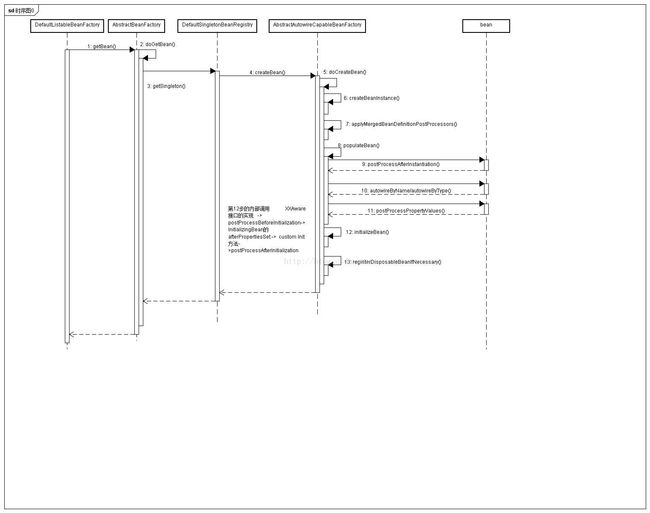
Spring BeanFacoty doCreateBean方法分析
上一篇,我们分析到了doCreateBean,现在继续:
先看看时序图
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final Object[] args) {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
//*************************5.4.1
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
final Object bean = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance() : null);
Class beanType = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass() : null);
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
//*************************5.4.2
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
//*************************5.4.3 处理循环依赖的问题
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
addSingletonFactory(beanName, new ObjectFactory() {
public Object getObject() throws BeansException {
return getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean);
}
});
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
//*************************5.4.4 将mdb中的值放到instanceWrapper中
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
if (exposedObject != null) {
//*************************5.4.5 正儿八经的初始化
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
//似乎还是循环依赖的问题
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<String>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
//*************************5.4.6 注册销毁方法
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}
在5.4.1处
首先判断是否有factory-method属性
即:
<bean id="bar" class="...StaticBarInterfaceFactory" factory-method="getInstance"/>如果有就直接通过工厂方法生产之。 参见 拙作spring中工厂方法 http://blog.csdn.net/dlf123321/article/details/47856937#t6
如果没有有默认的构造方法,且bean中包含constructor-arg
<bean id="newsBean3" class="com.luhy.spring.hello.FXNewsBean" scope="singleton"> <constructor-arg> <value>This is a configurable message</value> </constructor-arg> </bean>就调用默认的含参构造方法。
否则调用instantiateBean
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java
protected BeanWrapper instantiateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
try {
Object beanInstance;
final BeanFactory parent = this;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
beanInstance = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
public Object run() {
return getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(mbd, beanName, parent);
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
beanInstance = getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(mbd, beanName, parent);
}
BeanWrapper bw = new BeanWrapperImpl(beanInstance);
initBeanWrapper(bw);
return bw;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Instantiation of bean failed", ex);
}
}
我们在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory里可以看到
/** Strategy for creating bean instances */ private InstantiationStrategy instantiationStrategy = new CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy(); getInstantiationStrategy()返回的是InstantiationStrategy接口的实现类,默认是CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy。通过cglib生成实例对象。
至5.4.1,BeanWrapper的生成基本清晰了。
5.4.2处是允许其他修改beanDefinition,这主要是允许其他组件提供xml不能提供的信息。如使用Annotation增强Bean定义等。这通过类ergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor来完成,如果容器中提供了此类实现,则会调用进行bean增强。如CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类,会在bean定义中追加如 @Resource之类的bean property引用信息。此代码如下所示:
protected void applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(RootBeanDefinition mbd, Class beanType, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
try {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor bdp = (MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) bp;
bdp.postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing failed of bean type [" + beanType + "] failed", ex);
}
}
在5.4.4处populateBean(String beanName, AbstractBeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw)
说实话,我第一回看到这方法的时候,populate,流行的?流行的bean? 呵呵,见笑了。
在populate里面
/**
* Populate the bean instance in the given BeanWrapper with the property values
* from the bean definition.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the bean definition for the bean
* @param bw BeanWrapper with bean instance
*/
protected void populateBean(String beanName, AbstractBeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw) {
PropertyValues pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
if (bw == null) {
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for null instance.
return;
}
}
// Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the
// state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example,
// to support styles of field injection.
