4.Realm(数据处理,交互)
上一章我们讲完了CacheManager,我们这一章讲的是Realm.
Realm是一个Security组件,它主要职责是通过各种手段(JDBC、hibernate、FILE IO..)从数据库(关系数据库、NOSQL、文件..)中访问应用程序的用户的验证信息(账户密码),授权信息(资源路径)。然后根据这些信息来操作用户的登陆验证操作,和访问资源文件的授权操作。
一般不直接实现该接口,而是继承他的子类之一。如:AuthenticatingRealm(登陆验证数据操作)、AuthorizingRealm(授权数据操作)
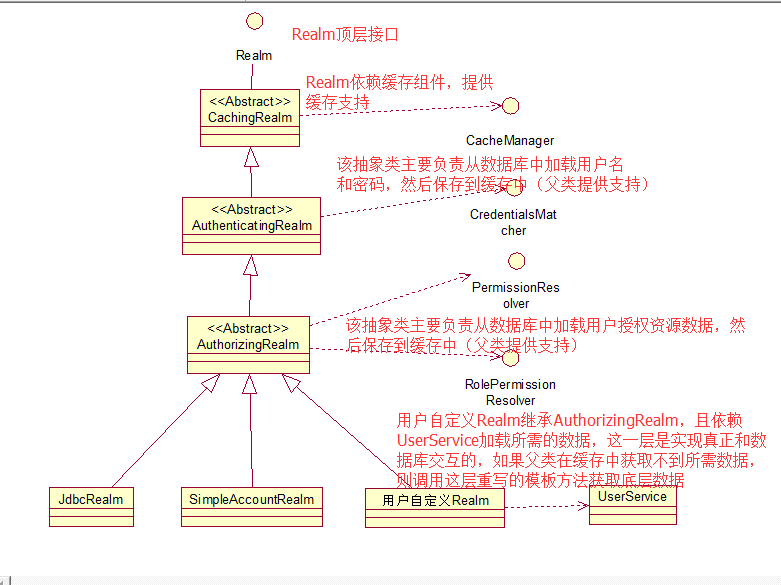
1.Realm
//Realm接口
public interface Realm {
//Realm在应用内唯一的名字
String getName();
//判断当前Realm是否支持该AuthenticationToken,如果支持则true,否则false.如果为false,则不会继续往下执行登录验证
boolean supports(AuthenticationToken token);
//根据token(用户名,密码)信息从底层数据库中获取相对应的用户信息,如果底层数据库不存在该用户的信息,则返回null,
AuthenticationInfo getAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException;
}2.CachingRealm
//CachingRealm CacheManagerAware,和Realm,是Realm接口最底层的抽象实现,主要为其子类提供CacheManager支持
public abstract class CachingRealm implements Realm, Nameable, CacheManagerAware, LogoutAware {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CachingRealm.class);
//如果实例化了多个realm,那么则用这个来做为Realm的CacheManager里面的Cache的名字的计数.防止多个Realm使用同一个缓存Cache
private static final AtomicInteger INSTANCE_COUNT = new AtomicInteger();
private String name;
private boolean cachingEnabled;
private CacheManager cacheManager;
public CachingRealm() {
this.cachingEnabled = true;
//获取类名 + INSTANCE_COUNT 的计数作为缓存名字
this.name = getClass().getName() + "_" + INSTANCE_COUNT.getAndIncrement();
}
public CacheManager getCacheManager() {
return this.cacheManager;
}
//设置cacheManager,减少直接与底层数据库交互次数来提升性能。默认cacheManager为null
public void setCacheManager(CacheManager cacheManager) {
this.cacheManager = cacheManager;
afterCacheManagerSet();
}
//是否启用缓存设置,默认为true。如果你的底层数据库都是基于内存操作的(所有的用户信息,授权信息都保存在内存中了),那么可以设置为false,因为直接操作内存是很快的。
public boolean isCachingEnabled() {
return cachingEnabled;
}
public void setCachingEnabled(boolean cachingEnabled) {
this.cachingEnabled = cachingEnabled;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
//Template method应该被子类实现。对SetCacheManager做后置处理
protected void afterCacheManagerSet() {
}
//该方法会清掉关于该用户的缓存,如果子类想重写这个方法,得保证首先调用父类的该方法.
