face alignment by 3000 fps系列学习总结(三)
训练
我们主要以3000fps matlab实现为叙述主体。
总体目标
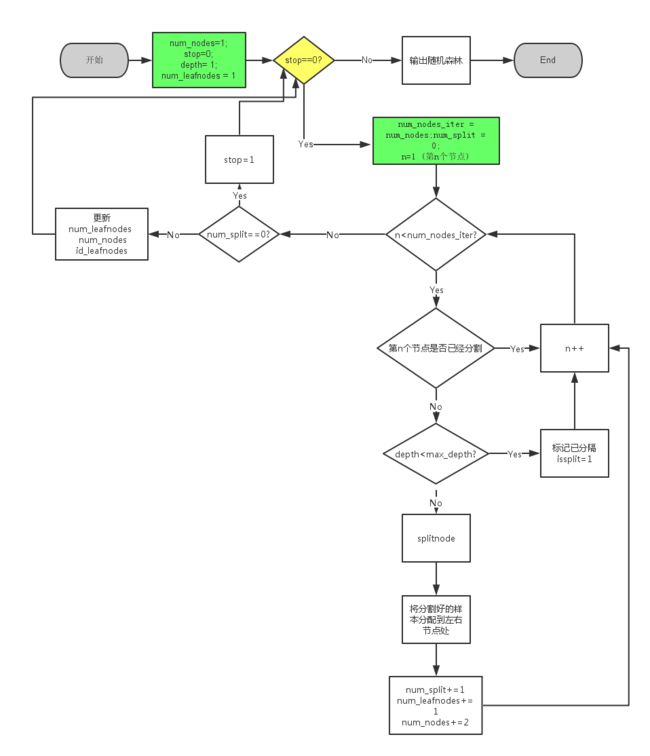
- 我们需要为68个特征点的每一个特征点训练5棵随机树,每棵树4层深,即为所谓的随机森林。
开始训练
- 分配样本
事实上,对于每个特征点,要训练随机森林,我们需要从现有的样本和特征中抽取一部分,训练成若干个树。
现在,我们有N(此处N=1622)个样本(图片和shape)和无数个像素差特征。训练时,对于每棵树,我们从N个样本采取有放回抽样的方法随机选取若干样本,再随机选取M个特征点。然后使用这些素材加以训练。这是一般的方法。不过为了简化,我们将N个样本平均分成5份,且允许彼此之间有重叠。然后分配好的样本用来作为68个特征点的共同素材。
dbsize = length(Tr_Data);
% rf = cell(1, params.max_numtrees);
overlap_ratio = params.bagging_overlap;%重叠比例
Q = floor(double(dbsize)/((1-params.bagging_overlap)*(params.max_numtrees))); %每颗树分配的样本个数
Data = cell(1, params.max_numtrees); %为训练每棵树准备的样本数据
for t = 1:params.max_numtrees
% calculate the number of samples for each random tree
% train t-th random tree
is = max(floor((t-1)*Q - (t-1)*Q*overlap_ratio + 1), 1);
ie = min(is + Q, dbsize);
Data{t} = Tr_Data(is:ie);
end% divide local region into grid
params.radius = ([0:1/30:1]');
params.angles = 2*pi*[0:1/36:1]';
rfs = cell(length(params.meanshape), params.max_numtrees); %随机森林的大小为68*5
%parfor i = 1:length(params.meanshape)
for i = 1:length(params.meanshape)
rf = cell(1, params.max_numtrees);
disp(strcat(num2str(i), 'th landmark is processing...'));
for t = 1:params.max_numtrees
% disp(strcat('training', {''}, num2str(t), '-th tree for', {''}, num2str(lmarkID), '-th landmark'));
% calculate the number of samples for each random tree
% train t-th random tree
is = max(floor((t-1)*Q - (t-1)*Q*overlap_ratio + 1), 1); %样本的序号
ie = min(is + Q, dbsize);
max_numnodes = 2^params.max_depth - 1; %最大的节点数自然是满二叉树的节点个数
rf{t}.ind_samples = cell(max_numnodes, 1); %节点包含的样本序号
rf{t}.issplit = zeros(max_numnodes, 1);%是否分割
rf{t}.pnode = zeros(max_numnodes, 1);
rf{t}.depth = zeros(max_numnodes, 1);%当前深度
rf{t}.cnodes = zeros(max_numnodes, 2);%当前节点的左右子节点序号
rf{t}.isleafnode = zeros(max_numnodes, 1); %判断节点是否是叶子节点
rf{t}.feat = zeros(max_numnodes, 4); %围绕特征点随机选取的2个点的坐标(r1,a1,r2,a2)
rf{t}.thresh = zeros(max_numnodes, 1); %分割节点的阈值
rf{t}.ind_samples{1} = 1:(ie - is + 1)*(params.augnumber); %第t棵树的样本序号,也是根节点包含的样本序号
rf{t}.issplit(1) = 0;
rf{t}.pnode(1) = 0;
rf{t}.depth(1) = 1;
rf{t}.cnodes(1, 1:2) = [0 0];
rf{t}.isleafnode(1) = 1;
rf{t}.feat(1, :) = zeros(1, 4);
