WebService之Axis2(1):用POJO实现0配置的WebService
Axis2是一套崭新的WebService引擎,该版本是对Axis1.x重新设计的产物。Axis2不仅支持SOAP1.1和SOAP1.2,还集成了非常流行的REST WebService,同时还支持Spring、JSON等技术。这些都将在后面的系列教程中讲解。在本文中主要介绍了如何使用Axis2开发一个不需要任何配置文件的WebService,并在客户端使用Java和C#调用这个WebService。一、Axis2的下载和安装
读者可以从如下的网址下载Axis2的最新版本:
http://ws.apache.org/axis2/
在本文使用了目前Axis2的最新版本1.4.1。读者可以下载如下两个zip包:
axis2-1.4.1-bin.zip
axis2-1.4.1-war.zip
其中axis2-1.4.1-bin.zip文件中包含了Axis2中所有的jar文件, axis2-1.4.1-war.zip文件用于将WebService发布到Web容器中。
将axis2-1.4.1-war.zip文件解压到相应的目录,将目录中的axis2.war文件放到<Tomcat安装目录>/webapps目录中(本文使用的Tomcat的版本是6.x),并启动Tomcat。
在浏览器地址栏中输入如下的URL:
http:/ /localhost:8080/axis2/
如果在浏览器中显示出如图1所示的页面,则表示Axis2安装成功。
图1
二、编写和发布WebService
对于用Java实现的服务程序给人的印象就是需要进行大量的配置,不过这一点在Axis2中将被终结。在Axis2中不需要进行任何的配置,就可以直接将一个简单的POJO发布成WebService。其中POJO中所有的public方法将被发布成WebService方法。
下面我们来实现一个简单的POJO,代码如下:
- public class SimpleService
- {
- public String getGreeting(String name)
- {
- return "你好 " + name;
- }
- public int getPrice()
- {
- return new java.util.Random().nextInt(1000);
- }
- }
复制代码
在SimpleService类中有两个方法,由于这两个方法都是public方法,因此,它们都将作为WebService方法被发布。
编译SimpleService类后,将SimpleService.class文件放到<Tomcat安装目录>/webapps/axis2/WEB-INF/pojo目录中(如果没有pojo目录,则建立该目录)。现在我们已经成功将SimpleService类发布成了WebService。在浏览器地址栏中输入如下的URL:
http:/ /localhost:8080/axis2/services/listServices
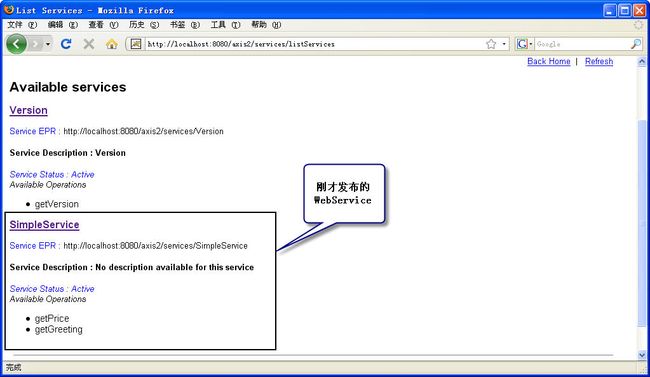
这时当前页面将显示所有在Axis2中发布的WebService,如图2所示。
在浏览器地址栏中输入如下的两个URL来分别测试getGreeting和getPrice方法:
http:/ /localhost:8080/axis2/services/SimpleService/getGreeting?name=bill
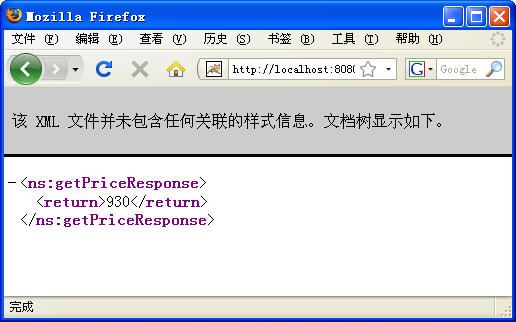
http:/ /localhost:8080/axis2/services/SimpleService/getPrice
图3和图4分别显示了getGreeting和getPrice方法的测试结果。
图3 getGreeting方法的测试结果
图4 getPrice方法的测试结果
在编写、发布和测试0配置的WebService时应注意如下几点:
1. POJO类不能使用package关键字声明包。
2. Axis2在默认情况下可以热发布WebService,也就是说,将WebService的.class文件复制到pojo目录中时,Tomcat不需要重新启动就可以自动发布WebService。如果想取消Axis2的热发布功能,可以打开<Tomcat安装目录>/webapps/axis2/WEB-INF/conf/axis2.xml,找到如下的配置代码:
- <parameter name="hotdeployment">true</parameter>
复制代码
将true改为false即可。要注意的是,Axis2在默认情况下虽然是热发布,但并不是热更新,也就是说,一旦成功发布了WebService,再想更新该WebService,就必须重启Tomcat。这对于开发人员调试WebService非常不方便,因此,在开发WebService时,可以将Axis2设为热更新。在axis2.xml文件中找到<parametername="hotupdate">false</parameter>,将false改为true即可。
3. 在浏览器中测试WebService时,如果WebService方法有参数,需要使用URL的请求参数来指定该WebService方法参数的值,请求参数名与方法参数名要一致,例如,要测试getGreeting方法,请求参数名应为name,如上面的URL所示。
4. 发布WebService的pojo目录只是默认的,如果读者想在其他的目录发布WebService,可以打开axis2.xml文件,并在<axisconfig>元素中添加如下的子元素:
