双向BFS初步——c++代码分析
我们从广为人知的POJ 2243这道题谈起:题目大意:给定一个起点和一个终点,按骑士的走法(走日字),从起点到终点的最少移动多少次
先看代码:加了注释,然后解释:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
struct knight
{
int x,y,step;
};
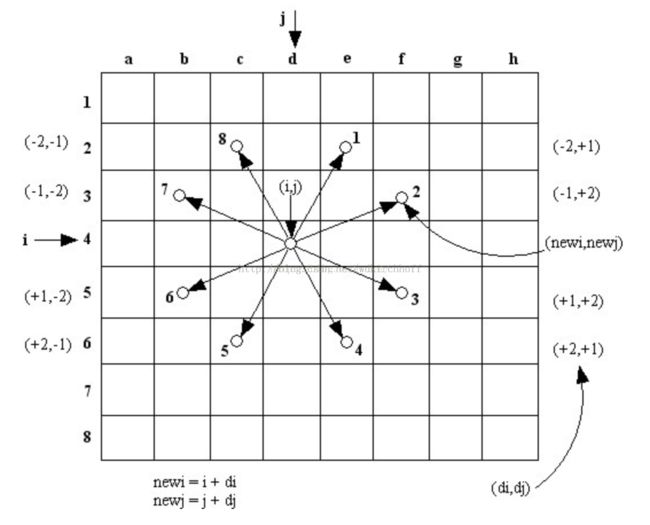
int dir[8][2]={{-2,-1},{-2,1},{2,-1},{2,1},{-1,-2},{-1,2},{1,-2},{1,2}};
int sx, sy, ex, ey;
int visit[8][8];
int color[8][8];
int bfs();
int main()
{
int x1, x2;
char y1, y2;
while(scanf("%c%d %c%d", &y1, &x1, &y2, &x2) != EOF)
{
getchar();
sx = x1 - 1;
sy = y1 - 'a';
ex = x2 - 1;
ey = y2 - 'a';
memset(visit, -1, sizeof(visit));
memset(color, 0, sizeof(color));
int cost = bfs();
printf("To get from %c%d to %c%d takes %d knight moves.\n", y1, x1, y2, x2, cost);
}
return 0;
}
int bfs()
{
if(sx == ex && sy == ey)
return 0;
queue<knight> que_front;//创建队列
queue<knight> que_back;
knight front, back;//结构体
front.x = sx; front.y = sy; front.step = 0;//赋初值
back.x = ex; back.y = ey; back.step = 1;
que_front.push(front);//进队列
que_back.push(back);//进队列
visit[sx][sy] = 0;
visit[ex][ey] = 1;
//由这两个来区分这两个队列
color[sx][sy] = 1;
color[ex][ey] = 2;
int ans1 = 0, ans2 = 0;
while(!que_front.empty() || !que_back.empty())//当两个队列都为空时退出
{
if(!que_front.empty())//队列不空
{
front = que_front.front();//结构体赋值
que_front.pop();//出队列
for(int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
int dx = front.x + dir[i][0];
int dy = front.y + dir[i][1];
if(dx >= 0 && dx < 8 && dy >= 0 && dy < 8 && color[dx][dy] != 1)//判断是否被队列1走过
{
if(color[dx][dy] == 0)
{
knight tmp;//建立新结构体,并赋值
tmp.x = dx; tmp.y = dy;
tmp.step = front.step + 1;
visit[dx][dy] = tmp.step;//记录相应步数
color[dx][dy] = 1;//赋队列1的标记值
que_front.push(tmp);//进队列
}
else //即不等于1也不等于0 则肯定是等于2,所以两个相交
return front.step + visit[dx][dy];
}
}
}
if(!que_back.empty())//第二个和第一个同理
{
back = que_back.front();
que_back.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
int dx = back.x + dir[i][0];
int dy = back.y + dir[i][1];
if(dx >= 0 && dx < 8 && dy >= 0 && dy < 8 && color[dx][dy] != 2)
{
if(color[dx][dy] == 0)
{
knight tmp;
tmp.x = dx; tmp.y = dy;
tmp.step = back.step + 1;
visit[dx][dy] = tmp.step;
color[dx][dy] = 2;
que_back.push(tmp);
}
else
return back.step + visit[dx][dy];
}
}
}
}
return -1;//没有路径相通,则返回-1
}
分析:其实其和BFS并没有多大差别,只是它用了两个队列,而其核心部分为1和2的标记,利用标记来判断其是否相交,所有color数组为其能够双向的核心部分,其次visit数组用来记录步数,也是其相连的关键!
综上:要格外注意visit[]和color[]这两个数组,,这是其核心!!!