rf{t}.thresh(1) = 0;
num_nodes = 1; %num_nodes为现有的节点个数
num_leafnodes = 1;%num_leafnodes为现有的叶子节点个数
stop = 0;
while(~stop) %这个循环用于产生随机树,直到没有再可以分割的点
num_nodes_iter = num_nodes; %num_nodes为现有的节点个数
num_split = 0; %分割节点的个数
for n = 1:num_nodes_iter
if ~rf{t}.issplit(n) %如果第t棵树第n个节点已经分过,就跳过去
if rf{t}.depth(n) == params.max_depth % || length(rf{t}.ind_samples{n}) < 20
if rf{t}.depth(n) == 1 %应该去掉吧????????????????
rf{t}.depth(n) = 1;
end
rf{t}.issplit(n) = 1;
else
% separate the samples into left and right path
[thresh, feat, lcind, rcind, isvalid] = splitnode(i, rf{t}.ind_samples{n}, Data{t}, params, stage);
%{
if ~isvalid
rf{t}.feat(n, :) = [0 0 0 0];
rf{t}.thresh(n) = 0;
rf{t}.issplit(n) = 1;
rf{t}.cnodes(n, :) = [0 0];
rf{t}.isleafnode(n) = 1;
continue;
end
%}
% set the threshold and featture for current node
rf{t}.feat(n, :) = feat;
rf{t}.thresh(n) = thresh;
rf{t}.issplit(n) = 1;
rf{t}.cnodes(n, :) = [num_nodes+1 num_nodes+2]; %当前节点的左右子节点序号
rf{t}.isleafnode(n) = 0;
% add left and right child nodes into the random tree
rf{t}.ind_samples{num_nodes+1} = lcind;
rf{t}.issplit(num_nodes+1) = 0;
rf{t}.pnode(num_nodes+1) = n;
rf{t}.depth(num_nodes+1) = rf{t}.depth(n) + 1;
rf{t}.cnodes(num_nodes+1, :) = [0 0];
rf{t}.isleafnode(num_nodes+1) = 1;
rf{t}.ind_samples{num_nodes+2} = rcind;
rf{t}.issplit(num_nodes+2) = 0;
rf{t}.pnode(num_nodes+2) = n;
rf{t}.depth(num_nodes+2) = rf{t}.depth(n) + 1;
rf{t}.cnodes(num_nodes+2, :) = [0 0];
rf{t}.isleafnode(num_nodes+2) = 1;
num_split = num_split + 1; %分割节点的次数,实际上一层分割节点的个数
num_leafnodes = num_leafnodes + 1;
num_nodes = num_nodes + 2;
end
end
end
if num_split == 0
stop = 1;
else
rf{t}.num_leafnodes = num_leafnodes;
rf{t}.num_nodes = num_nodes;
rf{t}.id_leafnodes = find(rf{t}.isleafnode == 1);
end
end
end
% disp(strcat(num2str(i), 'th landmark is over'));
rfs(i, :) = rf;
endfunction [thresh, feat, lcind, rcind, isvalid] = splitnode(lmarkID, ind_samples, Tr_Data, params, stage)
if isempty(ind_samples)
thresh = 0;
feat = [0 0 0 0];
rcind = [];
lcind = [];
isvalid = 1;
return;
end
% generate params.max_rand cndidate feature
% anglepairs = samplerandfeat(params.max_numfeat);
