SparkSQL(二)
SparkSQL可以处理多种类型的数据,本文就简单的以Parquet、Json、Relation Database为主线介绍下SparkSQL的处理过程。
1.Parquet format
Parquet是一种柱状的数据存储结构,特别针对大数据的存储和处理。Parquet有两个优势:一是数据加载量小,如有100行记录但仅取10行,在基于行的存储中需要加载100行记录,但在Parquet中,只需加载10行;二是由于每一列的数据类型相同,所以压缩就更高效。下面用例子来进行说明,如有以下数据:
基于行的存储如下:
![]()
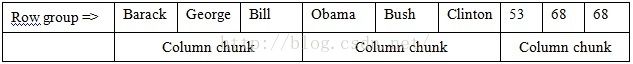
在Parquet中,柱状分布如下:
- Row group:显示数据在行的水平分区,Row group包含了Column chunk。
- Column chunk:在一个Row group中,每一个Column chunk的数据对应一个指定的列。每一个Column chunk物理上都是连续的。一个Row group中每列只有一个Column chunk。
- Page:Column chunk被分为Page。Page是存储单元不能再分。Page是被写回到Column chunk中的。Page的数据可以被压缩。
import org.apache.spark.{SparkContext, SparkConf}
import org.apache.spark.sql.SQLContext
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2015/10/17.
*/
object Parquet {
case class Person(firstName: String, lastName: String, age: Int)
def main (args: Array[String]): Unit ={
if(args.length != 2){
System.err.println("Usage: <data path> <parquet file>")
System.exit(1)
}
val conf = new SparkConf()
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
//Loaded with sqlContext(which is the instance of HiveContext not SQLContext)
val sqlContext = new SQLContext(sc)
import sqlContext.implicits._
val data = sc.textFile(args(0))
val personRDD = data.map(_.split(",")).map(person => Person(person(0), person(1), person(2).toInt))
//Convert the personRDD into the personDF DataFrame
val personDF = personRDD.toDF()
//Register the personDF as a table
personDF.registerTempTable("person")
//Run a SQL query against it
val people = sqlContext.sql("SELECT * FROM person")
// people.collect().foreach(println)
/************************************************Do Parquet*************************************************/
/**
* Save this people RDD in the Parquet format
* If you are using Spark 1.3.x, you should write like
* people.saveAsParquetFile("/spark/sql/people.parquet").
* And the result save in people.parquet directory
*/
people.write.parquet(args(1))
/**
* Load contents of the Parquet files.
* If you are using Spark 1.3.x, you should write like
* val personParquetDF = sqlContext.load("/spark/sql/people.parquet")
*/
val personParquetDF = sqlContext.read.parquet(args(1))
//Register the loaded parquet DF as a temp table
personParquetDF.registerTempTable("person")
//Run a SQL query against it
val peopleParquet = sqlContext.sql("SELECT * FROM person WHERE age < 30")
peopleParquet.collect().foreach(println)
sc.stop()
}
}
2.JSON format
SON的全称是JavaScript Object Notation,是一种轻量级的数据交换格式。 JSON与 XML具有相同的特性,例如易于人编写和阅读,易于机器生成和解析。但是 JSON比XML数据传输的有效性要高出很多。 JSON完全独立与编程语言,使用文本格式保存。
SON数据有两种结构:
- Name-Value 对构成的集合,类似于 Java中的 Map。
- Value的有序列表,类似于 Java中的 Array。
import org.apache.spark.{SparkContext, SparkConf}
import org.apache.spark.sql.SQLContext
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2015/10/17.
*/
object Json {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit ={
if(args.length != 1){
System.err.println("Usage: <data path>")
System.exit(1)
}
val conf = new SparkConf()
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
//Loaded with sqlContext(which is the instance of HiveContext not SQLContext)
val sqlContext = new SQLContext(sc)
/*
* Load contents of the Parquet files.
* If you are using Spark 1.3.x, you should write like
* val personParquetDF = sqlContext.jsonFile("/spark/sql/people.json")
*/
val personJsonDF = sqlContext.read.json(args(0))
//Register the loaded json DF as a temp table
personJsonDF.registerTempTable("person")
//Run a SQL query against it
val peopleParquet = sqlContext.sql("SELECT * FROM person WHERE age < 30")
peopleParquet.collect().foreach(println)
/**
* Save this people RDD in the Parquet format
* If you are using Spark 1.3.x, you should write like
* personJsonDF.toJSON.saveAsTextFile("/spark/sql/peopleresult.json").
* And the result save in peopleresult.json directory.
*/
// personJsonDF.write.json("/spark/sql/peopleresult.json")
sc.stop()
}
}
3.Relation Database
关于关系型数据库就不多说了,不过,个人不怎么习惯SparkSQL这种关系型数据库操作的方式。
import org.apache.spark.{SparkContext, SparkConf}
import org.apache.spark.sql.SQLContext
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2015/10/17.
*/
object RelationDB {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit ={
val conf = new SparkConf()
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
//Loaded with sqlContext(which is the instance of HiveContext not SQLContext)
val sqlContext = new SQLContext(sc)
//Construct a JDBC URL
val url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test"
//Create a connection properties object with username and password
val prop = new java.util.Properties
prop.setProperty("user","root")
prop.setProperty("password","admin")
//Load DataFrame with JDBC data source (url, table name, properties)
val people = sqlContext.read.jdbc(url,"person",prop)
//Show the results in a nice tabular format by executing the following command
people.show()
/**
* This has loaded the whole table. What if I only would like to load males (url, table
* name, predicates, properties)? To do this, run the following command
*/
val males = sqlContext.read.jdbc(url, "person", Array("gender = 'M'"), prop)
males.show()
//Show only first names by executing the following command
val first_names = people.select("first_name")
first_names.show()
//Show only people below age 60 by executing the following command
val below60 = people.filter(people("age") < 60)
below60.show()
//Group people by gender as follows
val grouped = people.groupBy("gender")
//Find the number of males and females by executing the following command
val gender_count = grouped.count()
gender_count.show()
//Find the average age of males and females by executing the following command
val avg_age = grouped.avg("age")
avg_age.show()
// Now if you'd like to save this avg_age data to a new table, run the following command
gender_count.write.jdbc(url,"gender_count",prop)
sc.stop()
}
}
4.其他数据源
其实,SparkSQL的DataFrames还可以加载或保存其他格式的源数据。操作和上面的方法差不多。
//Load the data from Parquet; since parquet is the default data source, you do not have to specify it
val people = sqlContext.read.load("/spark/sql/people.parquet")
//Load the data from Parquet by manually specifying the format
val peopleParquet_1 = sqlContext.read.format("org.apache.spark.sql.parquet").load("/spark/sql/people.parquet")
/**
* For inbuilt datatypes (parquet,json, and jdbc), you do not have to specify the full
* format name, only specifying "parquet", "json", or "jdbc" works
*/
val peopleParquet_2 = sqlContext.read.format("parquet").load("/spark/sql/people.parquet")
//Save people as JSON in the append mode
val peopleJson = people.write.format("parquet").mode("append").save("/spark/sql/people.json")