- <deployer extension=".class" directory="my" class="org.apache.axis2.deployment.POJODeployer"/>
复制代码
上面的配置允许在<Tomcat安装目录>/webapps/axis2/WEB-INF/my目录中发布WebService。例如,将本例中的SimpleService.class复制到my目录中也可以成功发布(但要删除pojo目录中的SimpleService.class,否则WebService会重名)。
三、 用Java实现调用WebService的客户端程序
WebService是为程序服务的,只在浏览器中访问WebService是没有意义的。因此,在本节使用Java实现了一个控制台程序来调用上一节发布的WebService。调用WebService的客户端代码如下:
- package client;
- import javax.xml.namespace.QName;
- import org.apache.axis2.addressing.EndpointReference;
- import org.apache.axis2.client.Options;
- import org.apache.axis2.rpc.client.RPCServiceClient;
- public class RPCClient
- {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
- {
- // 使用RPC方式调用WebService
- RPCServiceClient serviceClient = new RPCServiceClient();
- Options options = serviceClient.getOptions();
- // 指定调用WebService的URL
- EndpointReference targetEPR = new EndpointReference(
- "http://localhost:8080/axis2/services/SimpleService");
- options.setTo(targetEPR);
- // 指定getGreeting方法的参数值
- Object[] opAddEntryArgs = new Object[] {"超人"};
- // 指定getGreeting方法返回值的数据类型的Class对象
- Class[] classes = new Class[] {String.class};
- // 指定要调用的getGreeting方法及WSDL文件的命名空间
- QName opAddEntry = new QName("http://ws.apache.org/axis2", "getGreeting");
- // 调用getGreeting方法并输出该方法的返回值
- System.out.println(serviceClient.invokeBlocking(opAddEntry, opAddEntryArgs, classes)[0]);
- // 下面是调用getPrice方法的代码,这些代码与调用getGreeting方法的代码类似
- classes = new Class[] {int.class};
- opAddEntry = new QName("http://ws.apache.org/axis2", "getPrice");
- System.out.println(serviceClient.invokeBlocking(opAddEntry, new Object[]{}, classes)[0]);
- }
- }
复制代码
运行上面的程序后,将在控制台输出如下的信息:
你好 超人
443
在编写客户端代码时应注意如下几点:
1. 客户端代码需要引用很多Axis2的jar包,如果读者不太清楚要引用哪个jar包,可以在Eclipse的工程中引用Axis2发行包的lib目录中的所有jar包。
2. 在本例中使用了RPCServiceClient类的invokeBlocking方法调用了WebService中的方法。invokeBlocking方法有三个参数,其中第一个参数的类型是QName对象,表示要调用的方法名;第二个参数表示要调用的WebService方法的参数值,参数类型为Object[];第三个参数表示WebService方法的返回值类型的Class对象,参数类型为Class[]。当方法没有参数时,invokeBlocking方法的第二个参数值不能是null,而要使用new Object[]{}。
3. 如果被调用的WebService方法没有返回值,应使用RPCServiceClient类的invokeRobust方法,该方法只有两个参数,它们的含义与invokeBlocking方法的前两个参数的含义相同。
4. 在创建QName对象时,QName类的构造方法的第一个参数表示WSDL文件的命名空间名,也就是<wsdl:definitions>元素的targetNamespace属性值,下面是SimpleService类生成的WSDL文件的代码片段:
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <wsdl:definitions xmlns:wsdl="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/" xmlns:ns1="http://org.apache.axis2/xsd"
- xmlns:ns="http://ws.apache.org/axis2" xmlns:wsaw="http://www.w3.org/2006/05/addressing/wsdl"