% radiuspairs = [rand([params.max_numfeat, 1]) rand([params.max_numfeat, 1])];
[radiuspairs, anglepairs] = getproposals(params.max_numfeats(stage), params.radius, params.angles);
angles_cos = cos(anglepairs);
angles_sin = sin(anglepairs);
% extract pixel difference features from pairs
pdfeats = zeros(params.max_numfeats(stage), length(ind_samples)); %所有的样本均要提取相应阶段的像素差特征,即比如说1000*541
shapes_residual = zeros(length(ind_samples), 2);
for i = 1:length(ind_samples)
s = floor((ind_samples(i)-1)/(params.augnumber)) + 1; %共用样本的序号
k = mod(ind_samples(i)-1, (params.augnumber)) + 1; %不能共用盒子,而是对于同一张图片的不同shape使用各自的盒子,使用余运算,显然小于params.augnumber,又加1,所以答案从1:params.augnumber
% calculate the relative location under the coordinate of meanshape %x1=angles_cos(:, 1)).*radiuspairs(:, 1)
pixel_a_x_imgcoord = (angles_cos(:, 1)).*radiuspairs(:, 1)*params.max_raio_radius(stage)*Tr_Data{s}.intermediate_bboxes{stage}(k, 3);
pixel_a_y_imgcoord = (angles_sin(:, 1)).*radiuspairs(:, 1)*params.max_raio_radius(stage)*Tr_Data{s}.intermediate_bboxes{stage}(k, 4);
pixel_b_x_imgcoord = (angles_cos(:, 2)).*radiuspairs(:, 2)*params.max_raio_radius(stage)*Tr_Data{s}.intermediate_bboxes{stage}(k, 3);
pixel_b_y_imgcoord = (angles_sin(:, 2)).*radiuspairs(:, 2)*params.max_raio_radius(stage)*Tr_Data{s}.intermediate_bboxes{stage}(k, 4);
% no transformation
%{
pixel_a_x_lmcoord = pixel_a_x_imgcoord;
pixel_a_y_lmcoord = pixel_a_y_imgcoord;
pixel_b_x_lmcoord = pixel_b_x_imgcoord;
pixel_b_y_lmcoord = pixel_b_y_imgcoord;
%}
% transform the pixels from image coordinate (meanshape) to coordinate of current shape
%以下计算出的都是中心化的坐标
[pixel_a_x_lmcoord, pixel_a_y_lmcoord] = transformPointsForward(Tr_Data{s}.meanshape2tf{k}, pixel_a_x_imgcoord', pixel_a_y_imgcoord');
pixel_a_x_lmcoord = pixel_a_x_lmcoord';
pixel_a_y_lmcoord = pixel_a_y_lmcoord';
[pixel_b_x_lmcoord, pixel_b_y_lmcoord] = transformPointsForward(Tr_Data{s}.meanshape2tf{k}, pixel_b_x_imgcoord', pixel_b_y_imgcoord');
pixel_b_x_lmcoord = pixel_b_x_lmcoord';
pixel_b_y_lmcoord = pixel_b_y_lmcoord';
%转化为绝对坐标
pixel_a_x = int32(bsxfun(@plus, pixel_a_x_lmcoord, Tr_Data{s}.intermediate_shapes{stage}(lmarkID, 1, k)));
pixel_a_y = int32(bsxfun(@plus, pixel_a_y_lmcoord, Tr_Data{s}.intermediate_shapes{stage}(lmarkID, 2, k)));