public void onLogout(PrincipalCollection principals) {
clearCache(principals);
}
//根据PrincipalCollection 清理相对应的用户的缓存信息
protected void clearCache(PrincipalCollection principals) {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(principals)) {
doClearCache(principals);
log.trace("Cleared cache entries for account with principals [{}]", principals);
}
}
//子类重写该方法,执行真正的缓存删除操作
protected void doClearCache(PrincipalCollection principals) {
}
//根据Realm名从PrincipalCollection中获取该Realm的Principal,如果为空的话,则获取PrimaryPrincipal()
protected Object getAvailablePrincipal(PrincipalCollection principals) {
Object primary = null;
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(principals)) {
Collection thisPrincipals = principals.fromRealm(getName());
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(thisPrincipals)) {
primary = thisPrincipals.iterator().next();
} else {
//no principals attributed to this particular realm. Fall back to the 'master' primary:
primary = principals.getPrimaryPrincipal();
}
}
return primary;
}
}3.AuthenticatingRealm
/** Authentication Caching 如果你的应用架构是基于 REST 或者 Soap的,那么你每次请求过来都需要进行身份验证,这时,可以启用AuthenticationInfo的缓存机制。避免频繁的和底层数据库进行交互。 考虑到兼容性问题(shiro1.1及更早版本),默认不启用该功能.你可以根据setAuthenticationCachingEnabled=true来启用该功能。 如果你启用缓存功能,考虑到安全性问题,返回的AuthenticationInfo的credentials应该是加密的。 Authentication Cache Invalidation on Logout 如果authentication缓存是启用的,则在用户执行退出时候,会删除之前缓存的该用户的authentication data。 为了保证authentication data能在用户执行退出时候成功删除,getAuthenticationCacheKey(org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken)和getAuthenticationCacheKey(org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection)的返回值应该是一样的才对。否则,authentication data只能交由底层的cacheManager的实现来管理删除(根据某种策略,如:timeToIdle or timeToLive (TTL)) **/
public abstract class AuthenticatingRealm extends CachingRealm implements Initializable {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AuthenticatingRealm.class);
//区分多个Realm实例,不共用同一个缓存key(也就是不共用同一个缓存)
private static final AtomicInteger INSTANCE_COUNT = new AtomicInteger();
//realm缓存名字的后缀
private static final String DEFAULT_AUTHORIZATION_CACHE_SUFFIX = ".authenticationCache";
//密码匹配器,用来匹配用户的输入的密码(经过加密后)和数据库里的密码进行匹配
private CredentialsMatcher credentialsMatcher;
//authenticationInfo的缓存池,由cacheManager管理
private Cache<Object, AuthenticationInfo> authenticationCache;
//是否启用缓存
private boolean authenticationCachingEnabled;
//authenticationInfo缓存名字
private String authenticationCacheName;
//用来判断当前Realm是否支持该AuthenticationToken
private Class<? extends AuthenticationToken> authenticationTokenClass;
public AuthenticatingRealm() {
this(null, new SimpleCredentialsMatcher());
}
public AuthenticatingRealm(CacheManager cacheManager) {
this(cacheManager, new SimpleCredentialsMatcher());
}
public AuthenticatingRealm(CredentialsMatcher matcher) {
this(null, matcher);
}
public AuthenticatingRealm(CacheManager cacheManager, CredentialsMatcher matcher) {
authenticationTokenClass = UsernamePasswordToken.class;
//默认不启用缓存,考虑向后兼容性
this.authenticationCachingEnabled = false;
int instanceNumber = INSTANCE_COUNT.getAndIncrement();
//组合authenticationCacheName
this.authenticationCacheName = getClass().getName() + DEFAULT_AUTHORIZATION_CACHE_SUFFIX;
if (instanceNumber > 0) {
//区分多个Realm实例,不共用同一个缓存key(也就是不共用同一个缓存)
this.authenticationCacheName = this.authenticationCacheName + "." + instanceNumber;
}
if (cacheManager != null) {
setCacheManager(cacheManager);
}
if (matcher != null) {
setCredentialsMatcher(matcher);
}
}
//获取当前的密码验证器
public CredentialsMatcher getCredentialsMatcher() {
return credentialsMatcher;
}
//设置密码验证器,默认是SimpleCredentialsMatcher
public void setCredentialsMatcher(CredentialsMatcher credentialsMatcher) {
this.credentialsMatcher = credentialsMatcher;
}
//获取当前Realm所支持的AuthenticationToken。默认的值是UsernamePasswordToken,因为90%的Realms使用的是username/password authentication,不管是什么协议 (jdbc,ldap,http..)