- xmlns:http="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/http/" xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
- xmlns:mime="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/mime/" xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/soap/"
- xmlns:soap12="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/soap12/"
- targetNamespace="http://ws.apache.org/axis2">
- <wsdl:types>
- </wsdl:types>
- </wsdl:definitions>
复制代码
四、用wsdl2java简化客户端的编写
也许有很多读者会说“有没有搞错啊,只调用两个WebService方法用要写这么多代码,太麻烦了”。
不过幸好Axis2提供了一个wsdl2java.bat命令可以根据WSDL文件自动产生调用WebService的代码。wsdl2java.bat命令可以在<Axis2安装目录>"bin目录中找到。在使用wsdl2java.bat命令之前需要设置AXIS2_HOME环境变量,该变量值是<Axis2安装目录>。
在Windows控制台输出如下的命令行来生成调用WebService的代码:
%AXIS2_HOME%/bin/wsdl2java -uri http://localhost:8080/axis2/services/SimpleService?wsdl-p client -s -o stub
其中-url参数指定了wsdl文件的路径,可以是本地路径,也可以是网络路径。-p参数指定了生成的Java类的包名,-o参数指定了生成的一系列文件保存的根目录。在执行完上面的命令后,读者就会发现在当前目录下多了个stub目录,在."stub"src"client目录可以找到一个SimpleServiceStub.java文件,该文件复杂调用WebService,读者可以在程序中直接使用这个类,代码如下:
- package client;
- import javax.xml.namespace.QName;
- import org.apache.axis2.addressing.EndpointReference;
- import org.apache.axis2.client.Options;
- import org.apache.axis2.rpc.client.RPCServiceClient;
- public class StubClient
- {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
- {
- SimpleServiceStub stub = new SimpleServiceStub();
- SimpleServiceStub.GetGreeting gg = new SimpleServiceStub.GetGreeting();
- gg.setName("比尔");
- System.out.println( stub.getGreeting(gg).get_return());
- System.out.println(stub.getPrice().get_return());
- }
- }
复制代码
上面的代码大大简化了调用WebService的步骤,并使代码更加简洁。但要注意的是,wsdl2java.bat命令生成的Stub类将WebService方法的参数都封装在了相应的类中,类名为方法名,例如,getGreeting方法的参数都封装在了GetGreeting类中,要想调用getGreeting方法,必须先创建GetGreeting类的对象实例。五、使用C#调用WebService
从理论上说,WebService可以被任何支持SOAP协议的语言调用。在Visual Studio中使用C#调用WebService是在所有语言中最容易实现的(VB.net的调用方法类似,也同样很简单)。
新建一个Visual Studio工程,并在引用Web服务的对话框中输入如下的URL,并输入Web引用名为“WebService”:
http:/ /localhost:8080/axis2/services/SimpleService?wsdl
然后引用Web服务的对话框就会显示该WebService中的所有的方法,如图5所示。
图5
在完成上面的工作后,只需要如下三行C#代码就可以调用getGreeting和getPrice方法,并显示这两个方法的返回值:
- WebService.SimpleService simpleService = new WSC.WebService.SimpleService();
- MessageBox.Show( simpleService.getGreeting("比尔"));
- MessageBox.Show(simpleService.getPrice()[email protected]());
复制代码
在.net解析WSDL文件时直接将getGreeting方法的参数映射为String类型,因此,可以直接进行传值。
从上面的调用过程可以看出,添加Web引用的过程就相当于在Java中调用wsdl2java.bat自动生成stub类的过程。只是在调用stub类时与C#有一定的区别,但从总体上来说,都大大简化了调用WebService的过程