pixel_b_x = int32(bsxfun(@plus, pixel_b_x_lmcoord, Tr_Data{s}.intermediate_shapes{stage}(lmarkID, 1, k)));
pixel_b_y = int32(bsxfun(@plus, pixel_b_y_lmcoord, Tr_Data{s}.intermediate_shapes{stage}(lmarkID, 2, k)));
width = (Tr_Data{s}.width);
height = (Tr_Data{s}.height);
pixel_a_x = max(1, min(pixel_a_x, width)); %意思是 pixel_a_x应该介于1和width之间
pixel_a_y = max(1, min(pixel_a_y, height));
pixel_b_x = max(1, min(pixel_b_x, width));
pixel_b_y = max(1, min(pixel_b_y, height));
%取像素两种方法,一是img_gray(i,j);二是img_gray(k),k是按列数第k个元素
pdfeats(:, i) = double(Tr_Data{s}.img_gray(pixel_a_y + (pixel_a_x-1)*height)) - double(Tr_Data{s}.img_gray(pixel_b_y + (pixel_b_x-1)*height));
%./ double(Tr_Data{s}.img_gray(pixel_a_y + (pixel_a_x-1)*height)) + double(Tr_Data{s}.img_gray(pixel_b_y + (pixel_b_x-1)*height));
% drawshapes(Tr_Data{s}.img_gray, [pixel_a_x pixel_a_y pixel_b_x pixel_b_y]);
% hold off;
shapes_residual(i, :) = Tr_Data{s}.shapes_residual(lmarkID, :, k);
end
E_x_2 = mean(shapes_residual(:, 1).^2);
E_x = mean(shapes_residual(:, 1));
E_y_2 = mean(shapes_residual(:, 2).^2);
E_y = mean(shapes_residual(:, 2));
% 整体方差,其中使用了方差的经典公式Dx=Ex^2-(Ex)^2
var_overall = length(ind_samples)*((E_x_2 - E_x^2) + (E_y_2 - E_y^2));
% var_overall = length(ind_samples)*(var(shapes_residual(:, 1)) + var(shapes_residual(:, 2)));
% max_step = min(length(ind_samples), params.max_numthreshs);
% step = floor(length(ind_samples)/max_step);
max_step = 1;
var_reductions = zeros(params.max_numfeats(stage), max_step);
thresholds = zeros(params.max_numfeats(stage), max_step);
[pdfeats_sorted] = sort(pdfeats, 2); %将数据打乱顺序,防止过拟合
% shapes_residual = shapes_residual(ind, :);
for i = 1:params.max_numfeats(stage) %暴力选举法,选出最合适的feature
% for t = 1:max_step
t = 1;
ind = ceil(length(ind_samples)*(0.5 + 0.9*(rand(1) - 0.5)));
threshold = pdfeats_sorted(i, ind); % pdfeats_sorted(i, t*step); %
thresholds(i, t) = threshold;
ind_lc = (pdfeats(i, :) < threshold); %逻辑数组
ind_rc = (pdfeats(i, :) >= threshold);
% figure, hold on, plot(shapes_residual(ind_lc, 1), shapes_residual(ind_lc, 2), 'r.')
% plot(shapes_residual(ind_rc, 1), shapes_residual(ind_rc, 2), 'g.')
