Android之Activity生命周期
Android之Activity生命周期
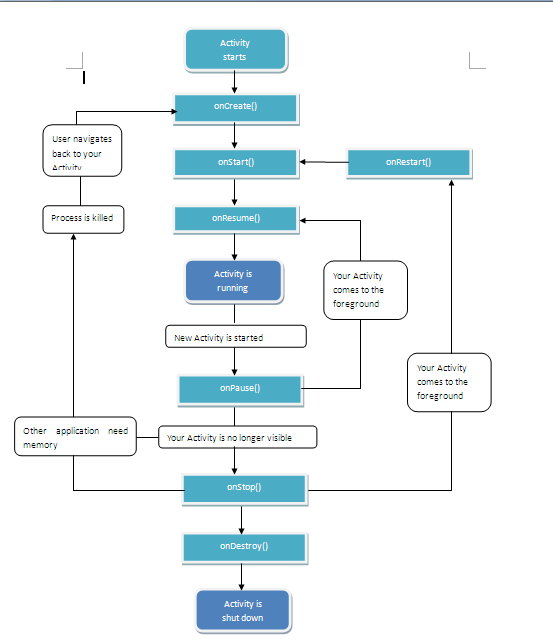
首先我们还是来看一下Android API提供的Activity生命周期图,如下图所示。可以看出,一个Activity的生命周期会经历onCreate()→onStart()→onResume()→onPause()→onStop()→onDestroy()这几个过程。不过光看图还是有点抽象,下面我们结合一个小例子来熟悉一下Activity的生命周期具体的流程。
首先我们新建一个项目ActivityLifecycle,通过在各个继承的函数中加入log信息来跟踪程序执行的状况。第一个Activity的代码如下所示:
public class ActivityTest extends Activity{
private static final String TAG="ActivityTest";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Log.e(TAG, "onCreate");
Button btn=(Button)findViewById(R.id.button1);
//监听button的事件信息
btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//新建一个Intent意图对象
Intent intent=new Intent();
//指定intent要启动的类
intent.setClass(ActivityTest.this, Activity2.class);
//启动一个新的Activity
startActivity(intent);
//关闭当前的Activity
ActivityTest.this.finish();
}
});
Button btn2=(Button)findViewById(R.id.button2);
//监听button的事件信息
btn2.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//关闭当前的Activity
ActivityTest.this.finish();
}
});
}
//程序开始
@Override
protected void onStart() {
super.onStart();
Log.e(TAG, "onStart");
}
//程序恢复
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
Log.e(TAG, "onResume");
}
//程序暂停
@Override
protected void onPause() {
super.onPause();
Log.e(TAG, "onPause");
}
//程序停止
@Override
protected void onStop() {
super.onStop();
Log.e(TAG, "onStop");
}
//程序销毁
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
Log.e(TAG, "onDestroy");
}
//程序重启
@Override
protected void onRestart() {
super.onRestart();
Log.e(TAG, "onRestart");
}
}
第二个Activity的代码如下所示。与ActivityTest类似,在每个地方中加上一些log信息,用于记录当前运行状态。
public class Activity2 extends Activity {
private static final String TAG = "Activity2";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_2);
Log.e(TAG, "onCreate");
Button btnStartNew = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnStartNew);
// 监听button的事件信息
btnStartNew.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// 新建一个Intent对象
Intent intent = new Intent();
// 指定intent要启动的类
intent.setClass(Activity2.this, ActivityTest.class);
// 启动一个新的Activity
startActivity(intent);
// 关闭当前的Activity
Activity2.this.finish();
}
});
Button btnExit=(Button)findViewById(R.id.btnExit);
btnExit.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//关闭当前的Activity
Activity2.this.finish();
}
});
}
//程序开始
@Override
protected void onStart() {
super.onStart();
Log.e(TAG, "onStart");
}
//程序恢复
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
Log.e(TAG, "onResume");
}
//程序暂停
@Override
protected void onPause() {
super.onPause();
Log.e(TAG, "onPause");
}
//程序停止
@Override
protected void onStop() {
super.onStop();
Log.e(TAG, "onStop");
}
//程序销毁
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
Log.e(TAG, "onDestroy");
}
//程序重启
@Override
protected void onRestart() {
super.onRestart();
Log.e(TAG, "onRestart");
}
}
我们在布局文件中简单定义了两个Button和一个TextView,一个Button用来切换到另一个Activity,另一个Button用于关闭当前界面,TextView用来显示当前Activity的名称。第一个Activity对应的布局文件activity_main.xml代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/info"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="ActivityTest" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="启动第二个Activity" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="关闭当前Activity" />
</LinearLayout>第二个Activity对应的布局文件activity_2.xml代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/info"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="第二个Activity" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnStartNew"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnExit"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button" />
</LinearLayout>
然后我们要在AndroidManifest.xml文件中声明这两个Activity,如下所示:
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.veione.activitytest"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" >
<uses-sdk
android:minSdkVersion="9"
android:targetSdkVersion="21" />
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
<activity android:name="com.veione.activitytest.ActivityTest" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<activity android:name="com.veione.activitytest.Activity2" />
</application>
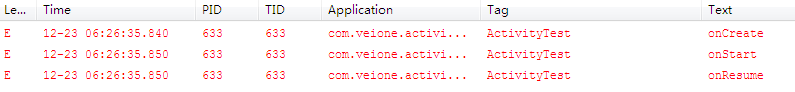
</manifest>最后我们运行此程序。首先我们启动程序,可以看到Activity经历了onCreate、onStart、onResume这3个函数,如图所示。
然后我们单击“启动第二个Activity”,可以看到ActivityTest显示了onPause,如图所示。接下来执行Activity中的onCreate->onStart->onResume(),然后在ActivityTest中执行了onStop->onDestroy将ActivityTest依次停止、销毁。
我们在第二个Activity中单击"关闭",可以看到log信息如图所示,Activity依次执行了onPause->onStop->onDestroy。
自此我们整个Activity的生命周期是不是都已经掌握了呢,反正我已经掌握了。