个数
NumberofTrainingData=size(P,2);
%测试样本个数
NumberofTestingData=size(TV.P,2);
%输入神经元个数
NumberofInputNeurons=size(P,1);
%若是分类,进行处理,否则跳出
if Elm_Type~=REGRESSION
%统计分类类别个数,并将分类结果的不同类别值存储在label中,label中元素个数即为分类的类别数
sorted_target=sort(cat(2,T,TV.T),2);
label=zeros(1,1); % Find and save in 'label' class label from training and testing data sets
label(1,1)=sorted_target(1,1);
j=1;
for i = 2:(NumberofTrainingData+NumberofTestingData)
if sorted_target(1,i) ~= label(1,j)
j=j+1;
label(1,j) = sorted_target(1,i);
end
end
number_class=j;
NumberofOutputNeurons=number_class;
%将所有训练样本单一输出值转换为矩阵输出,例如有两类输出,则神经元输出结果为[1;0]或[0;1]
temp_T=zeros(NumberofOutputNeurons, NumberofTrainingData);
for i = 1:NumberofTrainingData
for j = 1:number_class
if label(1,j) == T(1,i)
break;
end
end
temp_T(j,i)=1;
end
%将神经元输出值转换为(-1,1)之间
T=temp_T*2-1;
%T=temp_T;
%将所有测试样本单一输出值转换为矩阵输出,例如有两类输出,则神经元输出结果为[1;0]或[0;1]
temp_TV_T=zeros(NumberofOutputNeurons, NumberofTestingData);
for i = 1:NumberofTestingData
for j = 1:number_class
if label(1,j) == TV.T(1,i)
break;
end
end
temp_TV_T(j,i)=1;
end
TV.T=temp_TV_T*2-1;
%TV.T=temp_TV_T;
end
%结束分类
%Calculate weights & biases
start_time_train=cputime;
%%%%%%%%%%% Random generate input weights InputWeight (w_i) and biases BiasofHiddenNeurons (b_i) of hidden neurons
InputWeight=rand(NumberofHiddenNeurons,NumberofInputNeurons)*2-1;
BiasofHiddenNeurons=rand(NumberofHiddenNeurons,1);
tempH=InputWeight*P;
clear P; % Release input of training data
ind=ones(1,NumberofTrainingData);
BiasMatrix=BiasofHiddenNeurons(:,ind); % Extend the bias matrix BiasofHiddenNeurons to match the demention of H
tempH=tempH+BiasMatrix;
%%%%%%%%%%% Calculate hidden neuron output matrix H
switch lower(ActivationFunction)
case {'sig','sigmoid'}
%%%%%%%% Sigmoid
H = 1 ./ (1 + exp(-tempH));
case {'sin','sine'}
%%%%%%%% Sine
H = sin(tempH);
case {'hardlim'}
%%%%%%%% Hard Limit
H = double(hardlim(tempH));
case {'tribas'}
%%%%%%%% Triangular basis function
H = tribas(tempH);
case {'radbas'}
%%%%%%%% Radial basis function
H = radbas(tempH);
%%%%%%%% More activation functions can be added here
end
clear tempH; % Release the temparary array for calculation of hidden neuron output matrix H
%%%%%%%%%%% Calculate output weights OutputWeight (beta_i)
OutputWeight=pinv(H') * T'; % implementation without regularization factor //refer to 2006 Neurocomputing paper
%OutputWeight=inv(eye(size(H,1))/C+H * H') * H * T'; % faster method 1 //refer to 2012 IEEE TSMC-B paper
%implementation; one can set regularizaiton factor C properly in classification applications
%OutputWeight=(eye(size(H,1))/C+H * H') \ H * T'; % faster method 2 //refer to 2012 IEEE TSMC-B paper
%implementation; one can set regularizaiton factor C properly in classification applications
%If you use faster methods or kernel method, PLEASE CITE in your paper properly:
%Guang-Bin Huang, Hongming Zhou, Xiaojian Ding, and Rui Zhang, "Extreme Learning Machine for Regression and Multi-Class Classification," submitted to IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, October 2010.
end_time_train=cputime;
TrainingTime=end_time_train-start_time_train % Calculate CPU time (seconds) spent for training ELM
%%%%%%%%%%% Calculate the training accuracy
Y=(H' * OutputWeight)'; % Y: the actual output of the training data
if Elm_Type == REGRESSION
TrainingAccuracy=sqrt(mse(T - Y)) % Calculate training accuracy (RMSE) for regression case
end
clear H;
%%%%%%%%%%% Calculate the output of testing input
start_time_test=cputime;
tempH_test=InputWeight*TV.P;
clear TV.P; % Release input of testing data
ind=ones(1,NumberofTestingData);
BiasMatrix=BiasofHiddenNeurons(:,ind); % Extend the bias matrix BiasofHiddenNeurons to match the demention of H
tempH_test=tempH_test + BiasMatrix;
switch lower(ActivationFunction)
case {'sig','sigmoid'}
%%%%%%%% Sigmoid
H_test = 1 ./ (1 + exp(-tempH_test));
case {'sin','sine'}
%%%%%%%% Sine
H_test = sin(tempH_test);
case {'hardlim'}
%%%%%%%% Hard Limit
H_test = hardlim(tempH_test);
case {'tribas'}
%%%%%%%% Triangular basis function
H_test = tribas(tempH_test);
case {'radbas'}
%%%%%%%% Radial basis function
H_test = radbas(tempH_test);
%%%%%%%% More activation functions can be added here
end
TY=(H_test' * OutputWeight)'; % TY: the actual output of the testing data
end_time_test=cputime;
TestingTime=end_time_test-start_time_test % Calculate CPU time (seconds) spent by ELM predicting the whole testing data
if Elm_Type == REGRESSION
TestingAccuracy=sqrt(mse(TV.T - TY)) % Calculate testing accuracy (RMSE) for regression case
end
if Elm_Type == CLASSIFIER
%%%%%%%%%% Calculate training & testing classification accuracy
MissClassificationRate_Training=0;
MissClassificationRate_Testing=0;
for i = 1 : size(T, 2)
[x, label_index_expected]=max(T(:,i));
[x, label_index_actual]=max(Y(:,i));
if label_index_actual~=label_index_expected
MissClassificationRate_Training=MissClassificationRate_Training+1;
end
end
TrainingAccuracy=1-MissClassificationRate_Training/size(T,2)
for i = 1 : size(TV.T, 2)
[x, label_index_expected]=max(TV.T(:,i));
[x, label_index_actual]=max(TY(:,i));
if label_index_actual~=label_index_expected
MissClassificationRate_Testing=MissClassificationRate_Testing+1;
end
end
TestingAccuracy=1-MissClassificationRate_Testing/size(TV.T,2)
end
本文出自 “IT技术学习与交流” 博客,谢绝转载!