CentOS 7 安装Apache ServiceMix
Hi, welcome to our today's article on Apache ServiceMix. Let me give you an overview of what ServiceMix is and what you can do with it. Apache ServiceMix is a runtime container for service-oriented architecture components, web services or legacy system connectivity services. Apache ServiceMix is an enterprise-class open-source distributed enterprise service bus (ESB) based on the SOA model released under the Apache license. It is one of the most mature, open-source implementations of an enterprise service bus and an Apache top-level project. Apache ServiceMix provides an OSGi container in which we can run, configure and manage Camel and ActiveMQ instances and you can explore the other services that it can provide.
So, in the mean time, we'll be showing thine stall ServiceMix on CentOS 7 machine to deploy some basic integration routes and extend the container with some additional features.
System Requirements
Before starting the installation, we need to prepare our CentOS 7 server with some basic requirements. Atleast 200 MB of free disk space is required for the Apache, Karaf and few other binary distributions.
Let's connect to your server using the sudo or root user credentials and perform the following tasks,
OS Update
Run the command as given below to update your Operating system with latest updates and missing patches.
# yum update
Java Setup
For running Apache ServiceMix itself, you'll need Java Runtime Environment (JRE) 1.6.x (Java 6) or greater. Make sure that the JAVA_HOME environment variable must be set to the directory where the Java runtime is installed.
You check the installed version of Java and current settings of your JAVA_HOME and PATH variables using the below commands.
[root@servicemix ~]# java -version
java version "1.7.0_91"
[root@servicemix ~]# echo $JAVA_HOME
/usr/lib/jvm/jre
[root@servicemix ~]# echo $PATH
/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin
Apache Maven
Apache Maven is a software project management and comprehension tool. Based on the concept of a project object model (POM), Maven can manage a project’s build, reporting and documentation from a central piece of information. Run the below command get it install on your server before installing Apache ServiceMix.
# ]# wget http://www.eu.apache.org/dist/maven/maven-3/3.3.9/binaries/apache-maven-3.3.9-bin.tar.gz
Now extract this to the '/usr/local/' directory using the below command.
# tar -zxvf apache-maven-3.3.9-bin.tar.gz -C /usr/local/
Now change directory to '/usr/local/' folder and create a soft link with below command.
#cd /usr/local/
# ln -s apache-maven-3.3.9 maven
Now we will setup the Maven path system-wide by creating a new file and adding the parameters in as shown below.
# vim /etc/profile.d/maven.sh
export M2_HOME=/usr/local/maven
export PATH=${M2_HOME}/bin:${PATH}
After saving file you have to logout and then login back to implement environment variables. Then to verify successful installation of maven, check the version of maven by using the below command.
# mvn -version
Download Apache ServiceMix
After setting up the Java, you need to download the Apache ServiceMix by choosing the required package.
Copy the source link address and download it using the wget command in your server.
]# wget http://archive.apache.org/dist/servicemix/servicemix-4/4.5.3/apache-servicemix-4.5.3.tar.gz
Use below command to extract the package.
# tar -zxvf apache-servicemix-4.5.3.tar.gz
Installing Apache ServiceMix
Change your directory to the 'bin' directory of your extracted package and execute the the following command to start installation of ServiceMix as shown below.
[root@servicemix ~]# cd apache-servicemix-4.5.3/bin/
[root@servicemix bin]# ./servicemix
Using Apache ServiceMix Console
We have successfully installed and started Apache ServiceMix. Now we are going to show you that how you can manage your ServiceMix instance, add and remove bundles and install optional features.
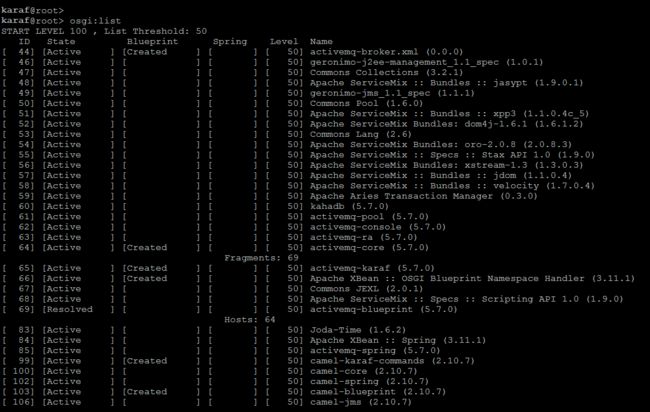
Let run the following command to get a list of all bundles currently installed on your server.
karaf@root> osgi:list
If you're looking for something specific in the list, you can use unix-like pipes and utilities to help you. Just for example run the below command to see all Apache related bundles in the list.
karaf@root> osgi:list | grep Apache
Many of the applications you write will have some form of log output. To look at the message in the log file, you can us the log:diplay command.
karaf@root> log:display
karaf@root> log:display-exception
Optional Features
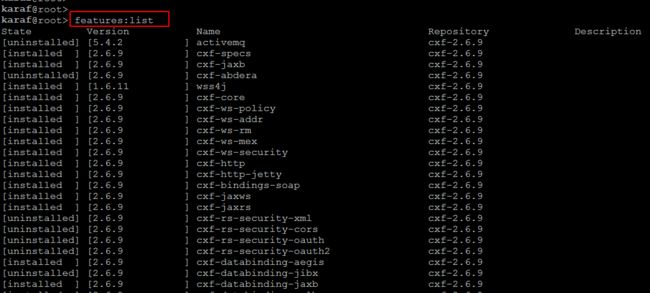
You can open the list of features using 'features:list' command. The overview shows you whether or not the feature is currently installed, the version and the name of the feature as shown below.
karaf@root> features:list
To get the web console installed in ServiceMix, install the feature from your console using the command as shown below.
karaf@root> features:install webconsole
Now verify that the feature is marked installed in the overview by executing the below command to grep the webconsole.
karaf@root> features:install webconsole
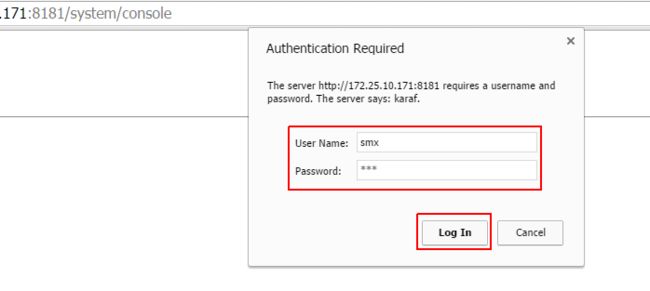
Now you will be able to point your browser to http://localhost:8181/system/console and login with user 'smx' and password 'smx' to access the web console.
From the webconsole, now you can start and stop bundles, configure settings, install optional features or view system information all from your web console as shown below.
Conclusion
At the end of this article we have learned the one of the most mature, open-source implementations of an enterprise service bus and an Apache top-level project that is Apache ServiceMix. ServiceMix for sure is not the first choice for application development, in terms of desktop software. But if you have to deal with more complex environments, where different applications are involved and need to interact with each other, an enterprise service bus can alleviate the burden of dealing with such systems to a great extent.