% close;
% compute
E_x_2_lc = mean(shapes_residual(ind_lc, 1).^2); %选出逻辑数组中为1的那些残差
E_x_lc = mean(shapes_residual(ind_lc, 1));
E_y_2_lc = mean(shapes_residual(ind_lc, 2).^2);
E_y_lc = mean(shapes_residual(ind_lc, 2));
var_lc = (E_x_2_lc + E_y_2_lc)- (E_x_lc^2 + E_y_lc^2);
E_x_2_rc = (E_x_2*length(ind_samples) - E_x_2_lc*sum(ind_lc))/sum(ind_rc);
E_x_rc = (E_x*length(ind_samples) - E_x_lc*sum(ind_lc))/sum(ind_rc);
E_y_2_rc = (E_y_2*length(ind_samples) - E_y_2_lc*sum(ind_lc))/sum(ind_rc);
E_y_rc = (E_y*length(ind_samples) - E_y_lc*sum(ind_lc))/sum(ind_rc);
var_rc = (E_x_2_rc + E_y_2_rc)- (E_x_rc^2 + E_y_rc^2);
var_reduce = var_overall - sum(ind_lc)*var_lc - sum(ind_rc)*var_rc;
% var_reduce = var_overall - sum(ind_lc)*(var(shapes_residual(ind_lc, 1)) + var(shapes_residual(ind_lc, 2))) - sum(ind_rc)*(var(shapes_residual(ind_rc, 1)) + var(shapes_residual(ind_rc, 2)));
var_reductions(i, t) = var_reduce;
% end
% plot(var_reductions(i, :));
end
[~, ind_colmax] = max(var_reductions);%寻找最大差的序号
ind_max = 1;
%{
if var_max <= 0
isvalid = 0;
else
isvalid = 1;
end
%}
isvalid = 1;
thresh = thresholds(ind_colmax(ind_max), ind_max); %当前阈值
feat = [anglepairs(ind_colmax(ind_max), :) radiuspairs(ind_colmax(ind_max), :)];
lcind = ind_samples(find(pdfeats(ind_colmax(ind_max), :) < thresh));
rcind = ind_samples(find(pdfeats(ind_colmax(ind_max), :) >= thresh));
end问题:训练时默认一旦可以分割节点,则必然分割成两部分。那么会不会出现选取一个阈值将剩余的样本都归于一类呢?
说明:
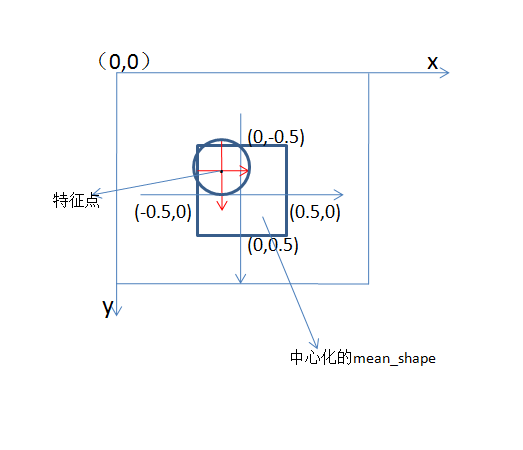
如图所示外面有一个current 坐标系,里面有mean_shape的中心化归一化的坐标。最里面是以一个特征点为中心取的极坐标。这份代码取 r , θ 来标注在特征点附近取到的任意两个像素点的坐标.可以说有三个坐标系(按前面顺序,分别称为坐标系一、二、三)。里面两个坐标系的尺寸一样,但是坐标原点不一样。
假定在坐标系三下,取到一像素点坐标为(x,y),而特征点在坐标系二的坐标为( x0,y0 ),则像素点在坐标系二的坐标为( x˜,y˜ ),则有:
(x˜,y˜)=(x,y)+(x0,y0)
.