//*******************5.4.4.1
boolean continueWithPropertyPopulation = true;
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
continueWithPropertyPopulation = false;
break;
}
}
}
}
if (!continueWithPropertyPopulation) {
return;
}
//*******************5.4.4.2
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME ||
mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != RootBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
//*******************5.4.4.3
if (hasInstAwareBpps || needsDepCheck) {
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw);
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
pvs = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvs == null) {
return;
}
}
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
}
//*******************5.4.4.4
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}好长呀,慢慢来,这里大概可以分为4部分
首先5.4.4.1
如果所要获取的bean实现了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口,就调用其postProcessAfterInstantiation方法。
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>// Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the
// state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example,
// to support styles of field injection.
boolean continueWithPropertyPopulation = true;
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
continueWithPropertyPopulation = false;
break;
}
}
}
}
if (!continueWithPropertyPopulation) {
return;
}多说几句,postProcessAfterInstantiation的返回值是一个boolean,如果返回值是false,就说明已经属性处理已经结束了。后面的代码就不运行了。
接着5.4.4.2
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME ||
mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}不需要解释了吧,就是处理autowire标签。
再然后5.4.4.3
给InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor机会以处理属性信息,比如在xml中描述了Annotation定义,使用了<context:annotation-config/>,那么就会使用类CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor进行注解类属性注入。如下代码所示:
if (hasInstAwareBpps || needsDepCheck) {
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw);
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
pvs = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvs == null) {
return;
}
}
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
}我们看下面的解释:
最后5.4.4.4
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs)干的事情就是填充值。
这里都干了什么事情,我举个例子。
<bean id="newsBean2" class="com.luhy.spring.hello.FXNewsBean" scope="prototype">
<property name="p">
<value>dlf</value>
</property>
</bean> com.luhy.spring.hello.FXNewsBean中p这个属性是一个Person。
如何将字符串"dlf"(在xml中,所有的信息不都是字符么)转换为person呢?
我们需要下面这个类:
public class PersonEditor extends PropertyEditorSupport {
@Override
public void setAsText(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException {
Person p = new Person();
p.setName(text);
System.out.println("setAsTest");
setValue(p);
}
}那么什么时候调用这个PersonEditor呢?就在5.4.5.4的applyPropertyValues里。
当然,这里我只是举个例子。这里还包括集合类型的转换,基本类型的转换等等。
关于类型转换参见 http://blog.csdn.net/dlf123321/article/details/47905533#t3
关于5.4.5
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
public Object run() {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
//处理XXAware接口的实现
//beanFactoryAware这这个处理
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
//处理postProcessBeforeInitialization
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//在这里处理ApplicationContextAware(使用ApplicationContextAwareProcessor)
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
//这里面调用了 InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet
//同时还有init-method指定的方法
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
//postProcessAfterInitialization方法
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}总结一下初始化顺序
XXAware接口的实现->postProcessBeforeInitialization->InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet-> custom Init方法->postProcessAfterInitialization
OK.这就是bean初始化的顺序啦!
5.4.6注册销毁方法
至此,获取对象完毕。
参考资料
http://blog.csdn.net/dlf123321/article/details/47856937#t6 spring中工厂方法
http://www.iflym.com/index.php/code/201208280001.html 循环引用
http://www.iflym.com/index.php/code/201208290001.html Spring中获取一个bean的流程-1
http://michael-softtech.iteye.com/blog/816469 spring源码分析之——spring bean的获取
http://blog.csdn.net/dlf123321/article/details/47905533#t3 关于类型转换
http://blog.csdn.net/zhoudaxia/article/details/36247883#t5 关于类型转换