public Class getAuthenticationTokenClass() {
return authenticationTokenClass;
}
public void setAuthenticationTokenClass(Class<? extends AuthenticationToken> authenticationTokenClass) {
this.authenticationTokenClass = authenticationTokenClass;
}
//设置Authentication的Cache缓存池,如果没有设置过,且isAuthenticationCachingEnabled=true,则可以从cacheManager中获取当前Realm实例的缓存池
public void setAuthenticationCache(Cache<Object, AuthenticationInfo> authenticationCache) {
this.authenticationCache = authenticationCache;
}
//获取当前Realm实例的缓存池
public Cache<Object, AuthenticationInfo> getAuthenticationCache() {
return this.authenticationCache;
}
//获取AuthenticationCacheName,然后根据该名字从cacheManager中查找Cache
public String getAuthenticationCacheName() {
return this.authenticationCacheName;
}
public void setAuthenticationCacheName(String authenticationCacheName) {
this.authenticationCacheName = authenticationCacheName;
}
//判断当前Realm的缓存是否开启
public boolean isAuthenticationCachingEnabled() {
return this.authenticationCachingEnabled && isCachingEnabled();
}
//设置当前Realm支持缓存。同时设置CacheRealm的CachingEnabled=true
@SuppressWarnings({"UnusedDeclaration"})
public void setAuthenticationCachingEnabled(boolean authenticationCachingEnabled) {
this.authenticationCachingEnabled = authenticationCachingEnabled;
if (authenticationCachingEnabled) {
setCachingEnabled(true);
}
}
//设置当前Realm实例在应用内的唯一名字
public void setName(String name) {
super.setName(name);
String authcCacheName = this.authenticationCacheName;
//这能设置名字一次,后面再设置名字就不会成功了(这样做的目的有可能是在spring配置了修改后有意义的缓存名字后,防止用户再次修改缓存名,否则会使得过去使用该缓存名的cache缓存失效,不再有Realm指引调用)
if (authcCacheName != null && authcCacheName.startsWith(getClass().getName())) {
//get rid of the default heuristically-created cache name. Create a more meaningful one
//based on the application-unique Realm name:
this.authenticationCacheName = name + DEFAULT_AUTHORIZATION_CACHE_SUFFIX;
}
}
/*-------------------------------------------- | M E T H O D S | ============================================*/
//判断当前Relam是否支持该token(比较token和该Realm设置的AuthenticationToken)
public boolean supports(AuthenticationToken token) {
return token != null && getAuthenticationTokenClass().isAssignableFrom(token.getClass());
}
//根据配置来初始化AuthenticationCache
public final void init() {
//trigger obtaining the authorization cache if possible
getAvailableAuthenticationCache();
onInit();
}
//子类重写该模板方法,该方法被init()调用
protected void onInit() {
}
//设置了CacheManager之后,马上调用getAvailableAuthenticationCache来初始化当前Realm的Authentication缓存
protected void afterCacheManagerSet() {
//trigger obtaining the authorization cache if possible
getAvailableAuthenticationCache();
}
//获取一个有效的Authentication缓存池,如果缓存池为null且当前开启Authentication缓存池,则初始化Authentication缓存池
private Cache<Object, AuthenticationInfo> getAvailableAuthenticationCache() {
Cache<Object, AuthenticationInfo> cache = getAuthenticationCache();
boolean authcCachingEnabled = isAuthenticationCachingEnabled();
if (cache == null && authcCachingEnabled) {
cache = getAuthenticationCacheLazy();
}
return cache;
}
//延迟初始化Authentication的缓存池,如果该缓存池为null
private Cache<Object, AuthenticationInfo> getAuthenticationCacheLazy() {
if (this.authenticationCache == null) {
log.trace("No authenticationCache instance set. Checking for a cacheManager...");
CacheManager cacheManager = getCacheManager();
if (cacheManager != null) {
String cacheName = getAuthenticationCacheName();
log.debug("CacheManager [{}] configured. Building authentication cache '{}'", cacheManager, cacheName);
this.authenticationCache = cacheManager.getCache(cacheName);
}
}
return this.authenticationCache;
}
//从AuthenticationInfo缓存池中根据AuthenticationToken的principle key取出相对应的缓存
private AuthenticationInfo getCachedAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) {
AuthenticationInfo info = null;
Cache<Object, AuthenticationInfo> cache = getAvailableAuthenticationCache();
if (cache != null && token != null) {
log.trace("Attempting to retrieve the AuthenticationInfo from cache.");
Object key = getAuthenticationCacheKey(token);
info = cache.get(key);
if (info == null) {
