layoutinflater详解
layoutinflater
ListView的Adapter的getView方法中基本都会出现,使用inflate方法去加载一个布局,用于ListView的每个Item的布局,但是这三个方法究竟有什么用,还是不是很清楚。
convertView = mInflater.inflate(R.layout.item, null);
convertView = mInflater.inflate(R.layout.item, parent ,false);
convertView = mInflater.inflate(R.layout.item, parent ,true);
于是就动手实践一下
在ListView里面实践一下
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
ViewHolder holder = null;
if (convertView == null) {
holder = new ViewHolder();
// 不能正确的处理长宽高
// convertView = layoutInflater.inflate(R.layout.item, null);
// 能够正常的处理长宽高
convertView = layoutInflater.inflate(R.layout.item, parent, false);
// convertView = layoutInflater.inflate(R.layout.item, parent, true);
holder.mBtn = (Button) convertView.findViewById(R.id.id_btn);
convertView.setTag(holder);
} else {
holder = (ViewHolder) convertView.getTag();
}
holder.mBtn.setText(mData.get(position));
return convertView;
}
Item的代码
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<Button xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/id_btn"
android:layout_width="120dp"
android:layout_height="120dp">
先尝试第一个
convertView = mInflater.inflate(R.layout.item, null);
然后第二个
convertView = mInflater.inflate(R.layout.item, parent ,false);
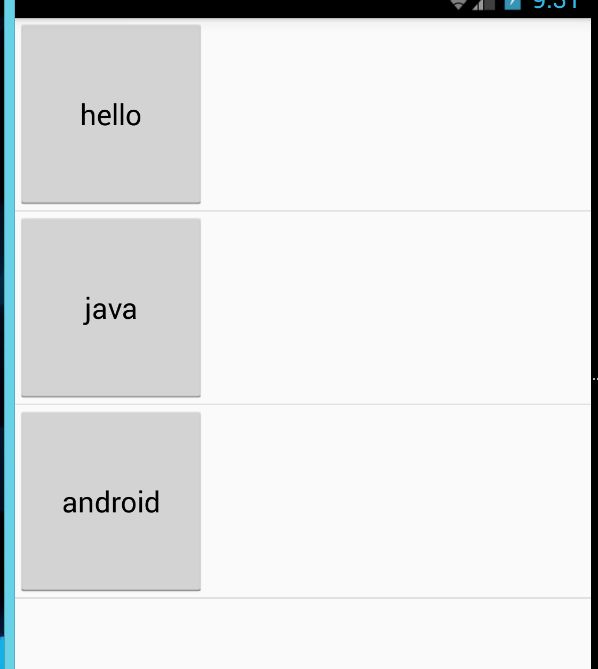
效果图
可以看出这些按钮都有了具体的长宽高 不同于上面没有具体的边距
最后尝试第三个
convertView = mInflater.inflate(R.layout.item, parent ,true);
到这里我就不明白了 于是我看了一下看了一下别人的博客然后推荐我看一下源代码
这里面是源代码
public View inflate(XmlPullParser parser, @Nullable ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot) {
synchronized (mConstructorArgs) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "inflate");
final Context inflaterContext = mContext;
final AttributeSet attrs = Xml.asAttributeSet(parser);
Context lastContext = (Context) mConstructorArgs[0];
mConstructorArgs[0] = inflaterContext;
View result = root;
try {
// Look for the root node.
int type;
while ((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.START_TAG &&
type != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) {
// Empty
}
if (type != XmlPullParser.START_TAG) {
throw new InflateException(parser.getPositionDescription()
+ ": No start tag found!");
}
final String name = parser.getName();
if (DEBUG) {
System.out.println("**************************");
System.out.println("Creating root view: "
+ name);
System.out.println("**************************");
}
if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name)) {
if (root == null || !attachToRoot) {
throw new InflateException("<merge /> can be used only with a valid "
+ "ViewGroup root and attachToRoot=true");
}
rInflate(parser, root, inflaterContext, attrs, false);
} else {
// Temp is the root view that was found in the xml
final View temp = createViewFromTag(root, name, inflaterContext, attrs);
ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = null;
if (root != null) {
if (DEBUG) {
System.out.println("Creating params from root: " +
root);
}
// Create layout params that match root, if supplied
params = root.generateLayoutParams(attrs);
if (!attachToRoot) {
// Set the layout params for temp if we are not
// attaching. (If we are, we use addView, below)
temp.setLayoutParams(params);
}
}
if (DEBUG) {
System.out.println("-----> start inflating children");
}
// Inflate all children under temp against its context.
