Netty4学习笔记(4)-- ByteBuf和设计模式
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/zxhoo/article/details/17577865
ByteBuf是Netty框架里最重要的类之一,简单的说,ByteBuf就是java.nio.ByteBuffer的Netty版。
ByteBuf逻辑结构
正如类名所反映出来的,ByteBuf逻辑上就是一个byte容器。ByteBuf里的数据被两个指针划分为三个部分,如下图所示:
- reader index前面的数据是已经读过的数据,这些数据可以扔掉
- 从reader index开始,到writer index之前的数据是可读数据
- 从writer index开始,为可写区域
正是因为这样的设计,ByteBuf可以同时读写数据(只要可读区域和可写区域都还有空闲空间),而java.nio.ByteBuffer则必须调用flip()方法才能从写状态切换到读状态。
ByteBuf API
ByteBuf提供了大量的方法,比较常用的有下面这些:
- writeXxx(xxx value) 这组方法将不同类型的数据写到buf里,同时将writerIndex往前移适当的距离
- readXxx() 这组方法从buf里读出某种类型的数据,同时将readerIndex往前移适当的距离
- skipBytes(int length) 将readerIndex往前移指定的距离
- setXxx(int index, xxx value) 这组方法将不同类型的数据写到buf的指定位置
- getXxx(int index) 这组方法从buf的指定位置读出一个某种类型的数据
- readerIndex()/writerIndex() 访问readerIndex和writerIndex
- readerIndex(int)/writerIndex(int) 设置readerIndex和writerIndex
- readableBytes() 返回可读区域的字节数
- writableBytes() 返回可写区域的字节数
- clear() 清除buf(把readerIndex和writerIndex都设为0)
- discardReadBytes() 扔掉已读数据
值得一提的是,discardReadBytes()方法需要把可读数据移动到buf的开头,因此是个比较慢的操作。而clear()方法只是将两个指针清0,所以相对而言速度很快。
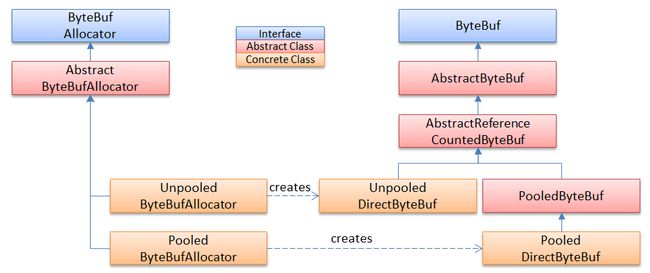
ByteBufAllocator - 抽象工厂模式
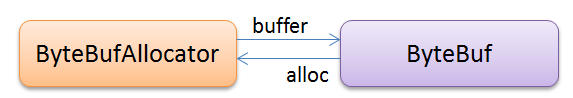
在Netty的世界里,ByteBuf实例通常应该由ByteBufAllocator来创建。ByteBuf和Allocator的关系如下图所示:
Allocator的buffer()方法创建ByteBuf实例,ByteBuf的alloc()方法返回创建自己的Allocator。ByteBufAllocator的实现使用了抽象工厂模式,如下图所示:
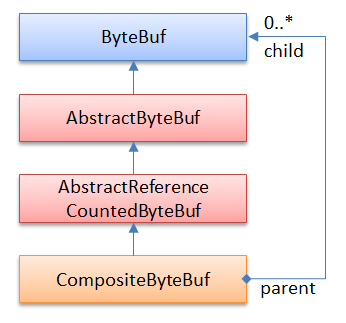
CompositeByteBuf - 组合模式
CompositeByteBuf可以让我们把多个ByteBuf当成一个大Buf来处理,ByteBufAllocator提供了compositeBuffer()工厂方法来创建CompositeByteBuf。CompositeByteBuf的实现使用了组合模式,如下图所示:
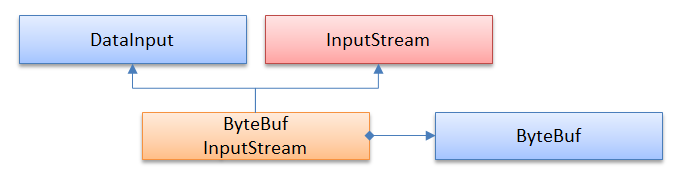
ByteBufInputStream - 适配器模式
ByteBufInputStream使用适配器模式,使我们可以把ByteBuf当做Java的InputStream来使用。同理,ByteBufOutputStream允许我们把ByteBuf当做OutputStream来使用。
比如说我们要实现一个自定义的消息协议,消息包括header和body两部分内容,body里放的是JSON字符串。那么就可以使用ByteBufInputStream来避免把ByteBuf里的字节拷贝到字节数组的开销:
- private Object decodeMessage(ByteBuf bb) {
- // read header
- // bb.readXxx()...
- // read body
- InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(new ByteBufInputStream(bb));
- return new Gson().fromJson(reader, JsonObject.class);
- }
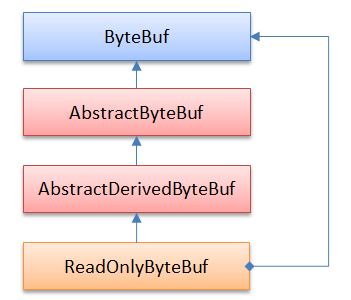
ReadOnlyByteBuf - 装饰器模式
ReadOnlyByteBuf用适配器模式把一个ByteBuf变为只读,ReadOnlyByteBuf通过调用Unpooled.unmodifiableBuffer(ByteBuf)方法获得:
类似的ByteBuf适配器还包括:
- DuplicatedByteBuf
- SlicedByteBuf
- SwappedByteBuf
ByteBuf - 工厂方法模式
前面也提到过了,我们很少需要直接通过构造函数来创建ByteBuf实例,而是通过Allocator来创建。从装饰器模式可以看出另外一种获得ByteBuf的方式是调用ByteBuf的工厂方法,比如:
- ByteBuf#duplicate()
- ByteBuf#slice()
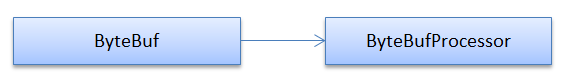
ByteBufProcessor - 访问者模式还是迭代器模式?
最后,ByteBuf提供了4个forEachByte()方法来对ByteBuf里的数据进行某种处理或查找,看起来像是访问者模式和迭代器模式的混合:
- public abstract int forEachByte(ByteBufProcessor processor);
- public abstract int forEachByte(int index, int length, ByteBufProcessor processor);
- public abstract int forEachByteDesc(ByteBufProcessor processor);
- public abstract int forEachByteDesc(int index, int length, ByteBufProcessor processor);