log.trace("No AuthorizationInfo found in cache for key [{}]", key);
} else {
log.trace("Found cached AuthorizationInfo for key [{}]", key);
}
}
return info;
}
//如果AuthenticationInfo缓存池启用且缓存池Cache不为null,则存AuthenticationInfo到缓存池
private void cacheAuthenticationInfoIfPossible(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info) {
//判断AuthenticationInfo缓存池是否启用
if (!isAuthenticationCachingEnabled(token, info)) {
log.debug("AuthenticationInfo caching is disabled for info [{}]. Submitted token: [{}].", info, token);
//return quietly, caching is disabled for this token/info pair:
return;
}
Cache<Object, AuthenticationInfo> cache = getAvailableAuthenticationCache();
if (cache != null) {
//根据token获取AuthenticationCache的key
Object key = getAuthenticationCacheKey(token);
cache.put(key, info);
log.trace("Cached AuthenticationInfo for continued authentication. key=[{}], value=[{}].", key, info);
}
}
//判断AuthenticationInfo缓存池是否启用
protected boolean isAuthenticationCachingEnabled(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info) {
return isAuthenticationCachingEnabled();
}
//根据token获取AuthenticationInfo
public final AuthenticationInfo getAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
//首先根据token从缓存池里获取,减少和底层数据库交互
AuthenticationInfo info = getCachedAuthenticationInfo(token);
if (info == null) {
//如果缓存池不存在该AuthenticationInfo则从底层数据库中加载该AuthenticationInfo
info = doGetAuthenticationInfo(token);
log.debug("Looked up AuthenticationInfo [{}] from doGetAuthenticationInfo", info);
if (token != null && info != null) {
//把从数据库中加载的AuthenticationInfo存入到缓存池中,便于下次使用
cacheAuthenticationInfoIfPossible(token, info);
}
} else {
log.debug("Using cached authentication info [{}] to perform credentials matching.", info);
}
if (info != null) {
//先判断用户输入的密码和底层数据库的密码是否匹配
assertCredentialsMatch(token, info);
} else {
log.debug("No AuthenticationInfo found for submitted AuthenticationToken [{}]. Returning null.", token);
}
return info;
}
protected void assertCredentialsMatch(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info) throws AuthenticationException {
//获取密码匹配器
CredentialsMatcher cm = getCredentialsMatcher();
if (cm != null) {
//根据密码匹配器匹配用户输入的密码和底层数据库的密码
if (!cm.doCredentialsMatch(token, info)) {
//not successful - throw an exception to indicate this:
//如果匹配失败,则抛出用户密码不正确
String msg = "Submitted credentials for token [" + token + "] did not match the expected credentials.";
throw new IncorrectCredentialsException(msg);
}
} else {
throw new AuthenticationException("A CredentialsMatcher must be configured in order to verify " +
"credentials during authentication. If you do not wish for credentials to be examined, you " +
"can configure an " + AllowAllCredentialsMatcher.class.getName() + " instance.");
}
}
//根据AuthenticationToken获取AuthenticationInfo的Key
protected Object getAuthenticationCacheKey(AuthenticationToken token) {
//默认为AuthenticationToken的Principal
return token != null ? token.getPrincipal() : null;
}
//获取当前Realm的Principle,这个方法主要用在获取key,然后从缓存池中删除,所以这里得保证获取到的key是和getAuthenticationCacheKey(AuthenticationToken token)获取到的key是一致的
protected Object getAuthenticationCacheKey(PrincipalCollection principals) {
return getAvailablePrincipal(principals);
}
//重写增强父类的doClearCache,首先调用父类的doClearCache()
@Override
protected void doClearCache(PrincipalCollection principals) {
super.doClearCache(principals);
clearCachedAuthenticationInfo(principals);
}
//该方法的提供便于用户在修改密码时候,能够删除旧的缓存。以免继续使用旧的验证缓存
protected void clearCachedAuthenticationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(principals)) {
//获取AuthenticationInfo缓存池
Cache<Object, AuthenticationInfo> cache = getAvailableAuthenticationCache();
//cache instance will be non-null if caching is enabled:
if (cache != null) {
//根据PrincipalCollection获取缓存key
Object key = getAuthenticationCacheKey(principals);
//从缓存池中根据key移除该缓存
cache.remove(key);
}
}
}
//从底层数据库中根据token获取相对应的AuthenticationInfo
protected abstract AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException;
}4.AuthorzaingRealm
//该抽象类主要实现Authorizer接口的方法,为子类提供授权功能.如果你不需要该功能.