又由前面一篇文章 《face alignment by 3000 fps系列学习总结(二)》中间进行的相似性变换,我们知道,将当前坐标由mean_shape的归一化中心化坐标转换为current_shape的中心化坐标,需要使用meanshape2tf变换。
即:
(x˜,y˜)/cR
进一步的,取中心化后得
(x˜,y˜)/cR+mean(immediateshape)=(x,y)+(x0,y0)cR+mean(immediateshape)=(x,y)cR+(x0,y0)cR+mean(immediateshape)=(x,y)cR+immediate_shape_at(x0,y0)
我们又知道:
cR=c˜R˜/immediate_bbox
所以上式= (x,y)∗immediate_bbox/{c˜R˜}+immediate_shape_at(x0,y0)
最后一句就解析清了代码的步骤:
% calculate the relative location under the coordinate of meanshape %x1=angles_cos(:, 1)).*radiuspairs(:, 1)
pixel_a_x_imgcoord = (angles_cos(:, 1)).*radiuspairs(:, 1)*params.max_raio_radius(stage)*Tr_Data{s}.intermediate_bboxes{stage}(k, 3);
pixel_a_y_imgcoord = (angles_sin(:, 1)).*radiuspairs(:, 1)*params.max_raio_radius(stage)*Tr_Data{s}.intermediate_bboxes{stage}(k, 4);
pixel_b_x_imgcoord = (angles_cos(:, 2)).*radiuspairs(:, 2)*params.max_raio_radius(stage)*Tr_Data{s}.intermediate_bboxes{stage}(k, 3);
pixel_b_y_imgcoord = (angles_sin(:, 2)).*radiuspairs(:, 2)*params.max_raio_radius(stage)*Tr_Data{s}.intermediate_bboxes{stage}(k, 4);
% no transformation
%{
pixel_a_x_lmcoord = pixel_a_x_imgcoord;
pixel_a_y_lmcoord = pixel_a_y_imgcoord;
pixel_b_x_lmcoord = pixel_b_x_imgcoord;
pixel_b_y_lmcoord = pixel_b_y_imgcoord;
%}
% transform the pixels from image coordinate (meanshape) to coordinate of current shape
%以下计算出的都是中心化的坐标
[pixel_a_x_lmcoord, pixel_a_y_lmcoord] = transformPointsForward(Tr_Data{s}.meanshape2tf{k}, pixel_a_x_imgcoord', pixel_a_y_imgcoord');
pixel_a_x_lmcoord = pixel_a_x_lmcoord';
pixel_a_y_lmcoord = pixel_a_y_lmcoord';
[pixel_b_x_lmcoord, pixel_b_y_lmcoord] = transformPointsForward(Tr_Data{s}.meanshape2tf{k}, pixel_b_x_imgcoord', pixel_b_y_imgcoord');
pixel_b_x_lmcoord = pixel_b_x_lmcoord';
pixel_b_y_lmcoord = pixel_b_y_lmcoord';
%转化为绝对坐标
pixel_a_x = int32(bsxfun(@plus, pixel_a_x_lmcoord, Tr_Data{s}.intermediate_shapes{stage}(lmarkID, 1, k)));
pixel_a_y = int32(bsxfun(@plus, pixel_a_y_lmcoord, Tr_Data{s}.intermediate_shapes{stage}(lmarkID, 2, k)));
pixel_b_x = int32(bsxfun(@plus, pixel_b_x_lmcoord, Tr_Data{s}.intermediate_shapes{stage}(lmarkID, 1, k)));
pixel_b_y = int32(bsxfun(@plus, pixel_b_y_lmcoord, Tr_Data{s}.intermediate_shapes{stage}(lmarkID, 2, k)));
width = (Tr_Data{s}.width);
height = (Tr_Data{s}.height);
pixel_a_x = max(1, min(pixel_a_x, width)); %意思是 pixel_a_x应该介于1和width之间
pixel_a_y = max(1, min(pixel_a_y, height));
pixel_b_x = max(1, min(pixel_b_x, width));
pixel_b_y = max(1, min(pixel_b_y, height));
%取像素两种方法,一是img_gray(i,j);二是img_gray(k),k是按列数第k个元素
pdfeats(:, i) = double(Tr_Data{s}.img_gray(pixel_a_y + (pixel_a_x-1)*height)) - double(Tr_Data{s}.img_gray(pixel_b_y + (pixel_b_x-1)*height));如此我们训练全程就搞懂了。