Hibernate联合主键映射
1.联合主键的映射规则
org.hibernate.exception.ConstraintViolationException: Could not execute JDBC batch update
3.将Student类中的两个主键属性提取为一个新的类PrimaryKey,即主键类
1) 类中的每个主键属性都对应到数据表中的每个主键列。
Hibernate要求具有联合主键的实体类实现Serializable接口,并且重写hashCode与equals方法,重写这两个方法的原因在于Hibernate要根据数据库的联合主键来判断某两行记录是否是一样的,如果一样那么就认为是同一个对象,如果不一样,那么就认为是不同的对象。这反映到程序领域中就是根据hashCode与equals方法来判断某两个对象是否能够放到诸如Set这样的集合当中。联合主键的实体类实现Serializable接口的原因在于使用get或load方法的时候需要先构建出来该实体的对象,并且将查询依据(联合主键)设置进去,然后作为get或load方法的第二个参数传进去即可。
2) 将主键所对应属性提取出一个类(称之为主键类),并且主键类需要实现Serializable接口,重写equals方法与hashCode方法,原因与上面一样。
以Student类为例,实现上述两种映射联合主键的配置:
2.Student中的两个属性作为联合主键属性
Student类:
public class Student implements Serializable {//必须要实现Serializable接口
private String cardID;//cardID和name映射为联合主键
private String name;
private int age;
//get、set、hashCode、equals方法省略
}注:可使用MyEclipse中的
Sourse-->Gennerate hashCode and equals来使用MyEclipse快速生成hashCode和equals方法
Student.hbm.xml配置:
<class name="bean.Student" table="student"> <composite-id><!--联合主键,student表中的主键为(student_name,card_id)--> <key-property name="name" column="student_name" type="string"></key-property><!--name及cardID为Student类中的属性--> <key-property name="cardID" column="card_id" type="string"></key-property> </composite-id> <property name="age" column="student_age" type="int"></property> </class>保存对象:
tx=session.beginTransaction();
Student s1=new Student();
s1.setName("lisi");
s1.setAge(22);
s1.setCardID("711");
System.out.println(s1);
session.save(s1);
tx.commit();注意:主键为(card_id,student_id)若连续执行上述的保存语句两次,当然会抛异常,应为主键重复:
org.hibernate.exception.ConstraintViolationException: Could not execute JDBC batch update
3.将Student类中的两个主键属性提取为一个新的类PrimaryKey,即主键类
主键类PrimaryKey:
public class PrimaryKey implements Serializable{
private String cardID;
private String name;
//get、set、hashCode、equals方法省略
}Student类中含有PrimaryKey类型的属性及对应set、get方法:
public class Student {
private int age;
private PrimaryKey primaryKey;
//set、get方法省略
}Student.hbm.xml文件中的配置:
<class name="bean.Student" table="student"> <composite-id name="primaryKey" class="bean.PrimaryKey"><!--PrimaryKey为我们自定义的主键类--> <key-property name="name" column="student_name" type="string"></key-property><!--name及cardID为PrimaryKey类中的属性--> <key-property name="cardID" column="card_id" type="string"></key-property> </composite-id> <property name="age" column="student_age" type="int"></property> </class>保存对象:
tx=session.beginTransaction();
Student s1=new Student();
s1.setAge(23);
PrimaryKey p=new PrimaryKey();
p.setCardID("102");
p.setName("zhangsan");
s1.setPrimaryKey(p);
session.save(s1);
tx.commit();
同样,对于上述代码的重复执行也会导致主键重复抛出异常。
查询:
PrimaryKey p=new PrimaryKey();
p.setCardID("711");
p.setName("lisi");
Student s=(Student)session.get(Student.class,p);//所以PrimaryKey要实现Serializable接口
System.out.println(s.getAge());
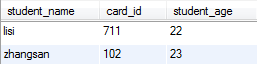
4.对于以上两种映射联合主键的方式,反映到数据库中的表的结构是相同的,student表的内容为:
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/jialinqiang/article/details/8704538