//可以直接继承AuthenticatingRealm且实现未实现的方法和添加自己需要的功能。
public abstract class AuthorizingRealm extends AuthenticatingRealm implements Authorizer, Initializable, PermissionResolverAware, RolePermissionResolverAware {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AuthorizingRealm.class);
//默认的AuthorizayionInfo缓存后缀名
private static final String DEFAULT_AUTHORIZATION_CACHE_SUFFIX = ".authorizationCache";
//区分多个Realm实例的缓存名,防止共用一个缓存池
private static final AtomicInteger INSTANCE_COUNT = new AtomicInteger();
//AuthorizayionInfo缓存是否开启
private boolean authorizationCachingEnabled;
//AuthorizayionInfo缓存池
private Cache<Object, AuthorizationInfo> authorizationCache;
//AuthorizayionInfo缓存名
private String authorizationCacheName;
//转换String资源值为Permission(是安全框架一个细粒度的基础组件,代表用户的一个操作行为或者访问的一个资源路径)值
private PermissionResolver permissionResolver;
//转换Role为一组Perimission,方便于细粒度验证
//默认没有提供实现,需要自己实现,因为这是和底层数据库进行交互的,没有其他操作。而和底层数据库交互,不同的应用表名列名也不相同
//所以留待用户自己实现(简单来讲,即根据角色名从底层数据库中加载一组字符串资源,然后转换成Permission)
private RolePermissionResolver permissionRoleResolver;
/*------------------------------------------- | C O N S T R U C T O R S | ============================================*/
public AuthorizingRealm() {
this(null, null);
}
public AuthorizingRealm(CacheManager cacheManager) {
this(cacheManager, null);
}
public AuthorizingRealm(CredentialsMatcher matcher) {
this(null, matcher);
}
public AuthorizingRealm(CacheManager cacheManager, CredentialsMatcher matcher) {
super();
if (cacheManager != null) setCacheManager(cacheManager);
if (matcher != null) setCredentialsMatcher(matcher);
//默认开启authorizationInfo缓存
this.authorizationCachingEnabled = true;
//默认的PermissionResolver转换器
this.permissionResolver = new WildcardPermissionResolver();
int instanceNumber = INSTANCE_COUNT.getAndIncrement();
//拼接authorizationInfo缓存池key
this.authorizationCacheName = getClass().getName() + DEFAULT_AUTHORIZATION_CACHE_SUFFIX;
if (instanceNumber > 0) {
this.authorizationCacheName = this.authorizationCacheName + "." + instanceNumber;
}
}
/*------------------------------------------- | A C C E S S O R S / M O D I F I E R S | ============================================*/
//设置Relam名字,首先调用父类的.setName(name)方法,只能设置一次()。
public void setName(String name) {
super.setName(name);
String authzCacheName = this.authorizationCacheName;
if (authzCacheName != null && authzCacheName.startsWith(getClass().getName())) {
//get rid of the default class-name based cache name. Create a more meaningful one
//based on the application-unique Realm name:
this.authorizationCacheName = name + DEFAULT_AUTHORIZATION_CACHE_SUFFIX;
}
}
public void setAuthorizationCache(Cache<Object, AuthorizationInfo> authorizationCache) {
this.authorizationCache = authorizationCache;
}
public Cache<Object, AuthorizationInfo> getAuthorizationCache() {
return this.authorizationCache;
}
public String getAuthorizationCacheName() {
return authorizationCacheName;
}
@SuppressWarnings({"UnusedDeclaration"})
public void setAuthorizationCacheName(String authorizationCacheName) {
this.authorizationCacheName = authorizationCacheName;
}
//判断AuthorizationInfo是否启用缓存
public boolean isAuthorizationCachingEnabled() {
//判断CachingRealm是否启用Cache功能和当前authorizationCaching是否启用
return isCachingEnabled() && authorizationCachingEnabled;
}
//设置AuthorizationInfo缓存功能是否启用
@SuppressWarnings({"UnusedDeclaration"})
public void setAuthorizationCachingEnabled(boolean authenticationCachingEnabled) {
this.authorizationCachingEnabled = authenticationCachingEnabled;
if (authenticationCachingEnabled) {
//如果AuthorizationInfo缓存功能启用,则顺带设置CachingRealm的缓存功能启用
setCachingEnabled(true);
}
}
public PermissionResolver getPermissionResolver() {
return permissionResolver;
}
public void setPermissionResolver(PermissionResolver permissionResolver) {
if (permissionResolver == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Null PermissionResolver is not allowed");
this.permissionResolver = permissionResolver;
}
public RolePermissionResolver getRolePermissionResolver() {
return permissionRoleResolver;
}
public void setRolePermissionResolver(RolePermissionResolver permissionRoleResolver) {
this.permissionRoleResolver = permissionRoleResolver;
}
/*-------------------------------------------- | M E T H O D S | ============================================*/
protected void onInit() {
super.onInit();
//如果可能的话,初始化AuthorzaionInfo缓存池
getAvailableAuthorizationCache();
}
//设置了cacheManager之后,如果可能的话,初始化AuthorzaionInfo缓存池
protected void afterCacheManagerSet() {
super.afterCacheManagerSet();
//trigger obtaining the authorization cache if possible
getAvailableAuthorizationCache();
}
//延迟初始化AuthorzaionInfo缓存池
private Cache<Object, AuthorizationInfo> getAuthorizationCacheLazy() {
if (this.authorizationCache == null) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("No authorizationCache instance set. Checking for a cacheManager...");
}
CacheManager cacheManager = getCacheManager();
if (cacheManager != null) {
String cacheName = getAuthorizationCacheName();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("CacheManager [" + cacheManager + "] has been configured. Building " +
"authorization cache named [" + cacheName + "]");
}
//调用cacheManager根据当前的AuthorzaionInfo缓存池的key名,获取相对应的Cache,然后关联到this.authorizationCache
this.authorizationCache = cacheManager.getCache(cacheName);
} else {
if (log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info("No cache or cacheManager properties have been set. Authorization cache cannot " +
"be obtained.");
}
}
}
return this.authorizationCache;
}
//获取有效的AuthorzaionInfo缓存池,如果不存在,且可能的话,则初始化AuthorzaionInfo缓存池
private Cache<Object, AuthorizationInfo> getAvailableAuthorizationCache() {
Cache<Object, AuthorizationInfo> cache = getAuthorizationCache();
if (cache == null && isAuthorizationCachingEnabled()) {
cache = getAuthorizationCacheLazy();
}
return cache;
}
//获取AuthorizationInfo(存储用户的权限资源相关的信息,资源、角色..)