rInflateChildren(parser, temp, attrs, true);
if (DEBUG) {
System.out.println("-----> done inflating children");
}
// We are supposed to attach all the views we found (int temp)
// to root. Do that now.
if (root != null && attachToRoot) {
root.addView(temp, params);
}
// Decide whether to return the root that was passed in or the
// top view found in xml.
if (root == null || !attachToRoot) {
result = temp;
}
}
} catch (XmlPullParserException e) {
InflateException ex = new InflateException(e.getMessage());
ex.initCause(e);
throw ex;
} catch (Exception e) {
InflateException ex = new InflateException(
parser.getPositionDescription()
+ ": " + e.getMessage());
ex.initCause(e);
throw ex;
} finally {
// Don't retain static reference on context.
mConstructorArgs[0] = lastContext;
mConstructorArgs[1] = null;
}
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
return result;
}
}
看到 View result = root; 把root的地址指向给view 最后 return result;可以看出最后返回的是result了
看一下第二个参数的判断
if (root == null || !attachToRoot) {
throw new InflateException("<merge /> can be used only with a valid "
+ "ViewGroup root and attachToRoot=true");
}
可以看出root==null 和 第三个参数为false 抛出异常
if (root != null) {
if (DEBUG) {
System.out.println("Creating params from root: " +
root);
}
// Create layout params that match root, if supplied
params = root.generateLayoutParams(attrs);
if (!attachToRoot) {
// Set the layout params for temp if we are not
// attaching. (If we are, we use addView, below)
temp.setLayoutParams(params);
}
}
这里是获取父类的信息
final View temp = createViewFromTag(root, name, inflaterContext, attrs);
root不为null的时候, params = root.generateLayoutParams(attrs);获取父组件的LayoutParams,会把父布局的setLayoutParams设置给唤醒的子类。相对父级设置这就是为什么按钮可以按照参数来设置长宽高.
接下来看一下第三个参数
if (root != null && attachToRoot) {
root.addView(temp, params);
}
// Decide whether to return the root that was passed in or the
// top view found in xml.
if (root == null || !attachToRoot) {
result = temp;
}
从代码中看出attachToRoot为true时可以往父组件上增加View 之后。如果root为null,或者attachToRoot为false则,将temp赋值给result。
最后返回result。
Inflate(resId , null ) 只创建temp ,返回temp
Inflate(resId , parent, false )创建temp,然后执行temp.setLayoutParams(params);返回temp
Inflate(resId , parent, true ) 创建temp,然后执行root.addView(temp, params);最后返回root
错误的原因:
@Override
public void addView(View child) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("addView(View) is not supported in AdapterView");
}
之后我们实践一下在没有在listview的情况下实践这三个方法
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private ListView mListView;
private MyAdapter myAdapter;
private List<String> mDatas = Arrays.asList("hello","java","android");
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// setContentView(R.layout.test_layout);
// mListView = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.listview);
// myAdapter = new MyAdapter(this,mDatas);
// mListView.setAdapter(myAdapter);
View view1 = LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.item,null);
View view2 = LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.item,(ViewGroup)findViewById(android.R.id.content),false);
View view3 = LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.item,(ViewGroup)findViewById(android.R.id.content),true);
Log.e("TAG", "view1 = " + view1 + " , view1.layoutParams = " + view1.getLayoutParams());
Log.e("TAG", "view2 = " + view2 +" , view2.layoutParams = " + view2.getLayoutParams());
Log.e("TAG", "view3 = " + view3 );
}
实践的结果
参考的博客: http://blog.csdn.net/lmj623565791/article/details/38171465