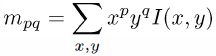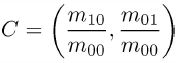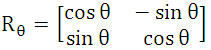【特征检测】ORB特征提取算法
简介
ORB的全称是ORiented Brief,是文章ORB: an efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF中提出的一种新的角点检测与特征描述算法。实际上,ORB算法是将FAST角点检测与BRIEF特征描述结合并进行了改进。
ORB算法
在上一篇文章《BRIEF特征点描述算法》中,指出了BRIEF的优缺点,ORB算法就是针对BRIEF算法的缺点1、2提出来的。ORB算法分为两个部分:FAST特征点检测、BRIEF特征描述。
FAST特征检测
在文章《FAST特征点检测算法》中,详细阐述了FAST算法。但该算法仅仅确定了特征点的位置,没有得到其他任何信息。在ORB算法中,依然采用FAST来检测特征点的位置,但算法进行了如下改动:(以FAST-9为例)
1、假设在图像中要提取N个特征点,则降低FAST的阈值,使FAST算法检测到的特征点大于N;
2、在特征点位置处,计算特征点的Harris响应值R,取前N个响应值大的点作为FAST特征点(Harris角点响应计算:Harris角点检测中的数学推导);
3、由于要解决BRIEF算法的旋转不变性,则需要计算特征点的主方向。
ORB中利用重心来计算,如下(其中(x,y)是特征邻域内的点):
atan2表示反正切,得到的θ值就是FAST特征点的主方向。
BRIEF特征描述
在文章《BRIEF特征点描述算法》种,阐述了BRIEF算法。该算法速度优势相当明显,但存在三个致命的缺点。针对尺度不变性,可以像SIFT算法一样,子尺度空间构造图像金字塔解决,此处不再说明。ORB算法主要解决前两天缺点:噪声敏感、旋转不变性。
1、解决噪声敏感问题
BRIEF中,采用了9x9的高斯算子进行滤波,可以一定程度上解决噪声敏感问题,但一个滤波显然是不够的。ORB中提出,利用积分图像来解决:在31x31的窗口中,产生一对随机点后,以随机点为中心,取5x5的子窗口,比较两个子窗口内的像素和的大小进行二进制编码,而非仅仅由两个随机点决定二进制编码。(这一步可有积分图像完成)
2、解决旋转不变性
利用FAST中求出的特征点的主方向θ,对特征点邻域进行旋转,Calonder建议先将每个块旋转后,再进行BRIEF描述子的提取,但这种方法代价较大。ORB算法采用的是:每一个特征点处,对产生的256对随机点(以256为例),将其进行旋转,后进行判别,再二进制编码。如下:S表示随机点位置(2xn的矩阵),Sθ表示旋转后的随机点的位置(2xn的矩阵),x1=(u1,v1)是一个坐标向量,其余雷同。n=256。
得到新的随机点位置后,利用积分图像进行二进制编码,即可。
实验
opencv代码
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/legacy/legacy.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int main()
{
Mat img_1 = imread("beaver1.png");
Mat img_2 = imread("beaver2.png");
if (!img_1.data || !img_2.data)
{
cout << "error reading images " << endl;
return -1;
}
ORB orb;
vector<KeyPoint> keyPoints_1, keyPoints_2;
Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;
orb(img_1, Mat(), keyPoints_1, descriptors_1);
orb(img_2, Mat(), keyPoints_2, descriptors_2);
BruteForceMatcher<HammingLUT> matcher;
vector<DMatch> matches;
matcher.match(descriptors_1, descriptors_2, matches);
double max_dist = 0; double min_dist = 100;
//-- Quick calculation of max and min distances between keypoints
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
double dist = matches[i].distance;
if( dist < min_dist ) min_dist = dist;
if( dist > max_dist ) max_dist = dist;
}
printf("-- Max dist : %f \n", max_dist );
printf("-- Min dist : %f \n", min_dist );
//-- Draw only "good" matches (i.e. whose distance is less than 0.6*max_dist )
//-- PS.- radiusMatch can also be used here.