protected AuthorizationInfo getAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
if (principals == null) {
return null;
}
AuthorizationInfo info = null;
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("Retrieving AuthorizationInfo for principals [" + principals + "]");
}
Cache<Object, AuthorizationInfo> cache = getAvailableAuthorizationCache();
//如果cache不为null则从cache中加载指定用户的AuthorizationInfo
if (cache != null) {
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("Attempting to retrieve the AuthorizationInfo from cache.");
}
//获取指定用户的缓存池中的key
Object key = getAuthorizationCacheKey(principals);
//从缓存池中获取相对应的AuthorizationInfo
info = cache.get(key);
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
if (info == null) {
log.trace("No AuthorizationInfo found in cache for principals [" + principals + "]");
} else {
log.trace("AuthorizationInfo found in cache for principals [" + principals + "]");
}
}
}
//如果缓存池中不存在指定用户的缓存的AuthorizationInfo,则从底层数据库中加载
if (info == null) {
//根据principals从底层数据库加载AuthorizationInfo
info = doGetAuthorizationInfo(principals);
// If the info is not null and the cache has been created, then cache the authorization info.
if (info != null && cache != null) {
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("Caching authorization info for principals: [" + principals + "].");
}
Object key = getAuthorizationCacheKey(principals);
//在返回AuthorizationInfo前,先把它存入到缓存中,方便下次使用
cache.put(key, info);
}
}
return info;
}
protected Object getAuthorizationCacheKey(PrincipalCollection principals) {
return principals;
}
//清除缓存AuthorizationInfo,该方法便于用户动态的修改用户的授权资源后,然后清除旧的缓存的授权资源
//防止用户继续使用旧的授权资源
protected void clearCachedAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
if (principals == null) {
return;
}
Cache<Object, AuthorizationInfo> cache = getAvailableAuthorizationCache();
//cache instance will be non-null if caching is enabled:
if (cache != null) {
Object key = getAuthorizationCacheKey(principals);
cache.remove(key);
}
}
//从底层数据库中加载AuthorizationInfo
protected abstract AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals);
//组合用户权限资源的string和permission为统一的Permission,且返回
protected Collection<Permission> getPermissions(AuthorizationInfo info) {
Set<Permission> permissions = new HashSet<Permission>();
if (info != null) {
//先获取Permission格式的
Collection<Permission> perms = info.getObjectPermissions();
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(perms)) {
permissions.addAll(perms);
}
//转换String格式的资源为Permission格式的资源集合
perms = resolvePermissions(info.getStringPermissions());
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(perms)) {
permissions.addAll(perms);
}
//转换角色为一组Permission集合
perms = resolveRolePermissions(info.getRoles());
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(perms)) {
permissions.addAll(perms);
}
}
if (permissions.isEmpty()) {
//shiro源码中大量运用了Colletions的空的集合,应该是减少不必要的内存浪费
return Collections.emptySet();
} else {
return Collections.unmodifiableSet(permissions);
}
}
//迭代String格式的资源,且转换为Permission格式的资源,然后返回
private Collection<Permission> resolvePermissions(Collection<String> stringPerms) {
Collection<Permission> perms = Collections.emptySet();
PermissionResolver resolver = getPermissionResolver();
if (resolver != null && !CollectionUtils.isEmpty(stringPerms)) {
perms = new LinkedHashSet<Permission>(stringPerms.size());
for (String strPermission : stringPerms) {
Permission permission = getPermissionResolver().resolvePermission(strPermission);
perms.add(permission);
}
}
return perms;
}
//转换一组角色为一组Permission资源
private Collection<Permission> resolveRolePermissions(Collection<String> roleNames) {
Collection<Permission> perms = Collections.emptySet();
RolePermissionResolver resolver = getRolePermissionResolver();
if (resolver != null && !CollectionUtils.isEmpty(roleNames)) {
perms = new LinkedHashSet<Permission>(roleNames.size());
//迭代角色名
for (String roleName : roleNames) {
//根据角色名从RolePermissionResolver中返回一组相对应的Permission集合
Collection<Permission> resolved = resolver.resolvePermissionsInRole(roleName);
