Spring 4 MVC HelloWorld 纯注解方式(带源码)【超赞】
【本系列其他教程正在陆续翻译中,点击分类:spring 4 mvc 进行查看】
【翻译 by 明明如月 QQ 605283073】
#项目下载地址:http://websystique.com/?smd_process_download=1&download_id=1722#。
上一篇:Spring 4 MVC hello world 教程-完全基于XML(带项目源码)
下一篇:
Spring 4 MVC 表单校验资源处理(带源码)
在上一个例子:Spring 4 MVC hello world 教程-完全基于XML(带项目源码) 中,
我们采用了纯xml方式演示了spring 4 mvc的hello world 教程。然而xml不是配置spring的唯一方式。
我们同样也可以采用纯注解的方式。
如果你回看一下上一篇文章你就会发现,主要有两个地方采用了xml方式。
第一:spring-servlet.xml 定义了view-resolver 来转到真是的视图,
通过component-scanning(组件扫描)来定位bean。
第二:web.xml 我们定义了 前置处理器和url pattern。
本教程,我们也是创建hello world例子,但是这次是基于java 注解。
我们将不再使用xml文件,起而代之的是java 对应的注解。
------------------------------------------------
所用的技术或者软件
- Spring 4.0.6.RELEASE
- Maven 3
- JDK 1.6
- Tomcat 8.0.21
- Eclipse JUNO Service Release 2
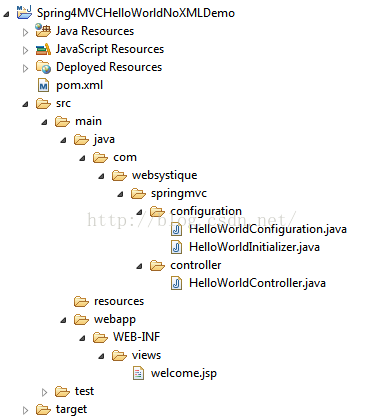
第1步:创建项目目录结构
第2步: 修改pom.xml添加Spring 和Servlet 依赖
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<project xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"
xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.websystique.springmvc</groupId>
<artifactId>Spring4MVCHelloWorldNoXMLDemo</artifactId>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<version>1.0.0</version>
<name>Spring4MVCHelloWorldNoXMLDemo</name>
<properties>
<springframework.version>4.0.6.RELEASE</springframework.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet.jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>2.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<pluginManagement>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.6</source>
<target>1.6</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.4</version>
<configuration>
<warSourceDirectory>src/main/webapp</warSourceDirectory>
<warName>Spring4MVCHelloWorldNoXMLDemo</warName>
<failOnMissingWebXml>false</failOnMissingWebXml>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</pluginManagement>
<finalName>Spring4MVCHelloWorldNoXMLDemo</finalName>
</build>
</project>
首先要注意的是 maven-war-plugin 的声明.
因为我们想完
第二个变化是,添加了JSP/Servlet/Jstl依赖,因为我们在视图代码里面将会用到servlet api和jstl表达式。
一般来说,容器已经包含了这些库,你可以在pom.xml文件中设置它们的scope为provided 。
另外, maven-compiler-plugin已经在这里明确指定了jdk的版本。
注意:上面的配置也指明了eclipse使用的jdk版本。如果没有上面的配置而且你在eclipse里执行了mvn-update,eclipse 将切换到jdk默认的版本( 1.5)。
第3步:添加控制器(Controller)
com.websystique.springmvc.controller.HelloWorldController
package com.websystique.springmvc.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.ModelMap;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/")
public class HelloWorldController {
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String sayHello(ModelMap model) {
model.addAttribute("greeting", "Hello World from Spring 4 MVC");
return "welcome";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/helloagain", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String sayHelloAgain(ModelMap model) {
model.addAttribute("greeting", "Hello World Again, from Spring 4 MVC");
return "welcome";
}
}
@Controller annotation marks this class as spring bean which may handle different HTTP requests based on mapping specified on class or individual controller methods.
@RequestMapping 注解用来映射web请求到指定的处理器类或者处理方法。 在本例中,我们在类级别也用了它,就是说此类是所有http“/”请求的默认处理器, @RequestMapping 也有很多属性 [value,method,params,..]能给用来更加详细的进行映射。
第一个方法,没有进行任何url映射声明,因此它将会继承类上面的映射声明,左右http Get请求的默认处理方法。
第二个方法(添加了带value的映射声明),它将用来处理带/helloagain 的请求。method 属性是用来指明此方法处理的http请求类型。
如果@RequestMapping 里面没有指明 method 则它将处理映射url的所有类型(GET POST等)的请求。
ModelMap 是一个Map 的实现类,它的目的是取代以前的 request.getAttribute/ request.setAttribute方法,
它提供一种 从request或者session中设置 或者获取属性的方式。
留意一下这些方法的返回值。这些值将是view resolver 的前缀或者后缀,来产生视图文件的真是名称。
第4步: 添加视图( View)
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"
pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1">
<title>HelloWorld page</title>
</head>
<body>
Greeting : ${greeting}
</body>
</html>
第5步:添加配置类
package com.websystique.springmvc.configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.JstlView;
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.websystique.springmvc")
public class HelloWorldConfiguration {
@Bean
public ViewResolver viewResolver() {
InternalResourceViewResolver viewResolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver();
viewResolver.setViewClass(JstlView.class);
viewResolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/views/");
viewResolver.setSuffix(".jsp");
return viewResolver;
}
}
@Configuration
表明此类包含一个或者多个含有
@Bean注解的方法,提供spring 容器的bean的管理。
和上面配置类 等价的xml如下:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.websystique.springmvc" />
<mvc:annotation-driven />
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix">
<value>/WEB-INF/views/</value>
</property>
<property name="suffix">
<value>.jsp</value>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
@EnableWebMvc 等价于 xml中的mvc:annotation-driven . 他使得 @Controller注解的类通过@RequestMapping 来映射请求url对应的处理器。
@ComponentScan等价于 context:component-scan base-package="..." 通过此配置spring来扫描bean
第6步:添加初始化类
在servlet 3.0容器启动时,该类将被加载和实例化,其onStartup方法将被servlet容器调用。
com.websystique.springmvc.configuration.HelloWorldInitializer
package com.websystique.springmvc.configuration;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletRegistration;
import org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer;
import org.springframework.web.context.support.AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet;
public class HelloWorldInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
public void onStartup(ServletContext container) throws ServletException {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
ctx.register(HelloWorldConfiguration.class);
ctx.setServletContext(container);
ServletRegistration.Dynamic servlet = container.addServlet("dispatcher", new DispatcherServlet(ctx));
servlet.setLoadOnStartup(1);
servlet.addMapping("/");
}
}
此类代替了 web.xml。
更新:其实上面的类通过继承AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer类可以写的更简洁。
package com.websystique.springmvc.configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer;
public class HelloWorldInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class[] { HelloWorldConfiguration.class };
}
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return null;
}
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[] { "/" };
}
}
Step 7: 构建和部署应用