std::vector< DMatch > good_matches;
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
if( matches[i].distance < 0.6*max_dist )
{
good_matches.push_back( matches[i]);
}
}
Mat img_matches;
drawMatches(img_1, keyPoints_1, img_2, keyPoints_2,
good_matches, img_matches, Scalar::all(-1), Scalar::all(-1),
vector<char>(), DrawMatchesFlags::NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS);
imshow( "Match", img_matches);
cvWaitKey();
return 0;
}
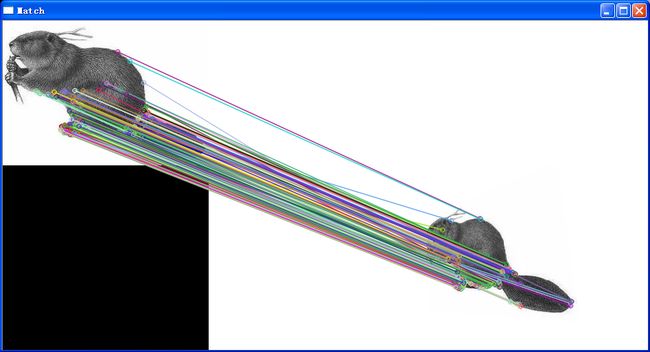
实验结果
ORB源码
static void//计算Harris角点响应
HarrisResponses(const Mat& img, vector<KeyPoint>& pts, int blockSize, float harris_k)
{
CV_Assert( img.type() == CV_8UC1 && blockSize*blockSize <= 2048 );
size_t ptidx, ptsize = pts.size();
const uchar* ptr00 = img.ptr<uchar>();
int step = (int)(img.step/img.elemSize1());
int r = blockSize/2;
float scale = (1 << 2) * blockSize * 255.0f;
scale = 1.0f / scale;
float scale_sq_sq = scale * scale * scale * scale;
AutoBuffer<int> ofsbuf(blockSize*blockSize);
int* ofs = ofsbuf;
for( int i = 0; i < blockSize; i++ )
for( int j = 0; j < blockSize; j++ )
ofs[i*blockSize + j] = (int)(i*step + j);
for( ptidx = 0; ptidx < ptsize; ptidx++ )
{
int x0 = cvRound(pts[ptidx].pt.x - r);
int y0 = cvRound(pts[ptidx].pt.y - r);
const uchar* ptr0 = ptr00 + y0*step + x0;
int a = 0, b = 0, c = 0;
for( int k = 0; k < blockSize*blockSize; k++ )
{
const uchar* ptr = ptr0 + ofs[k];
int Ix = (ptr[1] - ptr[-1])*2 + (ptr[-step+1] - ptr[-step-1]) + (ptr[step+1] - ptr[step-1]);
int Iy = (ptr[step] - ptr[-step])*2 + (ptr[step-1] - ptr[-step-1]) + (ptr[step+1] - ptr[-step+1]);
a += Ix*Ix;
b += Iy*Iy;
c += Ix*Iy;
}
pts[ptidx].response = ((float)a * b - (float)c * c -
harris_k * ((float)a + b) * ((float)a + b))*scale_sq_sq;
}
}
//计算FAST角点的主方向
static float IC_Angle(const Mat& image, const int half_k, Point2f pt,
const vector<int> & u_max)
{
int m_01 = 0, m_10 = 0;
const uchar* center = &image.at<uchar> (cvRound(pt.y), cvRound(pt.x));
// Treat the center line differently, v=0
for (int u = -half_k; u <= half_k; ++u)
m_10 += u * center[u];
// Go line by line in the circular patch
int step = (int)image.step1();
for (int v = 1; v <= half_k; ++v)
{
// Proceed over the two lines
int v_sum = 0;
int d = u_max[v];
for (int u = -d; u <= d; ++u)
{
int val_plus = center[u + v*step], val_minus = center[u - v*step];
v_sum += (val_plus - val_minus);
m_10 += u * (val_plus + val_minus);
}
m_01 += v * v_sum;
}
return fastAtan2((float)m_01, (float)m_10);
}
#define GET_VALUE(idx) \
(x = pattern[idx].x*a - pattern[idx].y*b, \ //计算旋转后的位置
y = pattern[idx].x*b + pattern[idx].y*a, \
ix = cvRound(x), \
iy = cvRound(y), \
*(center + iy*step + ix) )
//判决,并二进制编码
for (int i = 0; i < dsize; ++i, pattern += 16)
{
int t0, t1, val;
t0 = GET_VALUE(0); t1 = GET_VALUE(1);
val = t0 < t1;
t0 = GET_VALUE(2); t1 = GET_VALUE(3);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 1;
t0 = GET_VALUE(4); t1 = GET_VALUE(5);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 2;
t0 = GET_VALUE(6); t1 = GET_VALUE(7);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 3;
t0 = GET_VALUE(8); t1 = GET_VALUE(9);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 4;
t0 = GET_VALUE(10); t1 = GET_VALUE(11);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 5;
t0 = GET_VALUE(12); t1 = GET_VALUE(13);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 6;
t0 = GET_VALUE(14); t1 = GET_VALUE(15);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 7;
desc[i] = (uchar)val;
}
//产生512个随机点的坐标位置
static void makeRandomPattern(int patchSize, Point* pattern, int npoints)
{
RNG rng(0x34985739); // we always start with a fixed seed,
// to make patterns the same on each run
for( int i = 0; i < npoints; i++ )
{
pattern[i].x = rng.uniform(-patchSize/2, patchSize/2+1);
pattern[i].y = rng.uniform(-patchSize/2, patchSize/2+1);
}
}
总结
ORB算法利用了FAST检测特征点的快,BRIEF特征描述子的简单和快,二者结合并进行了改进,导致ORB算法的又好又快。
参考文献
1、ORB: an efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF[J],IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision,2011.
2、基于ORB和改进RANSAC算法的图像拼接技术[J],2015.
3、基于ORB特征的目标检测与跟踪的研究[硕士论文],2013.
4、基于背景差分与ORB算法的运动目标检测与跟踪算法研究[硕士论文],2014.