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(resolved)) {
perms.addAll(resolved);
}
}
}
return perms;
}
//String格式的授权判断,传入字符串Permission和当前用户PrincipalCollection
public boolean isPermitted(PrincipalCollection principals, String permission) {
//转换String格式的资源为Permission对象格式的
Permission p = getPermissionResolver().resolvePermission(permission);
return isPermitted(principals, p);
}
public boolean isPermitted(PrincipalCollection principals, Permission permission) {
//根据PrincipalCollection获取相对应的用户的AuthorizationInfo
AuthorizationInfo info = getAuthorizationInfo(principals);
return isPermitted(permission, info);
}
protected boolean isPermitted(Permission permission, AuthorizationInfo info) {
//获取AuthorizationInfo里的所有Permission格式的资源集合
Collection<Permission> perms = getPermissions(info);
if (perms != null && !perms.isEmpty()) {
//迭代判断该用户的所有Permission格式的资源集合,然后进行匹配,如果匹配上直接返回true,否则false
//我觉得其实这里如果用户的权限资源过多,且用户量大的时候,对系统性能有很很大影响。
//如果是根据特定的约定,如:user:create user为用户模块,则只查找user模块的资源文件,或者更细粒度点
for (Permission perm : perms) {
if (perm.implies(permission)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
//判断一组String格式资源文件,且返回一组boolean[]
public boolean[] isPermitted(PrincipalCollection subjectIdentifier, String... permissions) {
List<Permission> perms = new ArrayList<Permission>(permissions.length);
for (String permString : permissions) {
perms.add(getPermissionResolver().resolvePermission(permString));
}
return isPermitted(subjectIdentifier, perms);
}
//判断一组Permission格式资源文件,且返回一组boolean[]
public boolean[] isPermitted(PrincipalCollection principals, List<Permission> permissions) {
AuthorizationInfo info = getAuthorizationInfo(principals);
return isPermitted(permissions, info);
}
protected boolean[] isPermitted(List<Permission> permissions, AuthorizationInfo info) {
boolean[] result;
if (permissions != null && !permissions.isEmpty()) {
int size = permissions.size();
result = new boolean[size];
int i = 0;
for (Permission p : permissions) {
result[i++] = isPermitted(p, info);
}
} else {
result = new boolean[0];
}
return result;
}
//判断一组String格式的资源,如果全部为都授权成功则true,否则false
public boolean isPermittedAll(PrincipalCollection subjectIdentifier, String... permissions) {
if (permissions != null && permissions.length > 0) {
Collection<Permission> perms = new ArrayList<Permission>(permissions.length);
for (String permString : permissions) {
perms.add(getPermissionResolver().resolvePermission(permString));
}
return isPermittedAll(subjectIdentifier, perms);
}
return false;
}
//判断一组Permission实例格式的资源,如果全部为都授权成功则true,否则false
public boolean isPermittedAll(PrincipalCollection principal, Collection<Permission> permissions) {
AuthorizationInfo info = getAuthorizationInfo(principal);
return info != null && isPermittedAll(permissions, info);
}
protected boolean isPermittedAll(Collection<Permission> permissions, AuthorizationInfo info) {
if (permissions != null && !permissions.isEmpty()) {
for (Permission p : permissions) {
if (!isPermitted(p, info)) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
/** 下面的check和上面的is差不多,区别只是一个返回true or false,一个授权失败直接抛异常UnauthorizedException **/
public void checkPermission(PrincipalCollection subjectIdentifier, String permission) throws AuthorizationException {
Permission p = getPermissionResolver().resolvePermission(permission);
checkPermission(subjectIdentifier, p);
}
public void checkPermission(PrincipalCollection principal, Permission permission) throws AuthorizationException {
AuthorizationInfo info = getAuthorizationInfo(principal);
checkPermission(permission, info);
}
protected void checkPermission(Permission permission, AuthorizationInfo info) {
if (!isPermitted(permission, info)) {
String msg = "User is not permitted [" + permission + "]";
throw new UnauthorizedException(msg);
}
}
public void checkPermissions(PrincipalCollection subjectIdentifier, String... permissions) throws AuthorizationException {
if (permissions != null) {
for (String permString : permissions) {
checkPermission(subjectIdentifier, permString);
}
}
}
public void checkPermissions(PrincipalCollection principal, Collection<Permission> permissions) throws AuthorizationException {
AuthorizationInfo info = getAuthorizationInfo(principal);
checkPermissions(permissions, info);
}
protected void checkPermissions(Collection<Permission> permissions, AuthorizationInfo info) {
if (permissions != null && !permissions.isEmpty()) {
for (Permission p : permissions) {
checkPermission(p, info);
}
}
}
//判断用户是否有该角色roleIdentifier
public boolean hasRole(PrincipalCollection principal, String roleIdentifier) {
AuthorizationInfo info = getAuthorizationInfo(principal);
return hasRole(roleIdentifier, info);
}
protected boolean hasRole(String roleIdentifier, AuthorizationInfo info) {
return info != null && info.getRoles() != null && info.getRoles().contains(roleIdentifier);
}
public boolean[] hasRoles(PrincipalCollection principal, List<String> roleIdentifiers) {
AuthorizationInfo info = getAuthorizationInfo(principal);
boolean[] result = new boolean[roleIdentifiers != null ? roleIdentifiers.size() : 0];
if (info != null) {
result = hasRoles(roleIdentifiers, info);
}
return result;
}
protected boolean[] hasRoles(List<String> roleIdentifiers, AuthorizationInfo info) {
boolean[] result;
if (roleIdentifiers != null && !roleIdentifiers.isEmpty()) {
int size = roleIdentifiers.size();
result = new boolean[size];
int i = 0;
for (String roleName : roleIdentifiers) {
result[i++] = hasRole(roleName, info);
}
} else {
result = new boolean[0];
}
return result;
}
public boolean hasAllRoles(PrincipalCollection principal, Collection<String> roleIdentifiers) {
AuthorizationInfo info = getAuthorizationInfo(principal);
return info != null && hasAllRoles(roleIdentifiers, info);
}
private boolean hasAllRoles(Collection<String> roleIdentifiers, AuthorizationInfo info) {
if (roleIdentifiers != null && !roleIdentifiers.isEmpty()) {
for (String roleName : roleIdentifiers) {
if (!hasRole(roleName, info)) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
public void checkRole(PrincipalCollection principal, String role) throws AuthorizationException {
AuthorizationInfo info = getAuthorizationInfo(principal);
checkRole(role, info);
}
protected void checkRole(String role, AuthorizationInfo info) {
if (!hasRole(role, info)) {
String msg = "User does not have role [" + role + "]";
throw new UnauthorizedException(msg);
}
}
public void checkRoles(PrincipalCollection principal, Collection<String> roles) throws AuthorizationException {
AuthorizationInfo info = getAuthorizationInfo(principal);
checkRoles(roles, info);
}
public void checkRoles(PrincipalCollection principal, String... roles) throws AuthorizationException {
checkRoles(principal, Arrays.asList(roles));
}
protected void checkRoles(Collection<String> roles, AuthorizationInfo info) {
if (roles != null && !roles.isEmpty()) {
for (String roleName : roles) {
checkRole(roleName, info);
}
}
}
//重写增强父类的doClearCache方法
@Override
protected void doClearCache(PrincipalCollection principals) {
//首先调用父类AuthenticatingRealm的doClaerCache方法,删除AuhtenticationInfo缓存
super.doClearCache(principals);
//再调用clearCachedAuthorizationInfo方法删除AuthorizationInfo缓存
clearCachedAuthorizationInfo(principals);
}
}后面的几个Realm简单讲下就好了,我觉得不是什么重点
5.SimpleAccountRealm
SimpleAccountRealm可以理解为个小数据库,里面存放了从shiro从Ini或者Properties中加载的用户数据(用户名、密码、角色、资源)
6.TextConfigurationRealm
TextConfigurationRealm继承SimpleAccountRealm,该类主要提供用户的账户密码 和 角色资源的字符串的分隔规则,
提供公共的方法(特定规则分隔字符串,然后把分隔后得到的数据存入到父类SimpleAccountRealm的相对应的
users Map或roles map中)让子类继承使用.
7.IniRealm
IniRealm继承TextConfigurationRealm,该类主要是从Ini中获得属于[users]和[roles]的字符串数据,然后传给父类TextConfigurationRealm,
父类TextConfigurationRealm对字符串按规则进行切分,然后存入到父类SimpleAccountRealm的相对应的users Map或roles map中)
让子类继承使用.
8.PropertiesRealm
PropertiesRealm继承TextConfigurationRealm,如果加载文件的类型是 “file:” 则该类提供了动态修改Propertis配置文件,
默认每10秒检查一次是否配置已修改,如果是则重新加载.该类主要是从propertis中获得属于”user.”和”role.”的字符串数据,
然后把他们拼接为特定格式(和ini的string一样的格式),然后传给父类TextConfigurationRealm。同上.
还有几个Relam实现,我也不是很懂
AbstractLdapRealm和JndiLdapRealm,不过归根到底都是从Realm加载所需得数据